Tax evasion involves illegally avoiding taxes by underreporting income or falsifying information, whereas tax avoidance uses legal methods to minimize tax liability through deductions and credits. Explore this article to understand the critical differences and implications of tax evasion versus tax avoidance.
Table of Comparison
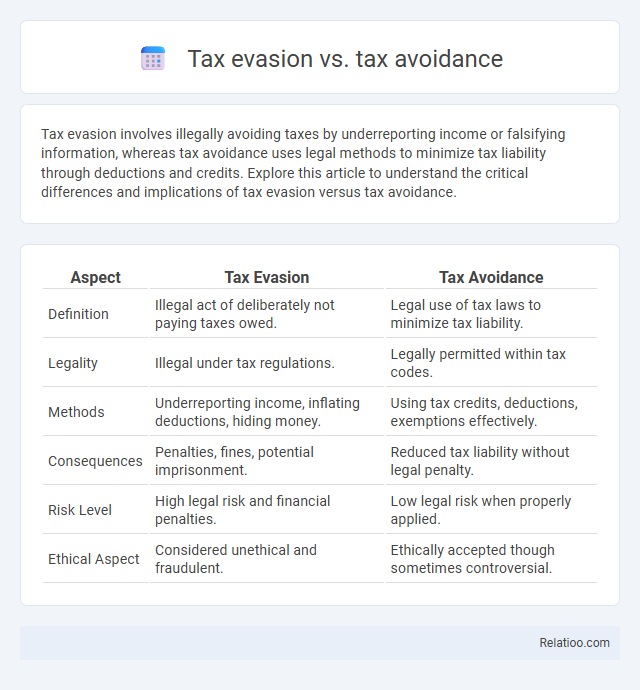
| Aspect | Tax Evasion | Tax Avoidance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Illegal act of deliberately not paying taxes owed. | Legal use of tax laws to minimize tax liability. |
| Legality | Illegal under tax regulations. | Legally permitted within tax codes. |
| Methods | Underreporting income, inflating deductions, hiding money. | Using tax credits, deductions, exemptions effectively. |
| Consequences | Penalties, fines, potential imprisonment. | Reduced tax liability without legal penalty. |
| Risk Level | High legal risk and financial penalties. | Low legal risk when properly applied. |
| Ethical Aspect | Considered unethical and fraudulent. | Ethically accepted though sometimes controversial. |
Introduction to Tax Evasion and Tax Avoidance
Tax evasion involves the illegal act of deliberately misrepresenting or concealing information to reduce tax liability, such as underreporting income or inflating deductions. Tax avoidance uses legal methods to minimize tax payments by exploiting loopholes and applying tax laws in a favorable way, like investing in tax-exempt bonds or claiming available credits. Understanding tax evasion and avoidance is crucial for distinguishing between unlawful tax practices and legitimate tax planning within the broader tax system.
Defining Tax Evasion: Key Concepts
Tax evasion involves the illegal act of deliberately misrepresenting or concealing income to reduce tax liability, violating tax laws and carrying penalties such as fines or imprisonment. Tax avoidance, in contrast, refers to the legal use of methods and strategies to minimize tax owed within the framework of the law. Understanding tax requires recognizing it as a mandatory financial charge imposed by governments on individuals and entities to fund public services and infrastructure.
Understanding Tax Avoidance: Legal Loopholes
Tax avoidance involves using legal loopholes and strategies within tax laws to minimize your tax liability without breaking the law, unlike tax evasion, which is illegal and punishable by fines or imprisonment. Understanding the difference between tax avoidance and tax evasion is crucial for compliance and maximizing financial benefits. Tax represents the mandatory financial charge imposed by governments to fund public services and infrastructure.
Major Differences Between Tax Evasion and Tax Avoidance
Tax evasion involves illegal practices to avoid paying taxes, such as underreporting income or inflating deductions, while tax avoidance uses legal methods like tax credits and exemptions to minimize tax liability. The major difference lies in legality: tax evasion is a criminal offense punishable by fines or imprisonment, whereas tax avoidance complies with tax laws and regulations. Understanding these distinctions helps you manage your taxes lawfully and avoid severe penalties.
Common Methods of Tax Evasion
Common methods of tax evasion include underreporting income, inflating deductions, and hiding money in offshore accounts to avoid paying taxes owed. Individuals and businesses may also engage in falsifying records or transactions to reduce taxable income illegally. These practices contrast with tax avoidance, which involves legally minimizing tax liability through planning and incentives provided by the tax code.
Popular Tax Avoidance Strategies
Popular tax avoidance strategies involve legally minimizing your tax liability through methods like maximizing deductions, contributing to retirement accounts, and utilizing tax credits. Unlike tax evasion, which is illegal and involves deliberately hiding income or falsifying information, tax avoidance follows tax laws to reduce taxable income. Understanding these strategies empowers you to optimize your finances while complying with tax regulations.
Legal Implications of Tax Evasion
Tax evasion involves the illegal non-payment or underpayment of taxes through fraudulent means, resulting in severe legal consequences such as fines, penalties, and potential imprisonment. Tax avoidance, by contrast, employs lawful strategies to minimize tax liabilities within the framework of tax laws, posing no legal risks. Understanding the distinction between these actions is crucial, as tax evasion violates statutory regulations and subjects individuals or businesses to criminal prosecution, whereas tax avoidance remains a legitimate financial practice.
Ethical Considerations in Tax Avoidance
Tax evasion involves illegal practices to avoid paying taxes, while tax avoidance uses legal methods to minimize tax liabilities, making the distinction crucial for ethical considerations. Ethical tax avoidance requires You to balance maximizing financial benefits with social responsibility, avoiding aggressive strategies that exploit loopholes and undermine public trust. Transparency and adherence to the spirit of tax laws help ensure Your tax planning respects both legal obligations and ethical standards.
Government Measures to Combat Tax Evasion and Avoidance
Governments implement stringent audits, enhanced reporting requirements, and advanced data analytics to detect and prevent tax evasion and avoidance, ensuring compliance with tax laws. Anti-avoidance rules such as General Anti-Avoidance Rules (GAAR) are enforced to close loopholes exploited for aggressive tax planning. International cooperation through organizations like the OECD promotes transparency and information exchange to address cross-border tax evasion and avoidance effectively.
Conclusion: Promoting Fair Tax Practices
Promoting fair tax practices ensures compliance with tax laws, reducing the risks associated with tax evasion, which is illegal and punishable by penalties or imprisonment. Tax avoidance, while legal, involves leveraging loopholes to minimize tax liabilities but may raise ethical concerns and regulatory scrutiny. You contribute to a fair tax system by understanding and adhering to tax obligations, supporting transparency, and fostering equitable public revenue distribution.
Infographic: Tax evasion vs tax avoidance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com