Family trusts protect family assets by distributing income to beneficiaries according to set terms, while discretionary trusts allow trustees to decide how income and capital are allocated among beneficiaries. Explore the key differences and benefits of family trusts versus discretionary trusts in this article.
Table of Comparison
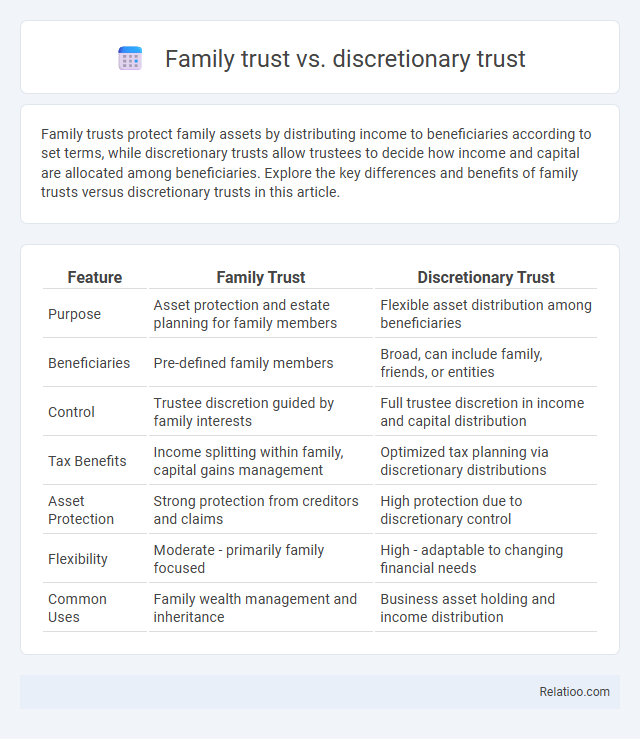
| Feature | Family Trust | Discretionary Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Asset protection and estate planning for family members | Flexible asset distribution among beneficiaries |
| Beneficiaries | Pre-defined family members | Broad, can include family, friends, or entities |
| Control | Trustee discretion guided by family interests | Full trustee discretion in income and capital distribution |
| Tax Benefits | Income splitting within family, capital gains management | Optimized tax planning via discretionary distributions |
| Asset Protection | Strong protection from creditors and claims | High protection due to discretionary control |
| Flexibility | Moderate - primarily family focused | High - adaptable to changing financial needs |
| Common Uses | Family wealth management and inheritance | Business asset holding and income distribution |
Understanding Family Trusts: Key Features
A Family Trust is a legal arrangement where assets are held and managed by a trustee for beneficiaries, typically family members, providing asset protection and estate planning benefits. Unlike a Discretionary Trust, a Family Trust allows the trustee to distribute income and capital among beneficiaries at their discretion, offering flexibility in tax planning and wealth management. Understanding your Family Trust's key features ensures effective control over asset distribution while safeguarding your family's financial future.
Discretionary Trusts Explained
Discretionary trusts provide trustees with flexibility to allocate income and capital among beneficiaries based on their needs and circumstances, optimizing tax planning and asset protection. Unlike fixed or family trusts, discretionary trusts do not specify fixed entitlements, allowing for tailored distributions that can adapt to changing family dynamics. These trusts are commonly used in estate planning to manage wealth efficiently while offering protection from creditors and legal challenges.
Legal Structure: Family Trust vs Discretionary Trust
A Family Trust is a legal structure established to hold and manage assets for the benefit of family members, often with rigid guidelines defining beneficiaries. A Discretionary Trust offers greater flexibility, allowing trustees to decide how income and capital are distributed among beneficiaries without fixed entitlements. Understanding your needs ensures the right choice between the structured benefit protection of a Family Trust and the adaptable asset management of a Discretionary Trust.
Beneficiaries and Distribution Flexibility
Family Trusts provide clear designation of beneficiaries, often family members, with planned distribution to ensure asset protection and estate planning benefits. Discretionary Trusts offer maximum distribution flexibility, allowing trustees to allocate income or capital among a broad class of beneficiaries based on changing circumstances or tax planning needs. Understanding how Your trust's beneficiary structure and distribution powers impact asset control and tax efficiency is essential for optimal wealth management.
Tax Implications: Comparing Both Trusts
Family trusts and discretionary trusts offer distinct tax implications; family trusts typically provide income distribution flexibility among beneficiaries, minimizing tax liabilities by allocating earnings to lower tax bracket members. Discretionary trusts allow trustees to decide how income and capital gains are distributed, enabling strategic tax planning and potential reduction of overall tax burden by maximizing beneficiaries' tax thresholds. Comparing both, family trusts emphasize controlled benefit allocation within a family unit, while discretionary trusts offer broader flexibility and adaptability, affecting tax outcomes based on trustee decisions and beneficiary circumstances.
Asset Protection and Risk Management
Family trusts, discretionary trusts, and hybrid family trusts offer distinct approaches to asset protection and risk management, with family trusts providing structured control over asset distribution primarily for estate planning. Discretionary trusts excel in risk management by allowing trustees to decide how income and capital are allocated, reducing vulnerability to creditors and legal claims. Your choice should depend on the level of flexibility needed for asset protection, with discretionary trusts typically offering greater protection against financial risks compared to rigid family trusts.
Estate Planning Considerations
Family Trusts offer tailored estate planning benefits by allowing your assets to be managed and distributed according to specific family needs, minimizing probate and reducing tax liabilities. Discretionary Trusts provide flexibility in asset allocation among beneficiaries, granting trustees the authority to decide distributions based on changing circumstances, which enhances protection against creditors and succession challenges. Understanding the distinctions between these trusts is crucial for effective estate planning, ensuring your wealth is preserved and transferred in alignment with your family's long-term financial goals.
Advantages of Family Trusts
Family trusts provide significant advantages including asset protection, tax efficiency, and flexible income distribution among beneficiaries. They allow settlors to maintain control over the trust assets while shielding them from creditors and ensuring wealth preservation across generations. Compared to discretionary trusts, family trusts typically offer clearer benefits in estate planning and succession management.
Benefits of Discretionary Trusts
Discretionary trusts offer significant benefits such as flexible income distribution, allowing trustees to allocate income and capital among beneficiaries based on their individual needs and tax circumstances. They provide asset protection from creditors and legal claims, ensuring family wealth is preserved across generations. Compared to family trusts, which often have fixed entitlements, discretionary trusts enhance financial control and estate planning versatility.
Choosing the Right Trust for Your Needs
Choosing the right trust for your needs involves understanding the distinct benefits of each type: a Family Trust provides asset protection and income distribution flexibility among family members, while a Discretionary Trust offers the trustee full control to allocate income and capital according to beneficiaries' changing circumstances. Family Trusts typically suit estate planning and multi-generational wealth preservation, whereas Discretionary Trusts are ideal for managing varying financial situations and minimizing tax liabilities efficiently. Evaluating your financial goals, beneficiary requirements, and asset protection preferences will help you determine which trust structure aligns best with your specific family and business needs.
Infographic: Family Trust vs Discretionary Trust
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com