A Health Proxy authorizes a trusted individual to make medical decisions on your behalf if incapacitated, while a Living Will specifies your treatment preferences in advance. Discover the key differences and decide which suits your needs best in this article.
Table of Comparison
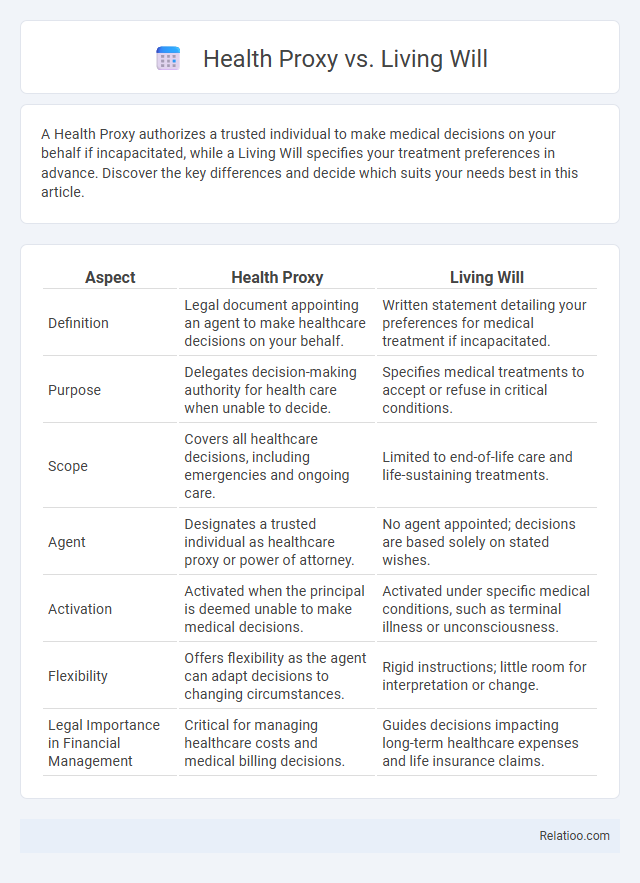
| Aspect | Health Proxy | Living Will |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal document appointing an agent to make healthcare decisions on your behalf. | Written statement detailing your preferences for medical treatment if incapacitated. |
| Purpose | Delegates decision-making authority for health care when unable to decide. | Specifies medical treatments to accept or refuse in critical conditions. |
| Scope | Covers all healthcare decisions, including emergencies and ongoing care. | Limited to end-of-life care and life-sustaining treatments. |
| Agent | Designates a trusted individual as healthcare proxy or power of attorney. | No agent appointed; decisions are based solely on stated wishes. |
| Activation | Activated when the principal is deemed unable to make medical decisions. | Activated under specific medical conditions, such as terminal illness or unconsciousness. |
| Flexibility | Offers flexibility as the agent can adapt decisions to changing circumstances. | Rigid instructions; little room for interpretation or change. |
| Legal Importance in Financial Management | Critical for managing healthcare costs and medical billing decisions. | Guides decisions impacting long-term healthcare expenses and life insurance claims. |
Understanding Health Proxies: Definition and Purpose
A health proxy is a legal document that appoints someone to make medical decisions on Your behalf if you become incapacitated, differing from a living will, which specifies the types of medical treatment you want or do not want. Understanding a health proxy involves recognizing its role in empowering a trusted individual to advocate for Your healthcare preferences when You cannot communicate them yourself. This distinction is crucial for ensuring that both immediate healthcare decisions and end-of-life wishes are respected according to Your intentions.
What Is a Living Will? Essential Overview
A living will is a legal document that specifies an individual's preferences for medical treatment if they become incapacitated and unable to communicate their decisions. It outlines instructions regarding life-sustaining treatments, such as resuscitation, mechanical ventilation, and feeding tubes, ensuring that healthcare providers and family members follow the person's wishes. Unlike a health proxy, which designates a healthcare agent to make decisions, a living will provides direct guidance on medical interventions in advance.
Key Differences Between Health Proxy and Living Will
A health proxy is a legal document that appoints an individual to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, while a living will outlines your preferences for medical treatment and end-of-life care. The key difference lies in the scope: a health proxy grants decision-making authority to a trusted person, whereas a living will provides directive instructions to healthcare providers based on your wishes. Both documents are essential for comprehensive advance care planning, ensuring your medical care aligns with your values when you cannot communicate.
When to Use a Health Proxy vs Living Will
A Health Proxy is essential when you want to appoint someone to make healthcare decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, offering flexibility in various medical scenarios. A Living Will specifically outlines your preferences for life-sustaining treatments, guiding healthcare providers during end-of-life care decisions. You should use a Health Proxy when you need a trusted person to interpret your wishes in real-time, while a Living Will is best used to provide clear directives for specific medical interventions.
Legal Requirements for Health Proxies
Health proxies require a formal, written document signed by you and witnessed or notarized according to state laws to ensure legal validity. Unlike living wills, which outline your healthcare preferences, health proxies appoint a trusted individual to make medical decisions on your behalf when you are incapacitated. Understanding these legal requirements safeguards your rights and guarantees your healthcare wishes are respected under the law.
Legal Framework Surrounding Living Wills
The legal framework surrounding living wills is established by state statutes that specify their validity, execution requirements, and scope in directing end-of-life medical care. Unlike health proxies, which designate a person to make healthcare decisions, living wills provide explicit instructions regarding life-sustaining treatments and interventions. Understanding the distinctions and legal recognition of these advance directives ensures effective communication of patient preferences in clinical settings.
Benefits of Assigning a Health Proxy
Assigning a health proxy ensures personalized medical decisions when an individual becomes incapacitated, offering greater flexibility than a living will's predefined instructions. It allows a trusted person to interpret evolving medical situations and make real-time choices aligned with the patient's values. This personalized approach enhances patient autonomy and reduces family conflicts during critical healthcare decisions.
Advantages of Creating a Living Will
Creating a living will provides clear instructions about your medical treatment preferences, ensuring your wishes are respected even if you cannot communicate them yourself. Unlike a health proxy, which appoints someone to make decisions on your behalf, a living will specifically outlines your consent or refusal of life-sustaining measures. Your advance directive offers peace of mind by minimizing conflicts among family members and guiding healthcare providers in critical situations.
Common Misconceptions About Health Proxies and Living Wills
Health proxies and living wills are often confused, but they serve distinct purposes in healthcare planning. A health proxy designates an agent to make medical decisions on behalf of an individual, while a living will documents specific treatment preferences if the individual becomes incapacitated. Common misconceptions include believing a living will covers all healthcare decisions and that a health proxy can override a living will, whereas both documents typically complement each other to ensure comprehensive medical decision-making aligned with the patient's wishes.
Choosing the Right Advance Directive for Your Needs
Choosing the right advance directive involves understanding the distinct roles of a Health Proxy and a Living Will. A Health Proxy, also called a Durable Power of Attorney for Healthcare, appoints a trusted person to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, while a Living Will specifies your preferences for medical treatments and end-of-life care. Evaluating personal healthcare wishes, potential scenarios, and the level of decision-making control desired helps determine whether appointing a Health Proxy, drafting a Living Will, or combining both provides the most comprehensive protection tailored to your needs.
Infographic: Health Proxy vs Living Will
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com