Quantitative goals in relationships emphasize measurable outcomes such as frequency of communication or time spent together, while qualitative goals focus on emotional connection and mutual understanding. Explore this article to learn how balancing both can strengthen your partnership effectively.
Table of Comparison
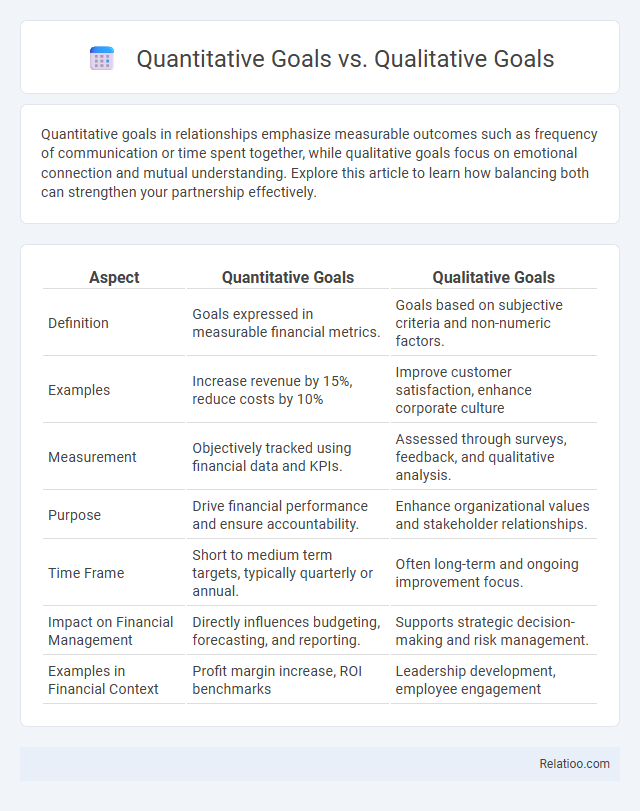
| Aspect | Quantitative Goals | Qualitative Goals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goals expressed in measurable financial metrics. | Goals based on subjective criteria and non-numeric factors. |
| Examples | Increase revenue by 15%, reduce costs by 10% | Improve customer satisfaction, enhance corporate culture |
| Measurement | Objectively tracked using financial data and KPIs. | Assessed through surveys, feedback, and qualitative analysis. |
| Purpose | Drive financial performance and ensure accountability. | Enhance organizational values and stakeholder relationships. |
| Time Frame | Short to medium term targets, typically quarterly or annual. | Often long-term and ongoing improvement focus. |
| Impact on Financial Management | Directly influences budgeting, forecasting, and reporting. | Supports strategic decision-making and risk management. |
| Examples in Financial Context | Profit margin increase, ROI benchmarks | Leadership development, employee engagement |
Introduction to Quantitative and Qualitative Goals
Quantitative goals are measurable and expressed with specific numbers, such as increasing sales by 20% or reducing customer complaints by 10%, providing clear benchmarks for success. Qualitative goals, on the other hand, focus on subjective attributes like improving brand reputation or enhancing employee morale, which are assessed through observations and feedback rather than exact figures. Your strategic planning benefits from balancing both goal types to drive comprehensive growth, while financial goals specifically target monetary outcomes like revenue, profit margins, or budget adherence.
Defining Quantitative Goals
Quantitative goals are specific, measurable objectives expressed in numerical terms, such as increasing sales by 15% or reducing production costs by 10%. These goals provide clear benchmarks and allow for precise tracking of progress, unlike qualitative goals which focus on subjective attributes like customer satisfaction or brand reputation. Financial goals, a subset of quantitative goals, concentrate explicitly on monetary outcomes such as revenue targets, profit margins, or return on investment.
Understanding Qualitative Goals
Qualitative goals emphasize improving customer satisfaction, enhancing brand reputation, and fostering employee engagement, which are vital for long-term business success beyond measurable metrics. Unlike quantitative goals that focus on numeric targets and financial goals centered on revenue or profit, qualitative goals capture the intangible aspects of your organization's growth and impact. Understanding these goals helps you create a balanced strategy that supports sustainable development and strengthens stakeholder relationships.
Key Differences Between Quantitative and Qualitative Goals
Quantitative goals are measurable objectives expressed in numerical terms, such as increasing sales by 15% or reducing customer acquisition costs by $10, whereas qualitative goals focus on intangible outcomes like improving brand reputation or enhancing customer satisfaction. Financial goals specifically target monetary metrics like revenue growth, profit margins, or budget adherence, serving as a subset of quantitative goals. The key difference between quantitative and qualitative goals lies in their measurability: quantitative goals rely on precise data and metrics for evaluation, while qualitative goals require subjective assessment of experiences, perceptions, and quality improvements.
Benefits of Setting Quantitative Goals
Setting quantitative goals enables precise measurement and tracking of progress through specific numerical benchmarks, enhancing accountability and motivation. These goals facilitate data-driven decision-making by providing clear metrics for evaluating success and identifying areas for improvement. Unlike qualitative or financial goals, quantitative targets offer concrete evidence of achievement, leading to more effective performance management and strategic planning.
Advantages of Qualitative Goal Setting
Qualitative goal setting enhances your ability to focus on intangible outcomes like customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and employee engagement, which are critical for long-term success. These goals foster creativity and innovation by encouraging adaptive strategies rather than rigid metrics, helping your organization respond effectively to changing market conditions. Emphasizing qualitative goals can improve team motivation and alignment by prioritizing values and behaviors that drive sustainable growth beyond immediate financial results.
When to Use Quantitative Versus Qualitative Goals
Quantitative goals are best used when precise, measurable outcomes are required, such as sales targets or production numbers, allowing for clear tracking and evaluation. Qualitative goals focus on subjective criteria like customer satisfaction or brand reputation, serving well in scenarios where quality, experience, or perception are paramount. Financial goals are specific to monetary achievements like profit margins or return on investment, and they often combine quantitative measures with strategic business planning.
Examples of Quantitative and Qualitative Goals
Quantitative goals include specific, measurable targets such as increasing sales by 20% within six months or reducing production costs by 10% annually. Qualitative goals focus on non-numeric outcomes like improving customer satisfaction through enhanced support services or fostering a collaborative company culture. Financial goals often overlap with quantitative goals but specifically target monetary outcomes, such as achieving $1 million in revenue or increasing profit margins by 5%.
Integrating Both Goal Types for Maximum Results
Integrating quantitative goals, which focus on measurable metrics like sales targets and performance indicators, with qualitative goals that emphasize customer satisfaction and employee engagement, leads to a more balanced business strategy. Financial goals, encompassing profit margins, revenue growth, and cost management, serve as a critical framework to align both quantitative and qualitative objectives for sustainable success. Combining these goal types ensures organizations not only track numerical progress but also nurture the qualitative aspects driving long-term value and competitive advantage.
Measuring Success: Tracking Quantitative and Qualitative Progress
Measuring success involves tracking both quantitative and qualitative progress to gain a comprehensive understanding of performance. Quantitative goals, such as sales targets or website traffic, provide clear, numerical benchmarks, while qualitative goals focus on customer satisfaction, brand perception, or employee engagement, which require subjective assessment tools like surveys or interviews. Your ability to analyze financial goals alongside these metrics ensures balanced growth and informed decision-making.
Infographic: Quantitative Goals vs Qualitative Goals
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com