A Savings Account offers lower risk and easy access to funds with modest interest, while an Investment Account provides higher growth potential through stocks, bonds, and mutual funds but carries greater market risk. Explore the key differences between Savings and Investment Accounts to choose the best option for your financial goals in this article.
Table of Comparison
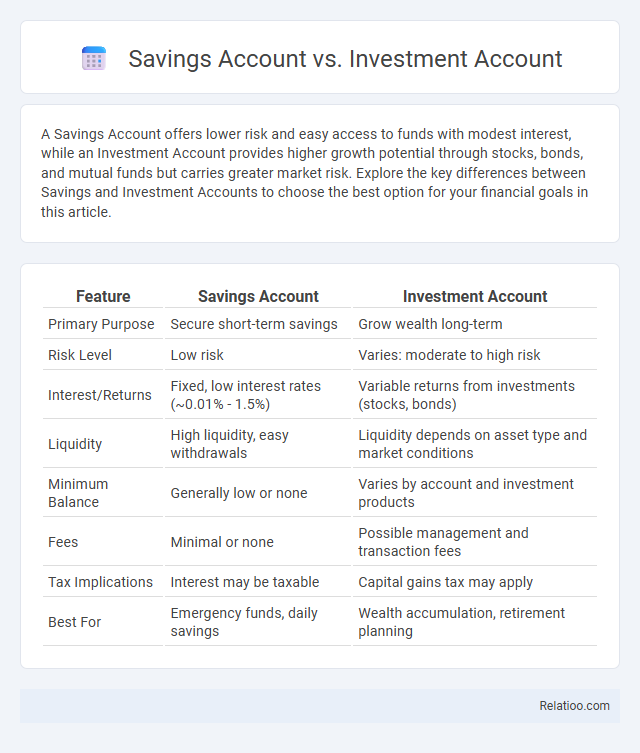
| Feature | Savings Account | Investment Account |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Secure short-term savings | Grow wealth long-term |
| Risk Level | Low risk | Varies: moderate to high risk |
| Interest/Returns | Fixed, low interest rates (~0.01% - 1.5%) | Variable returns from investments (stocks, bonds) |
| Liquidity | High liquidity, easy withdrawals | Liquidity depends on asset type and market conditions |
| Minimum Balance | Generally low or none | Varies by account and investment products |
| Fees | Minimal or none | Possible management and transaction fees |
| Tax Implications | Interest may be taxable | Capital gains tax may apply |
| Best For | Emergency funds, daily savings | Wealth accumulation, retirement planning |
Introduction to Savings Accounts vs Investment Accounts
Savings accounts offer a secure place for your money with easy access and interest accumulation, ideal for short-term goals and emergency funds. Investment accounts provide opportunities for higher returns by putting your money into stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, suitable for long-term growth but with varying risk levels. Understanding the differences between savings and investment accounts helps you tailor your financial strategy to meet your specific goals and risk tolerance.
Key Differences Between Savings and Investment Accounts
Savings accounts offer low-risk, liquid storage for your money with modest interest rates, ideal for emergency funds and short-term goals. Investment accounts involve higher risk but provide potential for greater returns through stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, suitable for long-term wealth growth. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right account based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs.
Purpose and Goals of Each Account Type
Savings accounts are designed for short-term financial goals and emergency funds, offering liquidity and safety with modest interest rates. Investment accounts aim to grow your wealth over the long term through diversified assets such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, accepting higher risk for potential higher returns. Understanding Your financial goals helps determine whether you prioritize accessibility and security in a savings account or wealth accumulation with an investment account.
Risk Factors: Savings vs Investments
Savings accounts offer low risk with guaranteed principal protection and FDIC insurance up to $250,000, making them ideal for emergency funds and short-term goals. Investment accounts carry higher risk due to market volatility, potential loss of principal, and lack of insurance, but they provide opportunities for greater long-term growth through stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Understanding individual risk tolerance and financial goals is crucial when choosing between stable savings accounts and potentially higher-yielding but riskier investment accounts.
Interest Rates and Potential Returns
Savings accounts offer lower interest rates, typically around 0.01% to 1%, providing secure but modest growth on your deposits. Investment accounts, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, present higher potential returns that can range from 5% to 10% or more annually, albeit with increased risk and market fluctuations. Choosing between these options depends on your risk tolerance and financial goals, as savings accounts prioritize stability while investment accounts aim for greater long-term growth.
Liquidity and Accessibility
Savings accounts offer high liquidity and easy accessibility, allowing you to withdraw funds anytime without penalties, making them ideal for emergency cash needs. Investment accounts typically provide lower liquidity due to market fluctuations and potential withdrawal restrictions, but they offer the potential for higher returns over time. Savings, when kept in liquid forms like money market funds or short-term deposits, balance accessibility and modest growth, but their liquidity varies based on the specific vehicle chosen.
Fees and Charges Comparison
Savings accounts typically have low or no fees, making them cost-effective for your everyday needs, though some may charge maintenance fees or minimum balance penalties. Investment accounts often incur higher fees, including trading commissions, management fees, and account maintenance charges that can reduce overall returns. Understanding these costs helps you choose between the low-fee, accessible nature of savings accounts and the potentially higher returns but greater fees associated with investment accounts.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Which Account?
Savings accounts suit individuals seeking low-risk, highly liquid options for short-term goals and emergency funds. Investment accounts are ideal for those aiming for higher returns through stocks, bonds, or mutual funds and willing to accept market volatility for long-term growth. Savings plans or accounts are best for conservative savers prioritizing capital preservation and steady interest over speculative gains.
Tax Implications of Savings and Investment Accounts
Savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates with interest income subject to standard income tax rates, impacting after-tax returns. Investment accounts can provide higher returns through dividends, capital gains, and interest, each taxed differently depending on holding period and asset type, allowing for strategic tax planning. Understanding specific tax treatments, such as tax-deferred growth in retirement accounts or capital gains tax rates, is essential for maximizing net returns on savings and investments.
How to Choose the Right Account for Your Needs
Choosing the right account depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs. A savings account offers easy access and low risk with modest interest, ideal for emergency funds or short-term goals, while investment accounts provide higher growth potential but involve market risk and longer time horizons suitable for wealth building. Evaluate your timeline, expected returns, and risk comfort to determine whether a savings account, investment account, or a combination fits best for your personal financial strategy.
Infographic: Savings Account vs Investment Account
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com