Refinancing replaces your existing mortgage with a new loan, often lowering interest rates or changing loan terms, while a home equity loan allows you to borrow against your home's equity without altering your primary mortgage. Discover the key differences and which option suits your financial goals in this article.
Table of Comparison
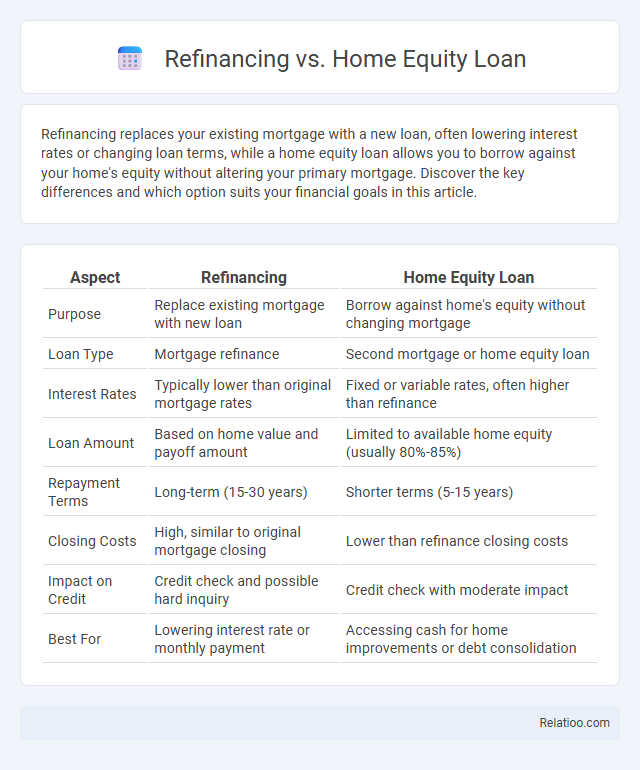
| Aspect | Refinancing | Home Equity Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Replace existing mortgage with new loan | Borrow against home's equity without changing mortgage |
| Loan Type | Mortgage refinance | Second mortgage or home equity loan |
| Interest Rates | Typically lower than original mortgage rates | Fixed or variable rates, often higher than refinance |
| Loan Amount | Based on home value and payoff amount | Limited to available home equity (usually 80%-85%) |
| Repayment Terms | Long-term (15-30 years) | Shorter terms (5-15 years) |
| Closing Costs | High, similar to original mortgage closing | Lower than refinance closing costs |
| Impact on Credit | Credit check and possible hard inquiry | Credit check with moderate impact |
| Best For | Lowering interest rate or monthly payment | Accessing cash for home improvements or debt consolidation |
Understanding Refinancing: Definition and Process
Refinancing involves replacing your existing mortgage with a new loan, often to secure a lower interest rate or change the loan term, improving your overall financial situation. The process includes evaluating your credit score, home value, and current interest rates, submitting an application, undergoing an appraisal, and closing the new loan. Understanding refinancing empowers you to make informed decisions that can reduce monthly payments or access home equity for other needs.
What Is a Home Equity Loan? Key Features Explained
A home equity loan is a type of second mortgage that allows homeowners to borrow against the equity built in their property, typically offering a fixed interest rate and set repayment term. Key features include a lump-sum disbursement, predictable monthly payments, and the ability to use funds for major expenses such as home improvements or debt consolidation. Unlike refinancing, which replaces the entire mortgage, a home equity loan provides additional funds without altering the original loan terms.
Eligibility Requirements: Refinancing vs Home Equity Loan
Eligibility requirements for refinancing typically include a strong credit score, a stable income, and sufficient home equity, with lenders often requiring a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio below 80%. Home equity loans demand a minimum amount of equity built up in your home, usually around 15-20%, along with a good credit score and stable financial history. You should evaluate these criteria carefully, as refinancing may offer better interest rates but has stricter eligibility compared to home equity loans, which can be easier to qualify for with lower credit thresholds.
Pros and Cons of Mortgage Refinancing
Mortgage refinancing can lower your interest rates and monthly payments, providing significant long-term savings and improving your financial flexibility. However, refinancing often involves closing costs, application fees, and potential extension of your loan term, which could increase overall interest paid. Unlike home equity loans that use your property's value as collateral, refinancing replaces your existing mortgage, consolidating debt but possibly resetting the amortization schedule.
Pros and Cons of Home Equity Loans
Home equity loans offer fixed interest rates and predictable monthly payments, making them suitable for borrowers seeking financial stability and a lump sum of cash. However, their cons include the risk of foreclosure since the home serves as collateral and the possibility of higher interest rates compared to traditional refinancing options. Unlike refinancing, home equity loans do not alter the primary mortgage terms, which may result in less favorable overall financial flexibility.
Interest Rates and Terms: A Comparative Analysis
Refinancing typically offers lower interest rates compared to home equity loans due to the longer loan terms and primary mortgage status, often ranging from 2.5% to 5%, while home equity loans usually have higher rates between 5% and 8% for shorter terms of 5 to 15 years. Refinancing allows borrowers to adjust the loan term from 15 up to 30 years, providing flexibility in monthly payments and interest savings over time, whereas home equity loans have fixed terms and rates with less opportunity for renegotiation. Comparing these options reveals that refinancing generally benefits those seeking lower long-term rates and extended repayment periods, while home equity loans serve borrowers needing smaller, fixed-rate loans with shorter durations.
Costs and Fees: What to Expect with Each Option
Refinancing typically involves closing costs ranging from 2% to 5% of the loan amount, including appraisal, origination, and title fees, which can be rolled into the new loan or paid upfront. Home equity loans generally have lower upfront costs, often including application fees, appraisal fees, and sometimes origination fees, but usually no closing costs comparable to full refinancing. Cash-out refinancing combines the costs of refinancing with accessing home equity, potentially leading to higher fees but consolidates debt into a single loan, which can affect overall financial planning and interest paid.
Impact on Credit Score and Financial Health
Refinancing typically involves a credit check that may temporarily lower your credit score but can improve financial health by securing lower interest rates and monthly payments. A home equity loan usually requires a good credit score for approval and can impact your credit utilization ratio, which influences your credit score and overall financial stability. You should weigh how each option affects your credit profile and long-term financial health before deciding, as responsible management can enhance your creditworthiness and reduce debt costs.
When Should You Choose Refinancing Over a Home Equity Loan?
Choosing refinancing over a home equity loan is ideal when you want to secure a lower interest rate on your entire mortgage, reduce your monthly payments, or change the loan term for better financial flexibility. Refinancing consolidates your existing mortgage balance into a new loan, often offering more favorable rates compared to a home equity loan, which is best for borrowing smaller amounts with potentially higher rates. Your decision should consider current mortgage rates, loan costs, and how long you plan to stay in your home to maximize savings and financial benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions: Refinancing vs Home Equity Loan
Refinancing replaces your existing mortgage with a new loan, often to secure a lower interest rate or adjust loan terms, while a home equity loan allows you to borrow against the equity built in your home, typically offering fixed interest rates and a lump sum payout. You should consider refinancing if your goal is to reduce monthly payments or change loan duration, whereas a home equity loan suits those needing funds for specific expenses like home improvements or debt consolidation. Frequently asked questions include differences in interest rates, tax implications, loan amounts, and repayment terms between refinancing and home equity loans.
Infographic: Refinancing vs Home Equity Loan
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com