Late fees are fixed charges imposed for missed payments, while interest accumulates as a percentage of the outstanding balance over time. Discover the detailed differences and impacts of late fees versus interest in this article.
Table of Comparison
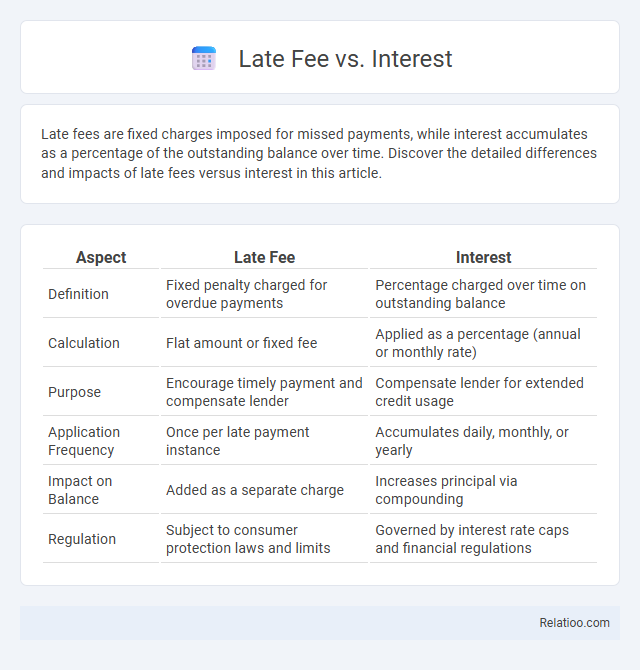
| Aspect | Late Fee | Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed penalty charged for overdue payments | Percentage charged over time on outstanding balance |
| Calculation | Flat amount or fixed fee | Applied as a percentage (annual or monthly rate) |
| Purpose | Encourage timely payment and compensate lender | Compensate lender for extended credit usage |
| Application Frequency | Once per late payment instance | Accumulates daily, monthly, or yearly |
| Impact on Balance | Added as a separate charge | Increases principal via compounding |
| Regulation | Subject to consumer protection laws and limits | Governed by interest rate caps and financial regulations |
Understanding Late Fees: Definition and Purpose
Late fees are predetermined charges imposed for missed or delayed payments, designed to encourage timely compliance and compensate for administrative costs. Interest, on the other hand, represents the cost of borrowed money calculated as a percentage of the principal over time, accruing continuously or periodically. Understanding late fees helps businesses enforce payment discipline, while distinguishing them from interest clarifies their role in contract terms and financial obligations.
What is Interest? Core Concepts Explained
Interest is the cost of borrowing money, typically expressed as a percentage of the principal amount over a specific period. It represents the compensation lenders receive for the risk and opportunity cost of lending funds. Unlike late fees, which are fixed penalties for overdue payments, interest accrues gradually and can compound over time, significantly impacting the total repayment amount.
Key Differences Between Late Fees and Interest
Late fees are fixed charges applied when a payment is overdue, serving as a penalty for missed deadlines, whereas interest accrues as a percentage of the outstanding balance over time, reflecting the cost of borrowing. Late fees are typically one-time charges per billing cycle, while interest compounds periodically until the debt is paid off. Understanding the distinction helps borrowers manage costs effectively and avoid escalating debt due to compounded interest rather than simple penalties.
Legal Framework: Regulations on Late Fees and Interest
Regulations on late fees and interest vary significantly across jurisdictions, often governed by consumer protection laws and financial regulations to prevent predatory practices. Late fees are typically fixed charges imposed after a payment due date, subject to caps or limits defined by state or federal statutes, while interest on overdue amounts accrues based on contractual agreements or statutory rates. Legal frameworks require clear disclosure of late fees and interest terms in contracts, balancing creditor rights with consumer fairness and ensuring compliance with usury laws and fee reasonableness standards.
Common Scenarios: When Are Late Fees Charged?
Late fees are typically charged when a payment is not received by the due date, reflecting a fixed penalty for tardiness, while interest accrues as a percentage on the outstanding balance over time, increasing the total amount owed. In common scenarios, late fees apply immediately after the payment deadline, often within days, whereas interest starts accumulating if the debt remains unpaid for an extended period. Understanding your billing terms helps differentiate when late fees are enforced versus when interest expenses begin to impact your financial obligations.
How Interest Accumulates on Outstanding Balances
Interest accumulates on outstanding balances by applying a percentage rate over time, increasing the total amount you owe beyond the principal. Unlike late fees, which are fixed penalties charged once for missed payments, interest compounds continuously or periodically according to the agreed terms. Understanding how interest grows helps you manage your payments more effectively and avoid escalating debt costs.
Impact on Credit Scores: Late Fees vs. Interest
Late fees and interest charges both negatively impact credit scores, but late fees directly affect your credit report when payments are reported as delinquent, signaling lenders about missed payments. Interest charges increase the overall debt balance, which can raise credit utilization rates and indirectly lower your credit score. Timely payment of fees is crucial to avoid damaging your credit history and maintaining a healthy credit score.
Consumer Rights and Protections
Consumers are protected by laws that limit the amount and application of late fees and interest charges on overdue accounts, ensuring fees are reasonable and disclosed clearly. Late fees are fixed penalties for missed payments, while interest is a percentage-based charge accruing over time on unpaid balances. Regulatory bodies enforce transparency and fairness, preventing abusive practices and safeguarding consumer rights in financial agreements.
Best Practices for Avoiding Late Fees and Interest
To avoid late fees and interest charges, prioritize timely payments by setting up automatic bill payments or calendar reminders integrated with digital finance tools. Clearly understand the terms of your agreements, including grace periods and applicable interest rates, to manage due dates effectively and budget accordingly. Regularly review account statements to catch billing errors early and negotiate with creditors for possible fee waivers or payment plans.
Choosing Financial Products: Evaluate Fees and Interest Rates
When choosing financial products, evaluating late fees and interest rates is crucial for minimizing overall costs and avoiding unexpected expenses. Late fees are fixed penalties for missed payments, while interest accrues over time based on the outstanding balance, significantly impacting the total repayment amount. Comparing these charges across credit cards, loans, and other financial products ensures informed decisions that optimize affordability and credit management.
Infographic: Late Fee vs Interest
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com