Asset allocation divides investments across major asset classes like stocks, bonds, and real estate to manage risk and return, while portfolio allocation fine-tunes the distribution within those classes to align with specific financial goals and risk tolerance. Discover how understanding the differences between asset allocation and portfolio allocation can enhance your investment strategy in this article.
Table of Comparison
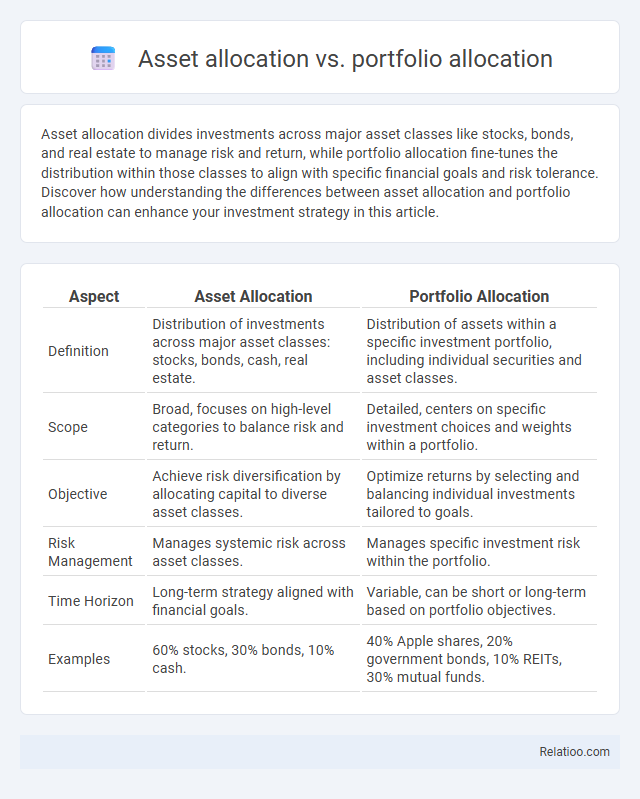
| Aspect | Asset Allocation | Portfolio Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distribution of investments across major asset classes: stocks, bonds, cash, real estate. | Distribution of assets within a specific investment portfolio, including individual securities and asset classes. |
| Scope | Broad, focuses on high-level categories to balance risk and return. | Detailed, centers on specific investment choices and weights within a portfolio. |
| Objective | Achieve risk diversification by allocating capital to diverse asset classes. | Optimize returns by selecting and balancing individual investments tailored to goals. |
| Risk Management | Manages systemic risk across asset classes. | Manages specific investment risk within the portfolio. |
| Time Horizon | Long-term strategy aligned with financial goals. | Variable, can be short or long-term based on portfolio objectives. |
| Examples | 60% stocks, 30% bonds, 10% cash. | 40% Apple shares, 20% government bonds, 10% REITs, 30% mutual funds. |
Introduction to Asset Allocation vs Portfolio Allocation
Asset allocation strategically distributes investments among asset classes like stocks, bonds, and cash to balance risk and return based on Your financial goals. Portfolio allocation involves dividing Your total investment portfolio into various individual assets or securities within those asset classes to optimize performance. Understanding the distinction between asset allocation and portfolio allocation enhances Your ability to manage investment risks and achieve diversified growth.
Defining Asset Allocation
Asset allocation involves strategically distributing investments among asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash to balance risk and reward according to your financial goals. Portfolio allocation refers to the process of selecting specific investments within each asset class to create a diversified and optimized investment portfolio. Understanding asset allocation is crucial for managing investment risk and achieving long-term financial stability.
Understanding Portfolio Allocation
Portfolio allocation strategically divides Your investments across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash to balance risk and optimize returns. Asset allocation refers specifically to how capital is distributed among these different asset categories, while allocation broadly covers the distribution of resources within any financial or business context. Understanding portfolio allocation enables You to create a diversified investment strategy that aligns with Your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Key Differences Between Asset and Portfolio Allocation
Asset allocation involves distributing investments across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash to manage risk and optimize returns. Portfolio allocation refers to the detailed breakdown of specific securities within those asset classes, focusing on individual holdings and their proportions. Key differences include asset allocation's broad strategy for diversification, while portfolio allocation emphasizes the precise composition and weight of each investment within the portfolio.
Objectives of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation strategically distributes Your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash, to balance risk and maximize returns based on Your financial goals and risk tolerance. Portfolio allocation is the broader process of organizing all assets within an investment portfolio, including asset classes, sectors, and individual securities, to achieve diversification and meet specific investment objectives. Allocation refers to the overall distribution strategy, but asset allocation specifically aims to optimize long-term growth, income generation, and capital preservation by targeting the right mix of asset classes aligned with Your objectives.
Objectives of Portfolio Allocation
Portfolio allocation focuses on strategically distributing investments across various asset classes to achieve specific financial goals, balancing risk tolerance and expected returns. Unlike general asset allocation that broadly categorizes assets, portfolio allocation fine-tunes the mix based on individual objectives such as growth, income, or capital preservation. This precise alignment ensures optimized performance tailored to investor timelines and risk preferences.
Benefits of Effective Allocation Strategies
Effective asset allocation balances investments across asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash to manage risk and enhance returns based on market conditions and investor goals. Portfolio allocation refines this by diversifying within those assets, optimizing the blend to achieve specific performance targets and risk tolerance levels. Strategic allocation improves financial outcomes by reducing volatility, maximizing growth potential, and ensuring adaptability to economic changes while aligning with an investor's time horizon and objectives.
Common Methods for Asset and Portfolio Allocation
Common methods for asset allocation include strategic asset allocation, which sets long-term target proportions, and tactical asset allocation, which adjusts those targets based on market conditions. Portfolio allocation integrates asset allocation by distributing investments across asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions to balance risk and return. Your effective investment strategy relies on understanding these allocation methods to optimize diversification and align with financial goals.
Factors Influencing Allocation Decisions
Asset allocation decisions are primarily influenced by factors such as investment objectives, risk tolerance, time horizon, and market conditions. Portfolio allocation expands this by considering the diversification across asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions to optimize risk-return balance. Allocation, in a broader sense, also takes into account liquidity needs, tax implications, and regulatory constraints that affect how resources are distributed among various investment opportunities.
Choosing the Right Allocation Strategy for Your Goals
Asset allocation involves distributing investments across major asset classes like stocks, bonds, and cash to balance risk and return according to financial goals and risk tolerance. Portfolio allocation refers to the detailed division of assets within an investment portfolio, considering factors like market sectors, geographic regions, and investment styles to optimize performance and diversification. Choosing the right allocation strategy requires aligning asset and portfolio allocation decisions with specific objectives, time horizons, and risk preferences to maximize growth potential while managing downside risk effectively.
Infographic: Asset allocation vs Portfolio allocation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com