A Pension Plan provides guaranteed lifetime income based on salary and years worked, while a 401(k) is a retirement savings account with contributions invested and growth dependent on market performance. Explore this article to understand the key differences and decide which retirement option suits you best.
Table of Comparison
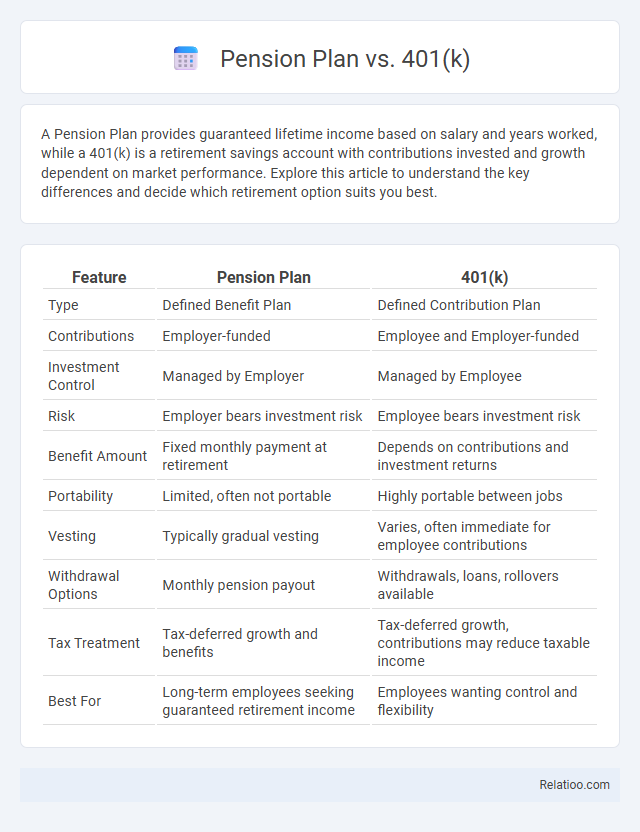
| Feature | Pension Plan | 401(k) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Defined Benefit Plan | Defined Contribution Plan |
| Contributions | Employer-funded | Employee and Employer-funded |
| Investment Control | Managed by Employer | Managed by Employee |
| Risk | Employer bears investment risk | Employee bears investment risk |
| Benefit Amount | Fixed monthly payment at retirement | Depends on contributions and investment returns |
| Portability | Limited, often not portable | Highly portable between jobs |
| Vesting | Typically gradual vesting | Varies, often immediate for employee contributions |
| Withdrawal Options | Monthly pension payout | Withdrawals, loans, rollovers available |
| Tax Treatment | Tax-deferred growth and benefits | Tax-deferred growth, contributions may reduce taxable income |
| Best For | Long-term employees seeking guaranteed retirement income | Employees wanting control and flexibility |
Understanding Pension Plans: A Brief Overview
Pension plans provide a defined benefit, guaranteeing a specific monthly income based on your salary and years of service, contrasting with 401(k) plans that depend on individual contributions and market performance. Pension plans are typically employer-funded and offer predictable retirement income, reducing financial uncertainty for retirees. Understanding these key differences helps you make informed decisions about your retirement strategy.
What is a 401(k) and How Does It Work?
A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement savings plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their salary on a pre-tax basis, often with matching contributions from the employer. Contributions grow tax-deferred until withdrawal, typically at retirement, which helps build a substantial retirement fund over time through compounding interest and investment growth. Participants can usually choose from various investment options such as mutual funds, stocks, and bonds, providing flexibility and control over their retirement savings strategy.
Key Differences Between Pension Plans and 401(k)s
Pension plans provide a defined benefit based on salary and years of service, guaranteeing a steady retirement income, while 401(k) plans are defined contribution accounts where Your retirement savings depend on contributions and investment performance. Pensions are employer-funded with little risk to the employee, whereas 401(k)s place investment risk and management responsibility on You. Withdrawal rules and tax treatments differ significantly, influencing your retirement planning strategy depending on whether you have a pension plan or a 401(k).
Employer Contributions: Pension vs 401(k)
Employer contributions in a pension plan are typically fixed and guaranteed for the employee's entire career, providing a defined benefit upon retirement. In contrast, employer contributions to a 401(k) plan often vary based on company policy, commonly involving matching percentages of employee contributions, which are subject to annual limits set by the IRS. Pension plans offer more predictable retirement income due to guaranteed employer funding, while 401(k) employer contributions depend on employee participation and company matching formulas.
Investment Control and Flexibility
A 401(k) offers greater investment control and flexibility, allowing employees to choose from various mutual funds, stocks, and bonds, with options to adjust contributions and roll over funds when changing jobs. In contrast, traditional pension plans provide limited individual control, as investments are managed by the employer with a fixed benefit payout formula. Hybrid approaches, such as cash balance plans, combine elements of both but generally offer less flexibility than a 401(k) in managing investment choices and distributions.
Vesting Schedules Explained
Vesting schedules determine when Your ownership of pension benefits, 401(k) contributions, or traditional pensions becomes non-forfeitable, affecting your access to these funds upon leaving an employer. In a pension plan, vesting typically follows a cliff or graded schedule, fully vesting after 3 to 7 years of service, while 401(k) plans may have immediate vesting on your contributions but employer matches often vest over time. Understanding these vesting terms is crucial for maximizing retirement savings and making informed decisions about your financial future.
Retirement Payout Options: Guaranteed Income vs. Market-Based Returns
Pension plans typically offer guaranteed income payouts throughout retirement, providing financial stability regardless of market fluctuations. In contrast, 401(k) accounts rely on market-based returns, meaning your retirement income can vary depending on investment performance. Understanding these differences helps you choose the best retirement payout option to secure your financial future.
Risks and Security: Pension Plan vs 401(k)
Pension plans offer greater financial security through guaranteed lifetime income, minimizing investment risk for retirees. In contrast, 401(k) accounts expose participants to market volatility and the risk of outliving their savings due to reliance on individual investment performance. The defined benefit nature of pension plans reduces longevity and market risks, whereas 401(k)s place full responsibility for retirement planning and investment decisions on the employee.
Tax Benefits and Implications
Pension plans typically offer defined benefits with tax-deferred growth, where contributions are made by employers and taxes are paid upon distribution, often at retirement when individuals may be in a lower tax bracket. 401(k) accounts provide employees the option to contribute pre-tax income, reducing taxable income in the contribution year, with taxes owed upon withdrawal, and Roth 401(k) variations allowing for tax-free withdrawals after meeting certain conditions. Understanding the tax implications involves analyzing contribution limits, employer matches, withdrawal rules, and required minimum distributions to optimize retirement savings across pension plans and 401(k) options.
Choosing the Right Retirement Plan for Your Future
Choosing the right retirement plan for your future involves understanding the key differences between a pension plan, a 401(k), and a traditional pension. A pension plan offers guaranteed lifetime income based on your salary and years of service, while a 401(k) lets you control your investments with potential for growth but no guaranteed payout. Evaluate your risk tolerance, employer contributions, and desired retirement income to make an informed decision tailored to your financial goals.
Infographic: Pension Plan vs 401(k)
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com