Revolving credit allows flexible borrowing up to a set limit with variable payments, while installment credit involves fixed payments over a set period for a specific loan amount. Discover the key differences and benefits of revolving credit versus installment credit in this article.
Table of Comparison
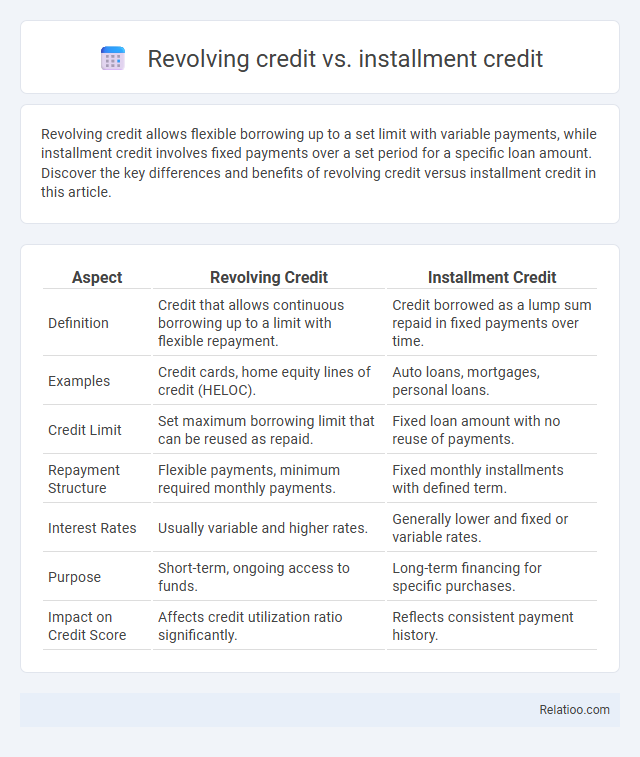
| Aspect | Revolving Credit | Installment Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Credit that allows continuous borrowing up to a limit with flexible repayment. | Credit borrowed as a lump sum repaid in fixed payments over time. |
| Examples | Credit cards, home equity lines of credit (HELOC). | Auto loans, mortgages, personal loans. |
| Credit Limit | Set maximum borrowing limit that can be reused as repaid. | Fixed loan amount with no reuse of payments. |
| Repayment Structure | Flexible payments, minimum required monthly payments. | Fixed monthly installments with defined term. |
| Interest Rates | Usually variable and higher rates. | Generally lower and fixed or variable rates. |
| Purpose | Short-term, ongoing access to funds. | Long-term financing for specific purchases. |
| Impact on Credit Score | Affects credit utilization ratio significantly. | Reflects consistent payment history. |
Understanding Revolving Credit
Revolving credit allows borrowers to access a credit limit repeatedly as they repay the balance, offering flexibility unlike installment credit, which requires fixed payments over a set term. Understanding revolving credit is essential for managing consumer loans, credit cards, and lines of credit, where interest is charged on outstanding balances. This credit type influences credit scores through factors like credit utilization ratio and payment history, making responsible use critical for maintaining financial health.
Understanding Installment Credit
Installment credit involves borrowing a fixed amount of money and repaying it through scheduled, consistent payments over a predetermined period, enhancing budget predictability for borrowers. Revolving credit allows users to borrow up to a certain limit, repay, and borrow again, offering flexible access but potentially variable payment amounts. Understanding installment credit is essential for managing loans such as mortgages, auto loans, and personal loans, where fixed interest rates and payment schedules provide financial stability.
Key Differences Between Revolving and Installment Credit
Revolving credit allows borrowers to access a fixed credit limit repeatedly as they repay, with interest charged on outstanding balances, while installment credit involves fixed payments over a set period until the loan is fully paid. Key differences include flexibility in repayment and borrowing: revolving credit adapts to changing needs without reapplying, whereas installment credit requires a one-time lump-sum borrowing with predetermined monthly payments. Credit cards exemplify revolving credit, whereas auto loans and mortgages illustrate installment credit, each impacting credit scores differently based on utilization and payment history.
How Revolving Credit Works
Revolving credit allows borrowers to access a predetermined credit limit and repay the balance flexibly, with interest charged only on the outstanding amount, making it ideal for ongoing expenses. Unlike installment credit, which involves fixed monthly payments over a set period, revolving credit accounts like credit cards offer continuous borrowing and repayment options without a fixed term. This flexible repayment structure supports cash flow management while impacting credit utilization ratios, a key factor in credit score calculations.
How Installment Credit Works
Installment credit involves borrowing a specific amount of money upfront, which you repay in fixed monthly installments over a predetermined period, typically at a set interest rate. This makes it easier to budget your finances, as each payment remains consistent until the loan is fully paid off. Understanding how installment credit works can help you manage your debt more effectively and maintain a healthy credit score.
Pros and Cons of Revolving Credit
Revolving credit offers flexibility by allowing borrowers to use and repay funds repeatedly up to a credit limit, making it ideal for managing fluctuating expenses; however, it typically carries higher interest rates and potential for accumulating debt if balances are not paid in full. Installment credit involves fixed payments over a specified period, providing predictable budgeting but less flexibility in borrowing additional funds without new credit approval. General credit represents the overall borrowing capacity, influencing credit scores and financial health through responsible usage and timely repayments.
Pros and Cons of Installment Credit
Installment credit offers predictable monthly payments and fixed interest rates, making budgeting easier and reducing the risk of overspending compared to revolving credit. However, it lacks flexibility since payments and loan terms are set upfront, preventing changes in the borrowing amount without refinancing. While installment credit builds credit history through consistent repayments, missing payments can significantly impact credit scores due to the structured repayment schedule.
Impact on Credit Score: Revolving vs Installment Credit
Revolving credit, such as credit cards, impacts credit scores by influencing credit utilization ratios, which account for approximately 30% of FICO score calculations, making timely payments and maintaining low balances critical. Installment credit, including mortgages and auto loans, affects credit scores through consistent, on-time payments that contribute positively over time by demonstrating repayment reliability. Both types of credit mix contribute about 10% to credit scoring, with balanced management enhancing overall credit health and scoring potential.
Choosing the Right Credit Option
Revolving credit offers flexible borrowing with a credit limit and variable payments, ideal for ongoing expenses and cash flow management. Installment credit provides fixed payments over a set term, making it suitable for predictable purchases like auto loans or mortgages. Selecting the right credit option depends on your financial goals, repayment ability, and the nature of the purchase to optimize interest costs and credit utilization.
Frequently Asked Questions about Credit Types
Revolving credit allows you to borrow up to a set limit and repay it over time, with fluctuating balances and interest, common in credit cards. Installment credit involves fixed payments over a defined period, such as auto loans or mortgages, providing predictable repayment schedules. Your choice between these credit types depends on your financial goals, repayment ability, and the nature of your borrowing needs.
Infographic: Revolving credit vs Installment credit
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com