A penalty is a punitive charge imposed for violating terms, while a surcharge is an additional fee applied to cover extra costs. Explore this article to understand the key differences between penalties and surcharges.
Table of Comparison
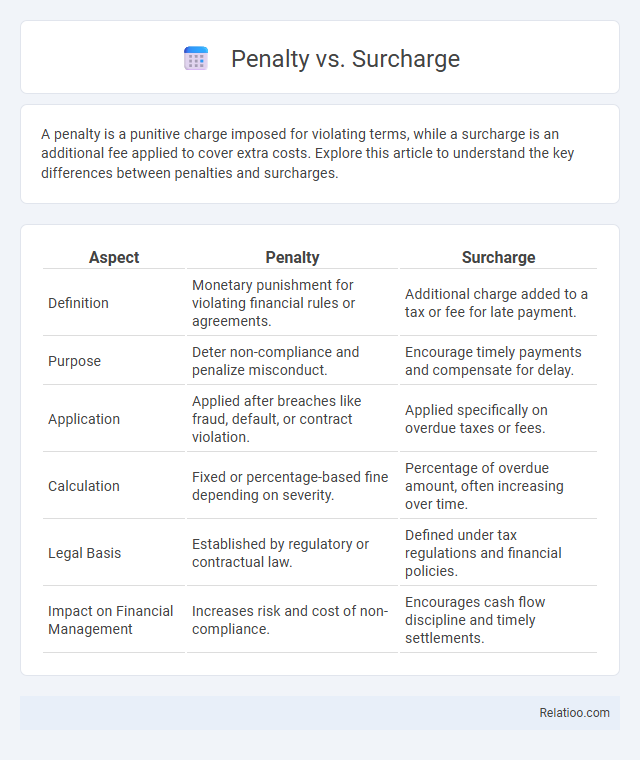
| Aspect | Penalty | Surcharge |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary punishment for violating financial rules or agreements. | Additional charge added to a tax or fee for late payment. |
| Purpose | Deter non-compliance and penalize misconduct. | Encourage timely payments and compensate for delay. |
| Application | Applied after breaches like fraud, default, or contract violation. | Applied specifically on overdue taxes or fees. |
| Calculation | Fixed or percentage-based fine depending on severity. | Percentage of overdue amount, often increasing over time. |
| Legal Basis | Established by regulatory or contractual law. | Defined under tax regulations and financial policies. |
| Impact on Financial Management | Increases risk and cost of non-compliance. | Encourages cash flow discipline and timely settlements. |
Understanding Penalties and Surcharges
Penalties are financial charges imposed as a consequence of violating laws, regulations, or contractual terms, often intended to deter undesirable behavior. Surcharges refer to additional fees added to the original price or bill, commonly used to cover extra costs such as taxes, fuel, or administrative expenses. Understanding penalties and surcharges involves recognizing that penalties serve a punitive function for non-compliance, whereas surcharges are supplemental charges reflecting increased costs or specific conditions.
Key Differences Between Penalty and Surcharge
Penalty refers to a financial punishment imposed for violating laws or regulations, often linked to non-compliance or late payments. Surcharge is an additional charge applied on top of a base price or fee, typically as a compensation for extra costs or services. The key difference lies in their purpose: penalties enforce compliance and deter misconduct, while surcharges recover specific expenses, without implying wrongdoing.
Legal Definitions: Penalty vs Surcharge
A penalty is a legal consequence imposed for violating a law or regulation, often intended to punish non-compliance, while a surcharge is an additional charge or fee levied on top of an existing amount, typically to cover extra costs or discourage late payments. In legal contexts, penalties are punitive measures codified into statutes or contracts, whereas surcharges serve as compensatory or preventive financial tools. Distinguishing these terms is crucial for interpreting regulatory obligations and contractual liabilities accurately.
Common Situations Involving Penalties
Common situations involving penalties include late payments, violations of contractual terms, and non-compliance with regulatory requirements, each triggering financial consequences to enforce adherence. Penalties differ from surcharges as they are punitive fees imposed for specific breaches, whereas surcharges are additional charges applied to cover extra costs like late fees or administrative expenses. Understanding how these charges affect your obligations ensures timely compliance and minimizes unexpected financial burdens.
When Surcharges Are Applied
Surcharges are applied when additional fees need to cover extra costs such as late payments, increased processing expenses, or regulatory requirements, distinct from penalties which are punitive for non-compliance or violations. While penalties are enforced to discourage undesirable behavior, surcharges serve to offset specific service-related expenses, directly impacting your final bill. Understanding the timing and reasons behind surcharges ensures you can better manage and anticipate extra charges on your accounts or services.
Penalty Calculation Methods
Penalty calculation methods vary based on the legal context, typically involving a fixed amount, a percentage of the unpaid tax or debt, or a daily accrual until compliance is achieved. Surcharges are generally calculated as a percentage over the base amount due, serving as an extra financial charge rather than a punitive measure. In contrast, penalties are specifically designed to discourage non-compliance and are often more complex, incorporating factors such as delay duration, severity of violation, and taxpayer history.
Surcharge Calculation Techniques
Surcharge calculation techniques typically involve applying a percentage rate to the outstanding balance or unpaid amount, often compounded over specific time intervals such as monthly or quarterly. Unlike penalties, which are fixed or flat charges imposed for violations, surcharges are dynamic and increase proportionally with the amount due, reflecting the extended usage or delayed payment. Accurate surcharge computations require clear definitions of the principal amount, applicable rates, and the period of delay to ensure transparent financial adjustments.
Impacts of Penalties on Consumers
Penalties impose financial burdens on consumers by increasing costs for non-compliance with regulations, leading to diminished purchasing power and potential credit score damage. Unlike surcharges, which are added fees explicitly disclosed and often reversible, penalties can restrict access to services, resulting in long-term economic consequences and decreased consumer trust. These punitive measures create deterrents but can also disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, exacerbating financial instability.
Effects of Surcharges on Businesses
Surcharges increase the overall cost burden on businesses, directly impacting cash flow and profitability by adding extra fees to overdue payments or regulatory breaches. Unlike penalties, which serve as punitive measures, surcharges function as financial incentives encouraging timely compliance and payment. Your business must carefully manage surcharges to avoid escalating expenses that can strain operational budgets and reduce competitive advantage.
Avoiding Penalties and Surcharges
Avoiding penalties and surcharges requires a clear understanding of their distinct implications: penalties are punitive charges for non-compliance, while surcharges are additional fees imposed for specific services or conditions. Businesses must ensure timely payments and adherence to contractual terms to minimize risk of penalties, while closely monitoring billing statements to identify and dispute unauthorized surcharges. Implementing automated compliance checks and regular audits significantly reduces exposure to unexpected financial liabilities.
Infographic: Penalty vs Surcharge
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com