The principal is the individual who authorizes an agent to act on their behalf, while the owner is the person who holds legal title to a property or asset. Explore this article to understand the distinct roles and responsibilities of principals versus owners.
Table of Comparison
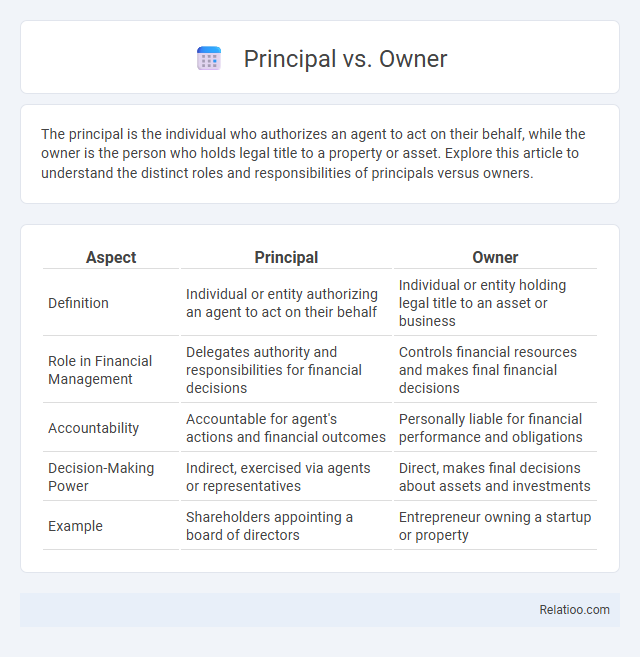
| Aspect | Principal | Owner |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual or entity authorizing an agent to act on their behalf | Individual or entity holding legal title to an asset or business |
| Role in Financial Management | Delegates authority and responsibilities for financial decisions | Controls financial resources and makes final financial decisions |
| Accountability | Accountable for agent's actions and financial outcomes | Personally liable for financial performance and obligations |
| Decision-Making Power | Indirect, exercised via agents or representatives | Direct, makes final decisions about assets and investments |
| Example | Shareholders appointing a board of directors | Entrepreneur owning a startup or property |
Understanding the Roles: Principal vs Owner
Understanding the roles of Principal and Owner is crucial in business and project management contexts. A Principal typically serves as a key decision-maker or lead professional responsible for overseeing operations, strategy, or project execution within an organization, whereas an Owner holds legal possession and ultimate control of the company or asset. The Principal manages day-to-day functions and strategic initiatives, while the Owner assumes financial risk and benefits from ownership equity.
Definition of Principal in Business
In business, the term "Principal" refers to an individual or entity with primary responsibility for a company, often holding decision-making authority or ownership interest. Unlike an Owner, who exclusively holds legal title to the business, a Principal may act as a key executive or stakeholder influencing strategic operations. Understanding the role of a Principal involves recognizing both legal responsibilities and operational influence within the organizational structure.
Definition of Owner in Business
An owner in business refers to an individual or entity holding legal title and possessing ultimate control over assets and decisions within a company. Unlike a principal, who may act on behalf of the business or represent it in legal matters, the owner retains equity interest and bears financial risks and rewards tied to the enterprise. Ownership rights include profit entitlement, decision-making authority, and responsibility for liabilities incurred by the business entity.
Key Differences Between Principal and Owner
A principal typically refers to an individual or entity with primary responsibility or control over a business or transaction, whereas an owner holds legal title and equity in the business. Key differences between principal and owner lie in decision-making authority versus ownership rights, where a principal may manage operations without holding ownership, and an owner may have equity without daily involvement. Understanding these distinctions helps you clarify roles in business structures or contractual agreements.
Legal Responsibilities of Principals
Principals hold significant legal responsibilities, including fiduciary duties to act in the best interest of their company and compliance with regulatory requirements. Owners, while having equity and control, may not be directly liable for daily legal obligations unless they also serve as principals. Your role as a principal requires careful attention to contracts, corporate governance, and risk management to ensure legal accountability.
Legal Responsibilities of Owners
Owners hold the ultimate legal responsibility for a business, including compliance with regulations, financial obligations, and contractual liabilities. Principals, often key executives or decision-makers, may manage daily operations but typically share responsibility rather than bearing full legal accountability. Understanding the distinct roles clarifies that owners possess the primary legal duties, making them accountable for the company's legal and financial outcomes.
Principal vs Owner: Decision-Making Authority
Principals hold primary decision-making authority within a business or project, often responsible for strategic direction and major operational choices. Owners possess ultimate control through equity or legal ownership but may delegate daily decisions to principals or managers. Understanding the distinction clarifies roles in governance, accountability, and leadership dynamics.
Financial Implications: Principal vs Owner
The financial implications of a Principal versus an Owner vary significantly based on legal structure and liability exposure. A Principal typically has decision-making authority and may receive a salary or profit share, but does not necessarily hold equity or bear personal financial risk. As the Owner, Your financial responsibility includes potential personal liability, equity investment, and direct impact on profits or losses, influencing long-term financial outcomes.
Examples of Principals and Owners in Various Industries
Principals often act as key decision-makers or leading figures within organizations such as law firms, consulting agencies, and investment companies, exemplified by a principal lawyer steering case strategy or a principal consultant managing client projects. Owners hold legal title and control over assets in sectors like real estate, retail, and hospitality, such as a restaurant owner overseeing daily operations or a property owner managing rental agreements. In some businesses, especially startups and private firms, an individual can simultaneously be both principal and owner, embodying strategic leadership and financial stakes, as seen in entrepreneur-founded tech companies.
Choosing the Right Role: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right role between Principal, Owner, and Principal Owner involves evaluating responsibilities, decision-making authority, and financial risk exposure. Principals typically lead projects or departments, Owners hold equity stakes with ultimate business control, while Principal Owners combine leadership with ownership stakes, balancing management duties with investment interests. Consider factors such as desired influence over operations, risk tolerance, and long-term commitment when selecting the appropriate role to align with career goals and business objectives.
Infographic: Principal vs Owner
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com