Gross revenue represents the total sales before deductions, while net revenue accounts for all expenses, taxes, and returns subtracted from gross revenue. Discover a detailed analysis of how these metrics impact business profitability in this article.
Table of Comparison
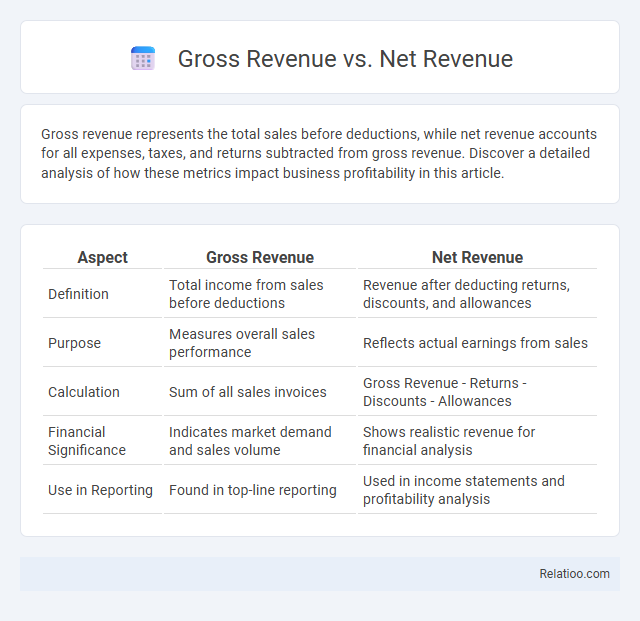
| Aspect | Gross Revenue | Net Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total income from sales before deductions | Revenue after deducting returns, discounts, and allowances |
| Purpose | Measures overall sales performance | Reflects actual earnings from sales |
| Calculation | Sum of all sales invoices | Gross Revenue - Returns - Discounts - Allowances |
| Financial Significance | Indicates market demand and sales volume | Shows realistic revenue for financial analysis |
| Use in Reporting | Found in top-line reporting | Used in income statements and profitability analysis |
Understanding Gross Revenue: Definition and Importance
Gross revenue represents the total income generated from sales or services before deducting any expenses, returns, or discounts, serving as a critical indicator of a company's overall market demand and sales performance. It is essential for assessing the business scale and revenue-generating capacity, providing a baseline for calculating profitability metrics such as net revenue and operating income. Understanding gross revenue helps investors and management evaluate top-line growth trends and forecast future financial health.
What is Net Revenue? Key Differences from Gross Revenue
Net revenue represents the actual income your business retains after deducting costs like returns, discounts, and allowances from gross revenue, providing a clearer picture of profitability. Unlike gross revenue, which reflects total sales without reductions, net revenue offers a more accurate measure of financial health by accounting for expenses directly tied to sales. Understanding the distinction between gross revenue, net revenue, and subscription revenue helps you manage cash flow and evaluate business performance effectively.
The Calculation: How to Determine Gross Revenue
Gross Revenue is calculated by totaling all sales generated before any deductions, such as returns, discounts, or allowances. This figure represents the overall income from your business activities without accounting for expenses or liabilities. Understanding Gross Revenue is essential for evaluating your company's top-line performance before considering net revenue or subscription-based earnings.
Deductions Explained: How Net Revenue is Calculated
Gross revenue represents the total income your business generates from sales before any deductions. Net revenue is calculated by subtracting returns, discounts, allowances, and subscription-related costs from gross revenue, giving a more accurate measure of your actual earnings. Understanding these deductions helps you optimize your subscription model and improve financial reporting accuracy.
Common Revenue Sources and Their Impact on Total Revenue
Gross revenue represents the total income generated from all sales before any deductions, while net revenue accounts for returns, discounts, and allowances, providing a more accurate measure of actual earnings. Subscription revenue, a growing segment in many industries, offers a recurring income stream that stabilizes cash flow and enhances lifetime customer value. Understanding these common revenue sources and their distinct impacts allows businesses to better forecast total revenue and optimize financial strategies.
Gross Revenue vs Net Revenue: Why the Distinction Matters
Gross revenue represents the total income from all sales before any deductions, while net revenue accounts for returns, discounts, and allowances, reflecting the actual income retained by a business. Understanding the distinction between gross revenue and net revenue is crucial for accurate financial analysis and forecasting, as net revenue offers a clearer picture of profitability and operational efficiency. Subscription models often impact net revenue significantly due to recurring discounts, cancellations, and churn rates that reduce the gross revenue figure.
Financial Reporting: Where Gross and Net Revenue Appear
Gross revenue appears on the top line of the income statement, representing the total sales before any deductions. Net revenue, also known as net sales, is reported below gross revenue and reflects deductions such as returns, allowances, and discounts, providing a more accurate picture of actual income. Subscription revenue, often recurring and recognized over the subscription period, is disclosed in financial statements either within net revenue or as a separate segment, depending on the company's reporting practices.
Industry Examples: Gross Revenue vs Net Revenue in Practice
Gross revenue represents the total income generated from sales before any deductions, commonly used by industries such as retail and e-commerce to showcase overall sales performance. Net revenue, calculated by subtracting returns, discounts, and allowances from gross revenue, provides a clearer measure of actual earnings, widely applied in the software-as-a-service (SaaS) and telecommunications sectors to assess profitability. Subscription-based companies, like streaming services and SaaS platforms, emphasize net revenue to track recurring income after accounting for churn and customer discounts, ensuring a realistic financial outlook.
Implications for Business Performance and Decision Making
Gross revenue represents the total income from sales before any deductions, reflecting your business's market reach and pricing strategy effectiveness. Net revenue, calculated after deducting returns, discounts, and allowances, offers a more accurate measure of profitability critical for informed budgeting and forecasting. Subscription revenue, a recurring income stream, enhances cash flow predictability and customer lifetime value, influencing strategic decisions on customer retention and product development.
Choosing the Right Metric: When to Use Gross or Net Revenue
Choosing the right metric between gross revenue, net revenue, and subscription revenue depends on your business goals and financial analysis needs. Gross revenue reflects your total sales before any deductions, ideal for understanding overall market demand, while net revenue accounts for returns, discounts, and allowances, offering a more accurate picture of your actual earnings. For subscription-based models, tracking subscription revenue is crucial for understanding recurring income and customer retention, ensuring Your financial decisions are based on relevant, precise data.
Infographic: Gross Revenue vs Net Revenue
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com