Operating income measures a company's profit from core business operations, excluding expenses like taxes and interest, while net income reflects the total profit after all expenses and incomes. Explore this article to understand how these financial metrics impact business performance evaluation.
Table of Comparison
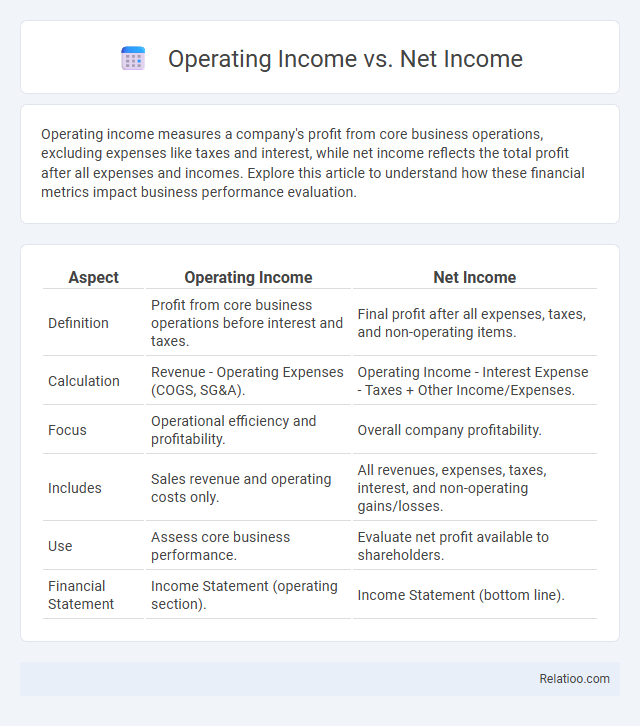
| Aspect | Operating Income | Net Income |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profit from core business operations before interest and taxes. | Final profit after all expenses, taxes, and non-operating items. |
| Calculation | Revenue - Operating Expenses (COGS, SG&A). | Operating Income - Interest Expense - Taxes + Other Income/Expenses. |
| Focus | Operational efficiency and profitability. | Overall company profitability. |
| Includes | Sales revenue and operating costs only. | All revenues, expenses, taxes, interest, and non-operating gains/losses. |
| Use | Assess core business performance. | Evaluate net profit available to shareholders. |
| Financial Statement | Income Statement (operating section). | Income Statement (bottom line). |
Introduction to Operating Income and Net Income
Operating income represents your core business profitability, calculated as gross profit minus operating expenses, excluding non-operating items like taxes and interest. Net income reflects the overall profitability after accounting for all revenues, expenses, taxes, and non-operating items, providing a comprehensive view of your company's financial performance. Understanding the distinction between operating income and net income helps you evaluate operational efficiency versus total profitability.
Definition of Operating Income
Operating income represents the profit generated from core business operations, excluding expenses like taxes, interest, and non-operating items, making it a key indicator of Your company's operational efficiency. Net income reflects the total profit after deducting all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, interest, and one-time items. Income, in financial terms, broadly refers to earnings or profit received by a business or individual.
Definition of Net Income
Net income represents the company's total profit after all expenses, taxes, and costs have been deducted from total revenue, reflecting the most comprehensive measure of profitability. Operating income, also known as operating profit, excludes non-operating expenses such as taxes and interest, focusing solely on earnings from core business operations. Unlike general income figures, net income provides a clear indicator of overall financial health by capturing the bottom-line financial performance.
Key Differences Between Operating Income and Net Income
Operating income represents the profit generated from core business operations, excluding non-operating expenses, taxes, and interest, reflecting operational efficiency. Net income accounts for total profitability after deducting all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, interest, and non-operating items, providing a comprehensive view of a company's financial performance. Key differences include the scope of expenses considered and the impact of financing and tax strategies on net income, whereas operating income isolates performance from primary business activities.
Components Included in Operating Income
Operating Income includes revenue from core business operations minus operating expenses such as cost of goods sold (COGS), selling, general and administrative expenses (SG&A), and depreciation. Net Income accounts for all revenues and expenses, including operating income, interest, taxes, and non-operating items like gains or losses from investments. Income, often used generically, can refer to gross income, operating income, or net income depending on the context, but Operating Income specifically excludes taxes and interest, focusing only on core operational profitability.
Components Included in Net Income
Net income encompasses all revenue streams and deducts total expenses, including operating expenses, interest, taxes, and non-operating items, making it the most comprehensive measure of profitability. Operating income, also known as operating profit or EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes), includes revenue minus operating expenses such as cost of goods sold, wages, and depreciation, excluding interest and tax expenses. Income, as a term, can refer to various profitability metrics, but net income specifically integrates all components affecting the bottom line, reflecting the company's overall financial performance after all costs and income sources are accounted for.
Importance of Operating Income in Financial Analysis
Operating income is a critical metric in financial analysis as it reflects a company's profitability from core business operations, excluding non-operating income and expenses. Unlike net income, which includes taxes, interest, and one-time items, operating income provides a clearer view of operational efficiency and performance. Analysts prioritize operating income to assess sustainable earnings and make informed decisions about operational scalability and cost management.
Importance of Net Income for Investors
Operating income measures a company's profit from core business operations before interest and taxes, while net income represents the total profit after all expenses, taxes, and non-operating items. Investors prioritize net income as it reflects the company's overall profitability and ability to generate returns, impacting earnings per share and dividend potential. Net income provides a comprehensive view of financial health, essential for making informed investment decisions.
How to Calculate Operating Income and Net Income
Operating Income is calculated by subtracting operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, and cost of goods sold, from gross profit, providing a clear view of your company's profitability from core operations. Net Income goes further by deducting non-operating expenses, interest, and taxes from the operating income, reflecting the total profit or loss. Understanding these calculations allows you to evaluate both operational efficiency and overall financial health accurately.
Which Metric Matters Most for Business Decision-Making?
Operating income measures profitability from core business operations, excluding non-operating income and expenses, while net income reflects the overall profitability after all costs, taxes, and interest, providing a comprehensive view of financial performance. Income, a broader term, can refer to various measures such as gross income or revenue, making it less precise for decision-making. Your business decisions should primarily focus on operating income to evaluate operational efficiency and core profitability, but net income remains crucial for understanding the overall financial health and sustainability.
Infographic: Operating Income vs Net Income
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com