Savings accounts offer flexible access to funds with lower interest rates, while fixed deposits provide higher returns through locked-in investments for a specified term. Discover the key differences and benefits of Savings Accounts versus Fixed Deposits in this article.
Table of Comparison
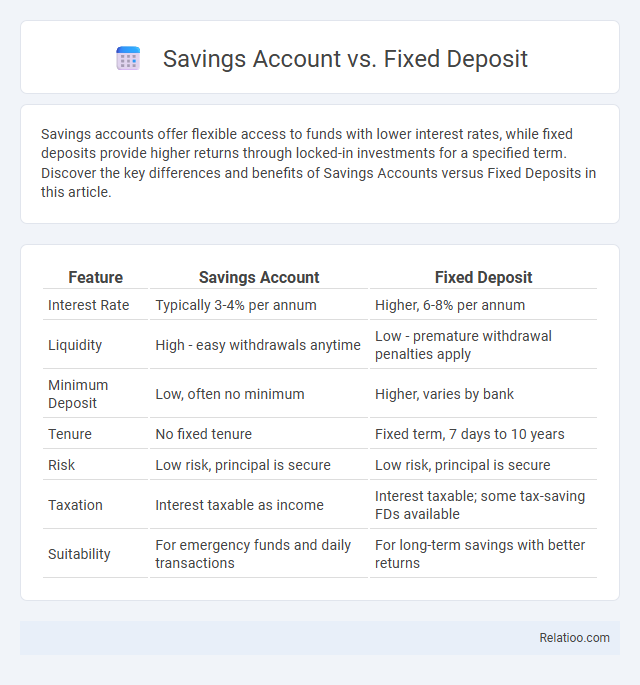
| Feature | Savings Account | Fixed Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Typically 3-4% per annum | Higher, 6-8% per annum |
| Liquidity | High - easy withdrawals anytime | Low - premature withdrawal penalties apply |
| Minimum Deposit | Low, often no minimum | Higher, varies by bank |
| Tenure | No fixed tenure | Fixed term, 7 days to 10 years |
| Risk | Low risk, principal is secure | Low risk, principal is secure |
| Taxation | Interest taxable as income | Interest taxable; some tax-saving FDs available |
| Suitability | For emergency funds and daily transactions | For long-term savings with better returns |
Introduction to Savings Accounts and Fixed Deposits
Savings accounts offer you easy access to funds while earning interest, making them ideal for daily transactions and emergency savings. Fixed deposits lock your money for a predetermined period at a higher interest rate, providing guaranteed returns with minimal risk. Both savings accounts and fixed deposits serve distinct financial needs, balancing liquidity and growth potential in your investment portfolio.
Key Differences Between Savings Account and Fixed Deposit
A Savings Account offers flexible access to funds with variable interest rates, ideal for everyday transactions and emergency savings. Fixed Deposits lock your money for a fixed tenure at higher, guaranteed interest rates, making them suitable for long-term financial goals. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize liquidity or higher returns with minimal risk.
Interest Rates Comparison
Savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates, averaging around 0.5% to 1.5% annually, providing easy liquidity for your daily transactions. Fixed deposits yield higher interest rates, often ranging from 4% to 7%, with returns locked in for a fixed tenure, making them ideal for long-term savings. Comparing the two, fixed deposits maximize your interest earnings while savings accounts prioritize accessibility and flexibility.
Liquidity and Accessibility
Savings accounts offer high liquidity and easy accessibility, allowing you to withdraw funds anytime without penalties. Fixed deposits restrict access to your money for a predetermined tenure, typically offering higher interest rates but with limited liquidity until maturity. Comparing both, savings accounts provide flexible fund availability, while fixed deposits prioritize capital growth over immediate access.
Risk Factors Involved
Your savings account offers high liquidity with minimal risk, making it ideal for everyday expenses despite lower interest rates. Fixed deposits carry a moderate risk due to locked-in funds and penalty charges for early withdrawal, but typically provide higher returns with guaranteed interest. Comparing these options helps you balance risk tolerance and investment horizon, ensuring your money grows securely according to your financial goals.
Suitability for Different Financial Goals
A Savings Account offers high liquidity and is suitable for emergency funds and short-term goals, providing easy access to Your money with moderate interest rates. Fixed Deposits are ideal for medium to long-term financial goals, offering higher interest rates in exchange for locking Your funds for a fixed period, making them beneficial for wealth accumulation. Savings Bonds or similar instruments suit conservative investors seeking stable returns with low risk, fitting retirement planning or preservation of capital.
Tax Implications and Benefits
Savings accounts offer liquidity with interest income often taxable as per individual tax slabs, while fixed deposits provide higher interest rates but attract tax deducted at source (TDS) if interest exceeds specified limits. Tax-saving fixed deposits under Section 80C allow deductions up to INR 1.5 lakh annually, whereas regular savings accounts do not offer such benefits. Interest from savings accounts up to INR 10,000 per financial year is exempt under Section 80TTA, providing modest tax relief for small depositors.
Minimum Balance and Penalties
Savings accounts typically require a low minimum balance, often ranging from $100 to $500, with penalties such as fees for dropping below the threshold or excessive withdrawals. Fixed deposits demand a higher initial commitment, usually starting around $1,000, but they offer no minimum balance requirements during the term, though early withdrawal incurs penalties that reduce your interest earned. Your choice should consider these minimum balance requirements and associated penalties to avoid unnecessary fees and maximize returns.
Tenure and Flexibility
Savings accounts offer high flexibility with no fixed tenure, allowing unlimited withdrawals and deposits anytime. Fixed deposits have a predetermined tenure ranging from 7 days to 10 years, with penalties for premature withdrawals, providing higher interest rates in return. Savings bonds combine features of both, offering moderate tenure options with some liquidity benefits depending on the specific product.
Which Option is Right for You?
Choosing between a Savings Account, Fixed Deposit, and Recurring Savings depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs. A Savings Account offers high liquidity and easy access for daily expenses, whereas a Fixed Deposit provides higher interest rates with locked-in funds for a fixed tenure, ideal for long-term savings. Recurring Savings plans help build disciplined monthly savings with moderate returns, making it essential to evaluate your cash flow and investment horizon to select the best option for you.
Infographic: Savings Account vs Fixed Deposit
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com