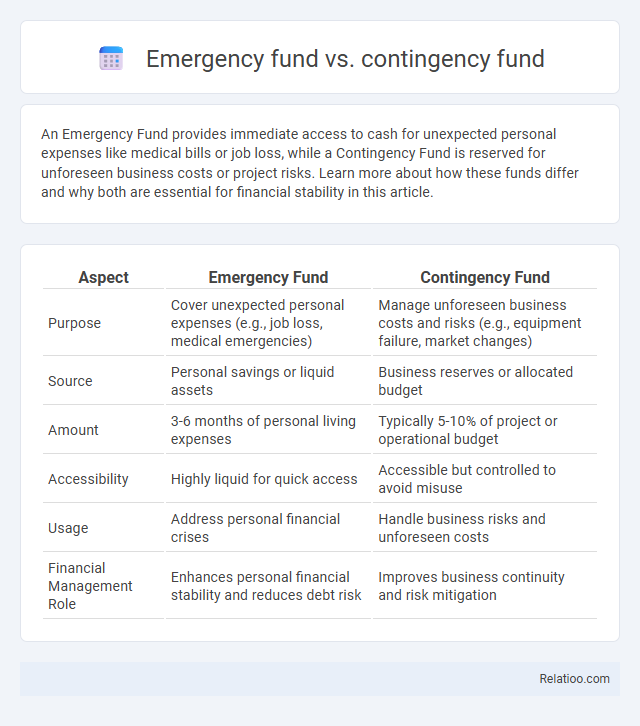
An Emergency Fund provides immediate access to cash for unexpected personal expenses like medical bills or job loss, while a Contingency Fund is reserved for unforeseen business costs or project risks. Learn more about how these funds differ and why both are essential for financial stability in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Emergency Fund | Contingency Fund |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cover unexpected personal expenses (e.g., job loss, medical emergencies) | Manage unforeseen business costs and risks (e.g., equipment failure, market changes) |
| Source | Personal savings or liquid assets | Business reserves or allocated budget |
| Amount | 3-6 months of personal living expenses | Typically 5-10% of project or operational budget |
| Accessibility | Highly liquid for quick access | Accessible but controlled to avoid misuse |
| Usage | Address personal financial crises | Handle business risks and unforeseen costs |
| Financial Management Role | Enhances personal financial stability and reduces debt risk | Improves business continuity and risk mitigation |
Introduction to Financial Safety Nets
Emergency Fund is a financial safety net designed to cover unexpected expenses like medical emergencies or job loss, providing peace of mind during uncertain times. Contingency Fund focuses on unplanned business or project-related costs, safeguarding organizational stability and operational continuity. Your understanding of these distinct funds enhances financial preparedness by addressing personal and professional risks efficiently.
Defining Emergency Funds
An Emergency Fund is a financial safety net specifically designed to cover unexpected personal expenses such as medical emergencies, job loss, or urgent home repairs. Unlike a Contingency Fund, which is often allocated by businesses or organizations for unforeseen project-related risks, your Emergency Fund focuses on individual financial security. Clearly defining and maintaining an adequate Emergency Fund ensures you are prepared for sudden financial disruptions without relying on debt.
What Is a Contingency Fund?
A contingency fund is a reserved amount of money set aside specifically to address unforeseen expenses or financial shortfalls that may arise during a project or business operation. Unlike an emergency fund, which is typically personal savings for unexpected life events, a contingency fund is strategically planned to mitigate risks and ensure project continuity without disrupting your overall financial stability. Understanding the purpose and proper allocation of a contingency fund helps you maintain control over unexpected challenges and safeguard your financial goals.
Key Differences: Emergency vs Contingency Funds
Emergency funds are specifically reserved for unforeseen personal financial crises such as medical emergencies or job loss, while contingency funds are broader reserves set aside for potential business risks or project uncertainties. Your emergency fund is typically liquid and covers 3-6 months of living expenses, ensuring immediate access during urgent situations. Contingency funds may be less liquid and used strategically to mitigate identified risks without disrupting operational cash flow.
Importance of Having Both Funds
Emergency funds provide immediate financial support for unexpected personal expenses such as medical emergencies or job loss, while contingency funds are reserved for unforeseen business-related costs like equipment failure or project delays. Having both funds ensures comprehensive financial protection, allowing individuals and organizations to maintain stability without disrupting long-term savings or operational budgets. Prioritizing these reserves safeguards against financial strain and supports quick recovery during crises.
Common Sources for Building Each Fund
Emergency funds are typically built from readily accessible savings accounts or low-risk investment vehicles like money market funds, ensuring liquidity for unforeseen personal expenses. Contingency funds are often sourced from reserved business profits, retained earnings, or specific budget allocations to address unexpected operational costs or project deviations. Both funds rely on disciplined savings and strategic allocation of resources, but emergency funds prioritize quick access while contingency funds focus on covering business uncertainties.
When to Use an Emergency Fund
An Emergency Fund is specifically designated for unexpected personal financial crises like job loss, medical emergencies, or urgent home repairs, ensuring quick access to cash without disturbing investments. A Contingency Fund, typically used by businesses or organizations, covers unforeseen operational expenses or project overruns that are not part of regular budgeting. Use an Emergency Fund immediately after sudden, unavoidable personal financial setbacks to maintain stability and avoid debt accumulation.
Situations Requiring a Contingency Fund
Situations requiring a contingency fund typically involve unforeseen project expenses, regulatory changes, or unexpected operational disruptions that fall outside regular budgeting. Unlike an emergency fund, which covers personal financial crises, and a general emergency fund for broader unexpected events, a contingency fund specifically addresses risks in business or project management to ensure stability. Your contingency fund acts as a financial buffer, enabling swift response to these uncertainties without compromising primary funds.
Tips for Managing and Growing Your Funds
Emergency funds, contingency funds, and sinking funds each serve unique financial purposes, requiring tailored management strategies to optimize growth and accessibility. Prioritize high-yield savings accounts or money market funds for emergency funds to ensure quick liquidity and inflation-beating interest rates. Diversify contingency funds across low-risk investment vehicles to balance safety with moderate returns, while sinking funds benefit from scheduled contributions and utilization of stable Treasury securities, enhancing fund growth aligned with future obligations.
Conclusion: Strengthening Financial Resilience
Emergency Fund, Contingency Fund, and Reserve Fund each play distinct and vital roles in strengthening financial resilience by covering different types of unforeseen expenses. An Emergency Fund provides immediate access to cash for personal crises, a Contingency Fund addresses project-specific risks or business uncertainties, and a Reserve Fund ensures long-term financial stability by supporting planned or cyclical expenses. Together, these funds create a comprehensive safety net that enhances overall financial security and mitigates the impact of unpredictable financial challenges.
Infographic: Emergency Fund vs Contingency Fund
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com