Marginal Utility measures the additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of a good, while Total Utility represents the overall satisfaction from all units consumed. Explore this article to understand how these concepts influence consumer choices and demand.
Table of Comparison
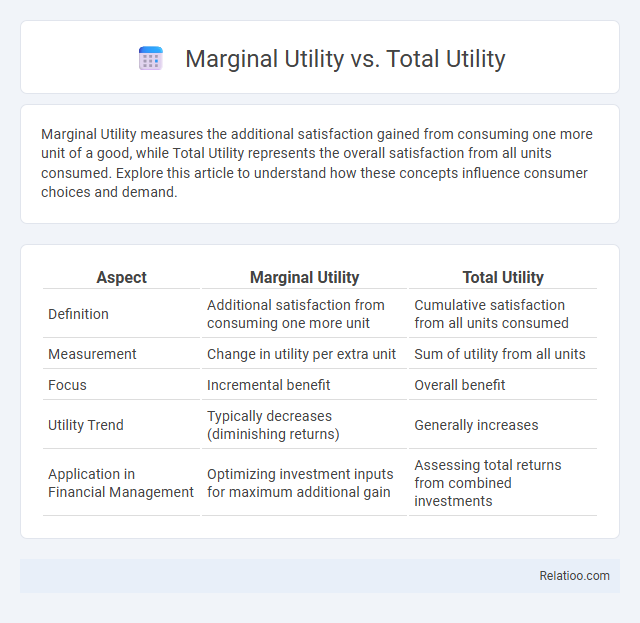
| Aspect | Marginal Utility | Total Utility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit | Cumulative satisfaction from all units consumed |
| Measurement | Change in utility per extra unit | Sum of utility from all units |
| Focus | Incremental benefit | Overall benefit |
| Utility Trend | Typically decreases (diminishing returns) | Generally increases |
| Application in Financial Management | Optimizing investment inputs for maximum additional gain | Assessing total returns from combined investments |
Introduction to Marginal Utility and Total Utility
Marginal Utility measures the additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of a good or service, while Total Utility represents the overall satisfaction derived from consuming a specific quantity of goods. Understanding the difference helps you make informed decisions about resource allocation by evaluating how each incremental unit affects your overall enjoyment. These concepts are fundamental in economics for analyzing consumer behavior efficiently.
Defining Marginal Utility
Marginal utility refers to the additional satisfaction or benefit gained from consuming one more unit of a good or service, highlighting changes in consumer preference. Total utility measures the overall satisfaction derived from consuming a certain quantity of goods, while utility represents the general concept of consumer satisfaction or happiness from consumption. Understanding marginal utility is crucial for analyzing consumer decision-making and optimizing resource allocation in economics.
Defining Total Utility
Total Utility refers to the overall satisfaction or benefit a consumer derives from consuming a certain quantity of goods or services. It accumulates as more units are consumed, reflecting the sum of all marginal utilities obtained from each unit. Understanding Total Utility helps in analyzing consumer behavior and the law of diminishing marginal utility.
Key Differences Between Marginal Utility and Total Utility
Marginal Utility measures the additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of a good or service, while Total Utility represents the overall satisfaction derived from all units consumed. A key difference lies in their focus: marginal utility analyzes the change in utility from incremental consumption, whereas total utility accounts for cumulative satisfaction. Understanding these distinctions helps explain consumer behavior and the law of diminishing marginal utility in economics.
Understanding the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Utility measures the satisfaction derived from consuming goods or services, with total utility representing the overall satisfaction from all units consumed and marginal utility indicating the additional satisfaction from one extra unit. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility explains that as You consume more units of a good, the marginal utility typically decreases, leading to less added satisfaction per additional unit. Understanding this relationship helps in optimizing consumption decisions and maximizing Your overall utility.
Calculation Methods for Marginal and Total Utility
Marginal Utility is calculated by measuring the change in total utility resulting from consuming one additional unit of a good or service, typically expressed as MU = DTU / DQ, where TU is Total Utility and Q is quantity. Total Utility sums the overall satisfaction gained from consuming all units of a good and is computed by adding up the utility derived from each unit consumed, often represented as the cumulative value of individual marginal utilities. Understanding these calculation methods helps you analyze how utility changes with consumption levels and make informed decisions based on maximizing satisfaction.
Real-life Examples of Marginal vs Total Utility
Understanding the difference between marginal utility and total utility is crucial for consumer choice analysis; marginal utility measures the added satisfaction from consuming one more unit of a good, while total utility represents overall satisfaction from all units consumed. For example, eating the first slice of pizza might bring high marginal utility, but by the fourth or fifth slice, marginal utility decreases even though total utility still increases but at a slower rate. This diminishing marginal utility explains why consumers decide to stop purchasing additional units despite total utility growing, influencing demand patterns in markets.
Importance in Consumer Choice Theory
Understanding Marginal Utility, Total Utility, and Utility is crucial in Consumer Choice Theory as they explain how consumers make decisions to maximize satisfaction. Marginal Utility measures the added satisfaction from consuming one more unit, while Total Utility represents the overall satisfaction from all units consumed. You use these concepts to optimize your consumption, ensuring each choice delivers the highest possible utility within your budget constraints.
Implications for Business and Marketing Strategies
Understanding Marginal Utility, Total Utility, and Utility is crucial for crafting effective business and marketing strategies, as these concepts reveal how consumers derive satisfaction from products. Marginal Utility, the additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit, helps businesses optimize pricing and product quantity to maximize consumer demand without oversupply. Your marketing efforts can leverage insights into Total Utility, the overall satisfaction from all units consumed, to tailor product bundles and loyalty programs that enhance perceived value and boost customer retention.
Conclusion: Marginal Utility vs Total Utility in Economics
Marginal utility measures the additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of a good, while total utility represents the overall satisfaction derived from all units consumed. You maximize your economic decisions when you understand that marginal utility typically decreases as consumption increases, even though total utility continues to rise until it reaches a maximum point. Recognizing this distinction helps optimize consumption choices by balancing the incremental benefits against the total satisfaction.
Infographic: Marginal Utility vs Total Utility
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com