An annuity provides fixed payments for a specific period, while a perpetuity offers endless payments without termination. Explore this article to understand the key differences and applications of annuity versus perpetuity in financial planning.
Table of Comparison
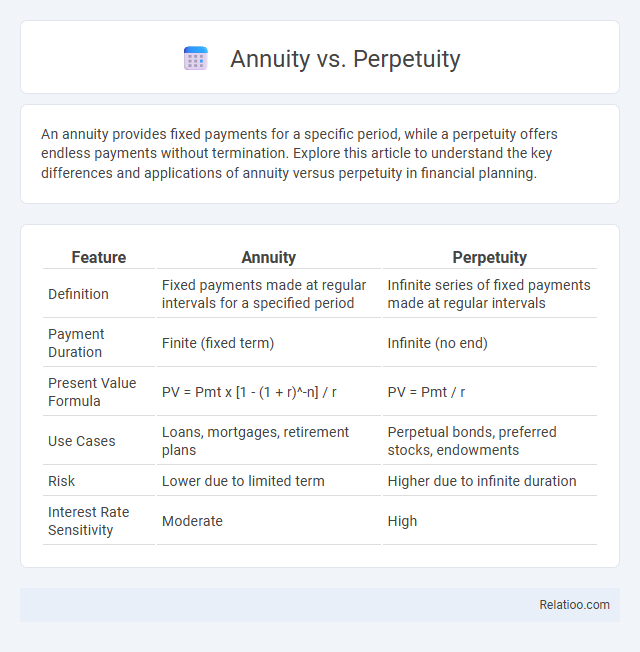
| Feature | Annuity | Perpetuity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed payments made at regular intervals for a specified period | Infinite series of fixed payments made at regular intervals |
| Payment Duration | Finite (fixed term) | Infinite (no end) |
| Present Value Formula | PV = Pmt x [1 - (1 + r)^-n] / r | PV = Pmt / r |
| Use Cases | Loans, mortgages, retirement plans | Perpetual bonds, preferred stocks, endowments |
| Risk | Lower due to limited term | Higher due to infinite duration |
| Interest Rate Sensitivity | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Annuity and Perpetuity
Annuities are financial products that provide a series of fixed payments over a specified period, commonly used for retirement income planning and structured settlements. Perpetuities differ by offering infinite payments with no end date, often valued in financial models to assess the present value of endless cash flows. Understanding the distinction between annuities and perpetuities is essential for accurate valuation and effective financial decision-making in investment and personal finance contexts.
Definition of Annuity
Annuity refers to a series of equal payments made at regular intervals over a specified period, providing a predictable income stream. Unlike perpetuity, which continues indefinitely, an annuity has a defined end date, making it ideal for planning Your financial goals. Understanding the distinction between fixed-term annuities and perpetuities is essential for optimizing investment and retirement strategies.
Definition of Perpetuity
Perpetuity is a financial instrument that provides a never-ending series of cash flows, typically fixed payments, with no maturity date. Unlike annuities, which have a specified term or end date, perpetuities continue indefinitely, making their present value calculation unique by using the formula PV = C / r, where C is the cash payment, and r is the discount rate. Understanding the definition of perpetuity helps you compare it effectively with annuities for long-term investment planning.
Key Differences Between Annuity and Perpetuity
Annuities consist of fixed payments made over a specified period, whereas perpetuities provide infinite cash flows without an end date. The key difference lies in their duration; annuities have a limited timeline, while perpetuities continue indefinitely. Valuation of annuities requires discounting a finite series of payments, whereas perpetuities use a formula that assumes perpetual payment streams.
Types of Annuities
Fixed annuities provide guaranteed payments at regular intervals, ensuring stable income over a specified period or for life. Variable annuities offer payments that fluctuate based on the performance of underlying investments, allowing potential for higher returns with increased risk. Indexed annuities link returns to a market index, balancing growth potential with downside protection, giving Your retirement planning versatile options tailored to income goals and risk tolerance.
Types of Perpetuities
Perpetuities are financial instruments that provide infinite, consistent cash flow payments without an end date, with common types including zero-coupon perpetuities, which pay a lump sum at infinity, and level perpetuities, offering fixed periodic payments indefinitely. Annuities differ by having a finite term with fixed payments over a set period, while perpetuities continue payments perpetually. Variations of perpetuities also include growing perpetuities, which increase payments at a constant growth rate, commonly used for valuing stocks or real estate investments.
Present Value Calculations: Annuity vs Perpetuity
Present value calculations for annuities involve discounting a series of fixed payments over a finite period, reflecting the time value of money within that set timeframe. Perpetuities, by contrast, entail calculating the present value of infinite, consistent cash flows, using a simplified formula dividing the payment by the discount rate to capture indefinite duration. Your financial decisions hinge on these distinctions, as annuities offer known cash flow endpoints, while perpetuities provide ongoing income with different valuation implications.
Common Uses in Financial Planning
Annuities are frequently used in retirement planning to provide predictable income streams over a specified period, helping you manage cash flow during retirement years. Perpetuities offer a strategy for investors seeking endless income, often used in valuing preferred stocks or perpetually paying assets. Unlike these, ordinary annuities focus on fixed payment intervals, useful for loan repayments or installment savings plans within your broader financial strategy.
Pros and Cons: Annuity vs Perpetuity
Annuities provide fixed payments over a specified period, offering predictability and helping with short- to medium-term financial planning but may lose value due to inflation. Perpetuities offer infinite, consistent cash flows, ideal for endowments or long-term investments, yet they lack the flexibility and finite duration beneficial for retirement planning. Annuities typically include principal return protections and taxation benefits, whereas perpetuities risk valuation fluctuations with changing interest rates and have no maturity date.
Which is Better: Annuity or Perpetuity?
An annuity provides a fixed stream of payments over a specific period, ideal for retirement planning or loan repayments, while a perpetuity offers infinite, constant payments but is less common in real-life scenarios. Choosing between an annuity and a perpetuity depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and cash flow needs, with annuities preferred for guaranteed income periods and perpetuities for long-term, indefinite income streams. Financial analysts often favor annuities for their predictability and legal contracts, whereas perpetuities are valued in theoretical models and certain types of preferred stock valuations.
Infographic: Annuity vs Perpetuity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com