Understanding the difference between the due date and the grace period is crucial for managing timely payments and avoiding late fees. Explore the details of due dates versus grace periods in this article to optimize your financial planning.
Table of Comparison
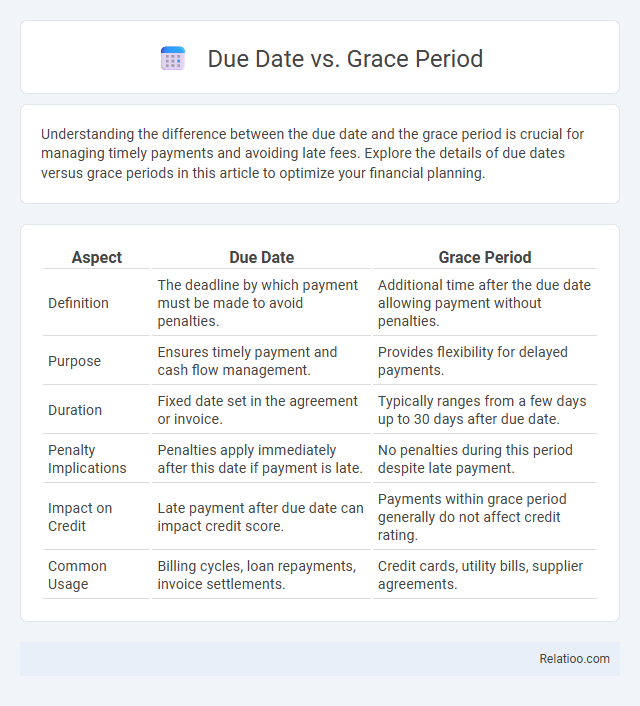
| Aspect | Due Date | Grace Period |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The deadline by which payment must be made to avoid penalties. | Additional time after the due date allowing payment without penalties. |
| Purpose | Ensures timely payment and cash flow management. | Provides flexibility for delayed payments. |
| Duration | Fixed date set in the agreement or invoice. | Typically ranges from a few days up to 30 days after due date. |
| Penalty Implications | Penalties apply immediately after this date if payment is late. | No penalties during this period despite late payment. |
| Impact on Credit | Late payment after due date can impact credit score. | Payments within grace period generally do not affect credit rating. |
| Common Usage | Billing cycles, loan repayments, invoice settlements. | Credit cards, utility bills, supplier agreements. |
Understanding Due Dates: Definition and Importance
Due dates specify the exact day a payment or task must be completed to avoid penalties or disruptions in service, serving as critical deadlines in financial and administrative processes. Grace periods follow due dates, granting a limited additional timeframe during which payments can be made without extra charges, while still maintaining service continuity. Understanding these concepts ensures timely compliance, prevents late fees, and supports effective financial management.
What is a Grace Period?
A grace period is a specified timeframe after the payment due date during which no late fees or penalties are applied, allowing borrowers extra time to make a payment without impacting their credit score. Unlike the due date, which marks the deadline for the minimum payment, the grace period provides a buffer for users managing cash flow or unexpected expenses. Understanding the distinctions between due date, grace period, and payment due helps avoid late charges and maintain good financial standing.
Key Differences Between Due Date and Grace Period
The due date is the exact deadline by which your payment must be received to avoid penalties, while the grace period is a short extension granted after the due date allowing you additional time to pay without late fees. The primary difference lies in timing and consequences: payments made after the due date but within the grace period do not incur penalties, whereas payments after the grace period are considered late. Understanding these distinctions helps you manage your finances effectively and avoid unnecessary charges.
How Due Dates Affect Payment Schedules
Due dates set the fixed deadline by which Your payment must be received to avoid penalties or service interruptions, directly influencing the timing and structure of payment schedules. Grace periods provide a short extension beyond the due date, allowing a buffer to make payments without incurring late fees, but they do not alter the original payment schedule set by the due date. Understanding the distinction between due date, grace period, and payment due is essential for managing financial obligations and maintaining timely account status.
The Role of Grace Periods in Financial Agreements
The grace period in financial agreements acts as a crucial buffer between the payment due date and the final deadline, allowing you extra time to fulfill your obligations without penalties. This period mitigates the risk of default by accommodating unforeseen delays, ultimately protecting your credit score and ensuring financial stability. Understanding the specific terms of your agreement's grace period helps you manage cash flow effectively and avoid late fees.
Consequences of Missing the Due Date
Missing the due date on your bill can result in late fees, increased interest charges, and a potential negative impact on your credit score. While the grace period allows some flexibility by extending the time to pay without penalty, once it ends, penalties are applied immediately. Understanding the distinction between due date, grace period, and payment due is crucial to avoid financial consequences and maintain good credit health.
Benefits of Having a Grace Period
A grace period offers you extra time beyond the payment due date to settle your bills without incurring late fees, significantly reducing financial stress and enhancing cash flow management. This buffer supports better budgeting decisions by preventing immediate penalties and maintaining a positive credit score. Incorporating a grace period into your payment terms balances flexibility with responsibility, encouraging timely payments while providing a safety net during unforeseen expenses.
Due Date vs Grace Period: Common Misconceptions
The Due Date is the official deadline when a payment must be received to avoid penalties, while the Grace Period allows extra time after the Due Date without incurring late fees, but interest or service disruptions may still apply. A common misconception is that payments made during the Grace Period are considered on-time; however, the payment is technically late and only exempt from penalties during this interval. Understanding the distinction between Due Date and Grace Period is essential for managing finances and avoiding unexpected charges.
Tips for Managing Your Due Dates and Grace Periods
Managing your due dates and grace periods effectively requires tracking the exact payment due dates specified by your creditors and understanding the length of your grace periods, which typically range from 15 to 30 days after the due date. You should prioritize making payments before the due date to avoid late fees and interest charges, even if a grace period allows extra time; however, carefully monitor your credit card or loan terms as grace periods can vary significantly. Setting up automated reminders or autopay through your bank can help you stay on top of payments and maintain a strong credit score.
Frequently Asked Questions About Due Dates and Grace Periods
A due date is the final deadline by which your payment must be received to avoid penalties, while a grace period is an additional timeframe after the due date allowing late payments without immediate fees. Frequently asked questions often clarify that the grace period does not extend the due date itself but provides a buffer to settle your balance without affecting your credit score. Understanding these distinctions helps you manage your payments effectively and avoid unnecessary late charges.
Infographic: Due Date vs Grace Period
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com