Zero-Based Budgeting prioritizes allocating resources based on current needs and justifying every expense from scratch, contrasting with Traditional Budgeting, which adjusts previous budgets incrementally. Discover how these budgeting methods impact financial planning and decision-making in this article.
Table of Comparison
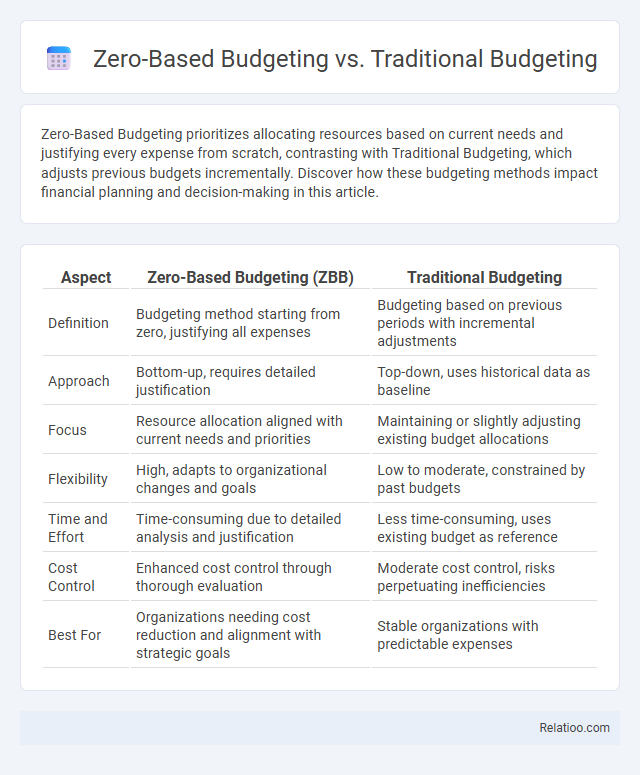
| Aspect | Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) | Traditional Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Budgeting method starting from zero, justifying all expenses | Budgeting based on previous periods with incremental adjustments |
| Approach | Bottom-up, requires detailed justification | Top-down, uses historical data as baseline |
| Focus | Resource allocation aligned with current needs and priorities | Maintaining or slightly adjusting existing budget allocations |
| Flexibility | High, adapts to organizational changes and goals | Low to moderate, constrained by past budgets |
| Time and Effort | Time-consuming due to detailed analysis and justification | Less time-consuming, uses existing budget as reference |
| Cost Control | Enhanced cost control through thorough evaluation | Moderate cost control, risks perpetuating inefficiencies |
| Best For | Organizations needing cost reduction and alignment with strategic goals | Stable organizations with predictable expenses |
Introduction to Budgeting Methods
Zero-based budgeting requires building a budget from scratch each period, justifying every expense to align resources with current priorities. Traditional budgeting relies on historical data, adjusting previous budgets incrementally without questioning foundational expenditures. Understanding these contrasting budgeting methods helps organizations optimize financial planning by either maintaining consistency with past trends or driving efficiency through thorough expense justification.
What is Zero-Based Budgeting?
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) is a budgeting method that requires you to justify every dollar of your budget from scratch, unlike Traditional Budgeting which often uses previous budgets as a baseline. By focusing on current needs and priorities, ZBB promotes efficient allocation of resources and eliminates unnecessary expenditures. This approach contrasts with Traditional Budgeting's tendency to incrementally adjust prior budgets, making ZBB highly effective for optimizing financial planning and control.
What is Traditional Budgeting?
Traditional budgeting is a financial planning method that relies on historical data to establish future budgets, making it a reactive approach to managing expenses. This method allocates funds based on last year's budget with incremental adjustments, often leading to inefficiencies or misallocations. Your organization may find traditional budgeting less flexible compared to zero-based budgeting, which requires justifying all expenses from scratch.
Key Differences Between Zero-Based and Traditional Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) requires each expense to be justified from scratch for every new period, promoting a more detailed and flexible allocation of resources compared to Traditional Budgeting, which relies on historical data and incremental adjustments. ZBB fosters cost efficiency by eliminating outdated expenditures and prioritizing activities based on current value, whereas Traditional Budgeting often perpetuates past spending patterns with less scrutiny. This fundamental difference impacts financial planning and control, making ZBB ideal for dynamic business environments demanding strategic cost management.
Pros and Cons of Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) requires justifying every expense from scratch, promoting efficient resource allocation and minimizing waste compared to Traditional Budgeting, which relies on past budgets and may perpetuate inefficiencies. ZBB enhances organizational agility by aligning spending with current priorities but can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring detailed analysis and frequent revisions. Traditional Budgeting offers simplicity and stability but often lacks responsiveness to changing business needs, while a general Budget provides a flexible financial framework without the rigorous scrutiny of ZBB.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting offers a straightforward framework for allocating financial resources based on historical data, making it easy for organizations to implement and understand. However, it often encourages incremental spending and may perpetuate inefficiencies by not thoroughly evaluating each expense, limiting flexibility and innovation. You might find that this approach lacks the precision and adaptability of zero-based budgeting, which requires justifying every dollar spent from scratch.
When to Use Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) is most effective during periods of financial constraint or organizational change, requiring a detailed evaluation of all expenses from the ground up to align resources with strategic priorities. Traditional Budgeting suits stable environments with predictable costs, relying on incremental adjustments based on prior budgets. Choosing ZBB is ideal for companies aiming to eliminate inefficiencies, reallocate funds dynamically, and foster cost-conscious decision-making in volatile markets.
When to Use Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting is ideal for organizations with stable financial conditions and predictable expenses, enabling consistent resource allocation based on historical data. It works best in industries where costs and revenues are relatively steady, such as manufacturing or utilities, allowing for streamlined planning and control processes. When the priority is maintaining financial stability rather than aggressive cost-cutting or radical changes, traditional budgeting offers a reliable and efficient framework.
Impact on Cost Control and Resource Allocation
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) enhances cost control by requiring every expense to be justified from scratch, reducing unnecessary spending and promoting efficient resource allocation aligned with your priorities. Traditional Budgeting relies on historical data, often perpetuating past inefficiencies and limiting flexibility in reallocating resources to high-impact areas. The conventional Budget approach offers simplicity but may lack the rigorous scrutiny needed to optimize spending and strategically allocate resources, potentially impacting overall financial performance.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method for Your Organization
Choosing the right budgeting method for your organization involves comparing Zero-Based Budgeting, Traditional Budgeting, and a general Budget approach based on your financial goals and resource allocation needs. Zero-Based Budgeting requires justifying every expense from scratch, promoting efficiency and cost control, while Traditional Budgeting uses previous budgets as a baseline, providing stability and ease of forecasting. Your decision should balance detailed financial scrutiny with practical forecasting to optimize resource use and drive organizational success.
Infographic: Zero-Based Budgeting vs Traditional Budgeting
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com