Centralized collection systems consolidate data into a single repository for streamlined access and uniform control, enhancing data integrity and security. Decentralized collection distributes data across multiple locations, promoting flexibility and resilience but posing challenges in consistency and coordination; explore this article to understand which approach best suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
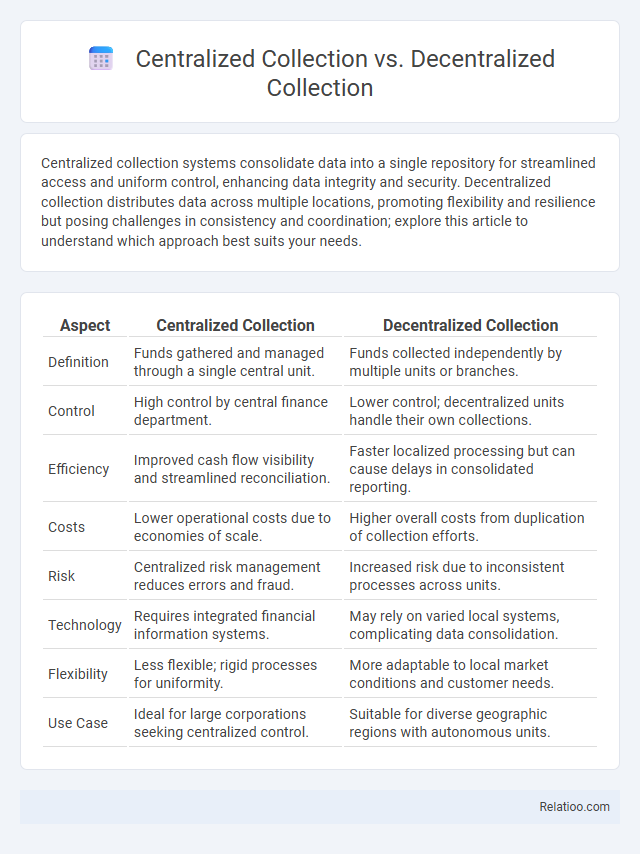
| Aspect | Centralized Collection | Decentralized Collection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funds gathered and managed through a single central unit. | Funds collected independently by multiple units or branches. |
| Control | High control by central finance department. | Lower control; decentralized units handle their own collections. |
| Efficiency | Improved cash flow visibility and streamlined reconciliation. | Faster localized processing but can cause delays in consolidated reporting. |
| Costs | Lower operational costs due to economies of scale. | Higher overall costs from duplication of collection efforts. |
| Risk | Centralized risk management reduces errors and fraud. | Increased risk due to inconsistent processes across units. |
| Technology | Requires integrated financial information systems. | May rely on varied local systems, complicating data consolidation. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; rigid processes for uniformity. | More adaptable to local market conditions and customer needs. |
| Use Case | Ideal for large corporations seeking centralized control. | Suitable for diverse geographic regions with autonomous units. |
Introduction to Collection Systems
Collection systems in data management differ primarily between centralized and decentralized approaches, each offering unique benefits for storing and processing information. Centralized collection consolidates data into a single repository, enhancing data consistency and making it easier for you to manage and analyze information. Decentralized collection distributes data across multiple locations, promoting flexibility and resilience while reducing dependency on a single system.
Defining Centralized Collection
Centralized Collection refers to a system where all data or resources are gathered and managed in a single, unified location, enabling streamlined control and consistent access. Unlike Decentralized Collection, which distributes data across multiple independent nodes to enhance redundancy and local control, Centralized Collection offers easier monitoring and maintenance but may present a single point of failure risk. Understanding your organization's needs helps determine whether a centralized approach improves efficiency or if a decentralized strategy better supports resilience and scalability.
Understanding Decentralized Collection
Decentralized collection distributes data gathering across multiple nodes or locations, enhancing resilience and reducing single points of failure compared to centralized collection, where all data is collected and managed from one central source. Your ability to leverage decentralized collection improves scalability and fault tolerance by allowing local autonomy and real-time processing across diverse sources. Understanding decentralized collection is crucial for optimizing data reliability, security, and responsiveness in complex systems.
Key Differences Between Centralized and Decentralized Collection
Centralized collection consolidates data or resources into a single system or location, enhancing control, consistency, and streamlined management. Decentralized collection disperses data across multiple nodes or locations, offering increased flexibility, fault tolerance, and scalability but potentially complicating coordination and data integrity. Understanding these differences helps you choose the optimal approach for efficient data handling and resource allocation in your organization.
Advantages of Centralized Collection
Centralized collection streamlines data management by consolidating information in a single repository, enhancing consistency and reducing redundancy. It improves decision-making through centralized control and easier data analysis, leading to faster reporting and actionable insights. Centralized systems also offer stronger security protocols and simpler compliance with regulatory standards compared to decentralized or mixed collection models.
Benefits of Decentralized Collection
Decentralized collection enhances data accuracy and timeliness by enabling local agents to gather and verify information directly, reducing bottlenecks inherent in centralized systems. It promotes scalability and resilience through distributed data sources, minimizing single points of failure and allowing continuous operation despite individual node disruptions. Furthermore, decentralized collection empowers localized decision-making, fostering tailored responses and increased stakeholder engagement in data-driven processes.
Challenges of Centralized Collection
Centralized collection faces challenges such as data bottlenecks, single points of failure, and limited scalability, impacting overall system efficiency. The concentration of data processing can lead to latency issues and increased vulnerability to cyberattacks or system outages. In contrast, decentralized collection distributes data gathering across multiple nodes, enhancing reliability, scalability, and fault tolerance.
Drawbacks of Decentralized Collection
Decentralized collection often suffers from inconsistent data quality due to varied input standards across multiple sources, leading to challenges in data integration and analysis. The lack of centralized oversight increases the risk of data duplication and errors, complicating the maintenance of a single source of truth. Additionally, decentralized systems typically incur higher operational costs and slower decision-making processes compared to centralized collection models because of fragmented workflows and coordination difficulties.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Collection Model
Choosing between centralized, decentralized, and hybrid collection models depends on factors such as control, efficiency, and scalability. Centralized collection offers streamlined data management and uniformity, ideal for organizations valuing consistency and simplicity. Decentralized collection enhances data accuracy and local responsiveness, making it suitable for entities that require agility and context-specific insights.
Future Trends in Collection Systems
Future trends in collection systems highlight a shift towards hybrid models that integrate centralized and decentralized collection to optimize efficiency and customer experience. Advances in AI-driven analytics and blockchain technology enable real-time data transparency and enhanced fraud detection, promoting more secure and adaptive collection processes. The rise of digital payment platforms and IoT devices further supports scalable, automated collection strategies, reducing operational costs and improving recovery rates.
Infographic: Centralized Collection vs Decentralized Collection
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com