Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, remain constant each month regardless of changes in income or activity levels, while variable expenses like groceries and utilities fluctuate based on consumption and usage. Understanding the balance between fixed and variable expenses is crucial for effective budget management; discover more insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
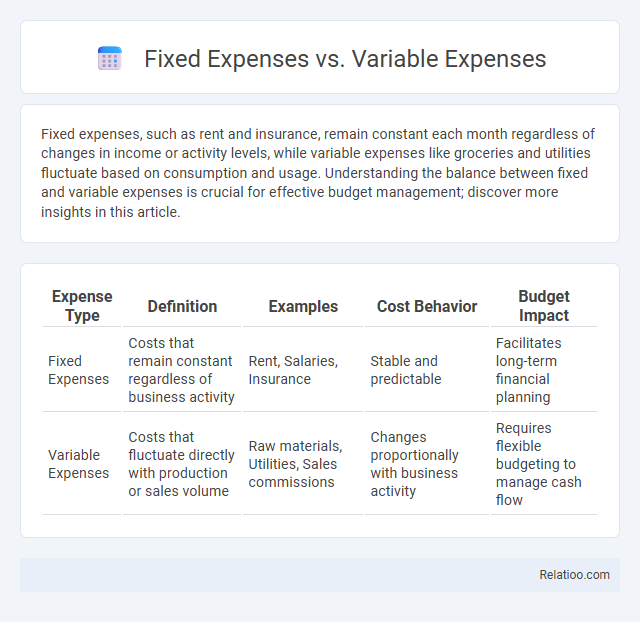
| Expense Type | Definition | Examples | Cost Behavior | Budget Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Expenses | Costs that remain constant regardless of business activity | Rent, Salaries, Insurance | Stable and predictable | Facilitates long-term financial planning |
| Variable Expenses | Costs that fluctuate directly with production or sales volume | Raw materials, Utilities, Sales commissions | Changes proportionally with business activity | Requires flexible budgeting to manage cash flow |
Understanding Fixed and Variable Expenses
Fixed expenses remain constant over time, such as rent or insurance payments, providing predictability in your budget. Variable expenses fluctuate based on usage or consumption, like utilities or groceries, requiring careful tracking to manage cash flow effectively. Understanding the distinction between fixed and variable expenses helps you optimize your financial planning and control your overall expenses.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Variable Expenses
Fixed expenses remain constant regardless of your business activity, such as rent, salaries, and insurance payments, providing predictable budgeting. Variable expenses fluctuate directly with production or sales volume, including costs like raw materials, hourly wages, and utilities. Understanding these key differences between fixed and variable expenses helps you manage cash flow effectively and optimize your financial planning.
Examples of Fixed Expenses
Fixed expenses remain constant each month, such as rent, mortgage payments, and insurance premiums, providing predictable financial commitments. Variable expenses fluctuate based on usage or consumption, including utilities, groceries, and entertainment costs, requiring flexible budget adjustments. Understanding your fixed expenses helps you manage essential costs and maintain financial stability while tracking variable expenses allows for better control over discretionary spending.
Examples of Variable Expenses
Variable expenses fluctuate depending on your consumption or activity level, such as utility bills, groceries, and fuel costs. Unlike fixed expenses like rent or insurance premiums, which remain constant, variable expenses change monthly based on your lifestyle and usage. Managing these expenses effectively can help optimize your budget and improve financial flexibility.
The Importance of Tracking Expenses
Tracking your fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, alongside variable expenses like utilities and groceries, is crucial for accurate budgeting and financial planning. Understanding the distinction between these expense types enables better cash flow management and helps identify areas where cost-cutting measures can be applied effectively. Consistent monitoring of your expenses empowers informed decisions that enhance financial stability and long-term savings growth.
How to Identify Your Fixed and Variable Expenses
To identify your fixed expenses, review monthly bills that remain constant, such as rent, insurance, or subscription services, which do not fluctuate with your usage or income. Variable expenses include costs like groceries, utilities, and entertainment, which change based on consumption or lifestyle choices. Tracking your spending through budgeting apps or financial statements helps you distinguish between fixed and variable expenses, enabling better financial management and planning.
Managing Fixed and Variable Expenses Effectively
Managing fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, requires consistent budgeting to ensure predictable monthly outflows do not disrupt cash flow stability. Variable expenses, including utilities and raw materials, demand continuous monitoring and adjustment to align with revenue fluctuations and operational needs. Implementing cost control measures and leveraging expense tracking tools enhances financial efficiency, supporting better decision-making and overall expense management.
Impact of Expenses on Personal Budgeting
Fixed expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, remain constant each month and provide stability in your personal budgeting by allowing predictable cash flow management. Variable expenses, including groceries and entertainment, fluctuate monthly, requiring careful tracking to avoid overspending and maintain budget balance. Understanding the difference between fixed and variable expenses helps you optimize your expense management, ensuring your personal budget adapts to both consistent obligations and changing financial needs.
Strategies to Control Variable Expenses
Variable expenses fluctuate based on your consumption or usage, making them more controllable compared to fixed expenses like rent or mortgage. Strategies to control variable expenses include tracking spending patterns, setting budgets for discretionary costs, and prioritizing needs over wants to minimize impulsive purchases. You can also negotiate with service providers or switch to cost-effective alternatives to reduce these fluctuating costs effectively.
Creating a Balanced Budget with Both Expense Types
Understanding the distinction between fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, and variable expenses like groceries and entertainment is crucial for creating a balanced budget. Your budget should allocate funds based on fixed costs that remain consistent each month while carefully managing variable expenses to avoid overspending. Balancing both expense types ensures financial stability and helps you achieve your savings goals effectively.
Infographic: Fixed Expenses vs Variable Expenses
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com