Refinancing replaces an existing loan with a new one, often to secure better interest rates or terms, while loan modification adjusts the current loan's terms to make payments more manageable without replacing the loan. Explore this article to understand which option best suits your financial needs and long-term goals.
Table of Comparison
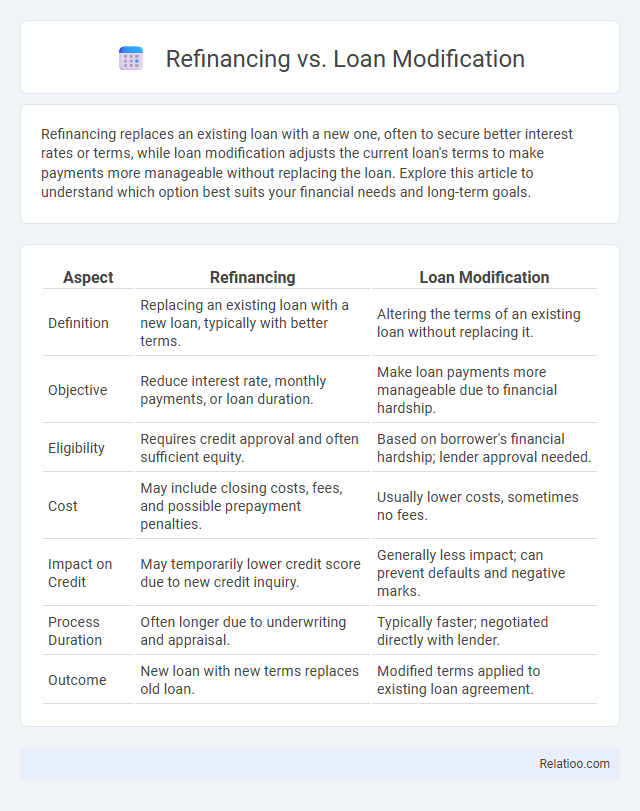
| Aspect | Refinancing | Loan Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replacing an existing loan with a new loan, typically with better terms. | Altering the terms of an existing loan without replacing it. |
| Objective | Reduce interest rate, monthly payments, or loan duration. | Make loan payments more manageable due to financial hardship. |
| Eligibility | Requires credit approval and often sufficient equity. | Based on borrower's financial hardship; lender approval needed. |
| Cost | May include closing costs, fees, and possible prepayment penalties. | Usually lower costs, sometimes no fees. |
| Impact on Credit | May temporarily lower credit score due to new credit inquiry. | Generally less impact; can prevent defaults and negative marks. |
| Process Duration | Often longer due to underwriting and appraisal. | Typically faster; negotiated directly with lender. |
| Outcome | New loan with new terms replaces old loan. | Modified terms applied to existing loan agreement. |
Introduction to Refinancing and Loan Modification
Refinancing involves replacing an existing loan with a new one, often to secure better interest rates, reduce monthly payments, or change loan terms. Loan modification adjusts the original loan agreement to make payments more affordable without replacing the loan, often through interest rate reduction, principal forbearance, or term extension. Understanding these options helps homeowners explore tailored solutions for managing mortgage debt effectively.
Key Differences Between Refinancing and Loan Modification
Refinancing replaces your existing loan with a new one, typically offering better interest rates or terms to reduce monthly payments or total cost. Loan modification changes the terms of your current loan without replacing it, often adjusting interest rates, extending the loan term, or altering principal to avoid foreclosure. Understanding the key differences helps you determine if refinancing or loan modification best suits Your financial goals and situation.
What is Refinancing?
Refinancing involves replacing an existing loan with a new one, typically to secure better interest rates, lower monthly payments, or improved loan terms. This process is commonly used for mortgages, auto loans, and student loans to reduce overall borrowing costs. Borrowers benefit from refinancing by potentially shortening the loan term or accessing equity through cash-out refinancing options.
What is Loan Modification?
Loan modification is a financial solution that alters the original terms of your mortgage to make payments more affordable without replacing the loan entirely, often involving lower interest rates, extended loan periods, or reduced principal. Unlike refinancing, which replaces your existing mortgage with a new loan typically at different terms, loan modification adjusts your current loan to prevent foreclosure and improve repayment options. Understanding loan modification is crucial for homeowners facing financial hardship seeking to maintain homeownership through manageable mortgage terms.
Pros and Cons of Refinancing
Refinancing your mortgage can lower interest rates and reduce monthly payments, offering potential long-term savings and improved cash flow. However, refinancing involves closing costs, possible fees, and a reset of your loan term, which may increase total interest paid over time. Carefully evaluating your current financial situation and market conditions ensures that refinancing aligns with your goals and benefits your overall financial health.
Pros and Cons of Loan Modification
Loan modification adjusts the original loan terms, such as interest rate or payment schedule, to make your mortgage more affordable, without requiring a full refinancing process. Pros include lower monthly payments and avoidance of closing costs, but cons involve potential credit score impacts and possibly extending the loan term, which can increase total interest paid. Unlike refinancing, loan modification is typically reserved for borrowers facing financial hardship and negotiated directly with the lender rather than through a new loan application.
Eligibility Criteria for Refinancing vs Loan Modification
Eligibility criteria for refinancing typically require a strong credit score, stable income, and sufficient home equity, making it suitable for borrowers with improved financial standing. Loan modification eligibility focuses on demonstrating financial hardship and an inability to meet current loan payments, often requiring documentation of income reduction or increased expenses. Understanding these distinct requirements helps you determine the best option to reduce monthly payments or improve loan terms effectively.
Impact on Credit Score: Refinancing vs Loan Modification
Refinancing typically requires a new credit check, which can cause a temporary dip in Your credit score but may improve it long-term by securing lower interest rates or better terms. Loan modifications usually have less immediate impact on credit scores since they involve adjusting existing loan terms without new credit inquiries, but missed payments prior to modification can harm Your score. Comparing refinancing vs loan modification in terms of credit impact helps You assess the best option based on current credit health and financial goals.
Which Option Is Better for Homeowners?
Choosing between refinancing, loan modification, or refinancing again depends on your financial goals and eligibility. Refinancing offers lower interest rates and monthly payments by replacing your existing mortgage, while loan modification adjusts the terms of your current loan without starting a new one, often benefiting those facing temporary financial hardship. Your best option hinges on factors like credit score, loan-to-value ratio, and long-term savings, with refinancing usually preferred for improved rates and loan modification suited for avoiding foreclosure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Refinancing and Loan Modification
Refinancing replaces your existing loan with a new one, often to secure a lower interest rate or better terms, while loan modification changes the terms of your current loan without refinancing. Frequently asked questions about refinancing focus on eligibility criteria, impact on credit score, and potential savings on monthly payments. Common loan modification FAQs address qualification requirements, duration of relief, and the implications for your loan balance and foreclosure status.
Infographic: Refinancing vs Loan Modification
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com