Out-of-court settlements offer a faster, more flexible resolution to financial disputes, while court-supervised bankruptcy provides formal legal protection and structured debt relief. Discover the key differences and benefits of each approach in this article.
Table of Comparison
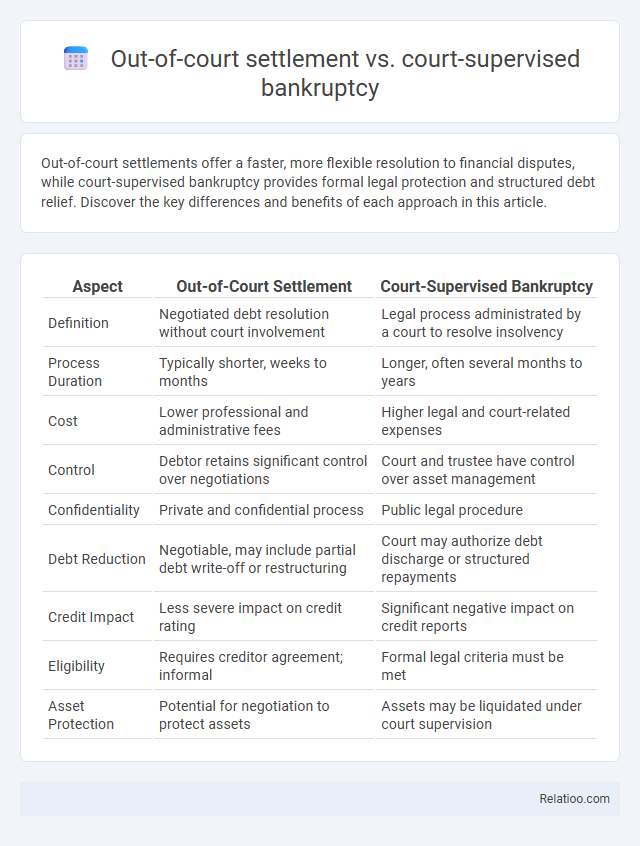
| Aspect | Out-of-Court Settlement | Court-Supervised Bankruptcy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Negotiated debt resolution without court involvement | Legal process administrated by a court to resolve insolvency |
| Process Duration | Typically shorter, weeks to months | Longer, often several months to years |
| Cost | Lower professional and administrative fees | Higher legal and court-related expenses |
| Control | Debtor retains significant control over negotiations | Court and trustee have control over asset management |
| Confidentiality | Private and confidential process | Public legal procedure |
| Debt Reduction | Negotiable, may include partial debt write-off or restructuring | Court may authorize debt discharge or structured repayments |
| Credit Impact | Less severe impact on credit rating | Significant negative impact on credit reports |
| Eligibility | Requires creditor agreement; informal | Formal legal criteria must be met |
| Asset Protection | Potential for negotiation to protect assets | Assets may be liquidated under court supervision |
Understanding Out-of-Court Settlements
Out-of-court settlements offer a flexible alternative to court-supervised bankruptcy and formal bankruptcy proceedings, allowing you to negotiate debt repayment terms directly with creditors without involving the court system. These settlements can reduce legal fees, preserve credit rating, and expedite resolution compared to court-supervised options, which involve more formal oversight and longer timelines. Understanding out-of-court settlements enables you to evaluate efficient debt relief strategies tailored to your financial situation before considering bankruptcy filings.
What Is Court-Supervised Bankruptcy?
Court-supervised bankruptcy is a legal process where a debtor's financial situation is managed under the supervision of a bankruptcy court to ensure fair treatment of creditors and orderly debt resolution. Unlike out-of-court settlements, which are negotiated privately without judicial oversight, court-supervised bankruptcy provides a structured framework governed by bankruptcy laws, such as Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 in the U.S. Bankruptcy involves liquidation or reorganization of assets to satisfy debts, with court-supervised bankruptcy specifically allowing debtors to propose repayment plans or discharge debts under judicial control.
Key Differences Between Settlement and Bankruptcy
Out-of-court settlements involve negotiated agreements between creditors and debtors, avoiding formal court processes and allowing more flexible repayment terms, while court-supervised bankruptcy entails judicial oversight to restructure or discharge debts under legal protection. Bankruptcy, whether Chapter 7 liquidation or Chapter 13 reorganization, results in legal intervention to manage asset distribution or repayment scheduling, often imposing stricter requirements and timelines than settlements. Key differences lie in the level of court involvement, impact on credit score, cost, and duration, with settlements offering privacy and speed, whereas bankruptcy provides comprehensive debt relief but with public record and potential asset loss.
Advantages of Out-of-Court Settlements
Out-of-court settlements offer a faster resolution compared to court-supervised bankruptcy and formal bankruptcy proceedings, reducing legal fees and preserving business relationships. Your credit score is less impacted, and confidentiality is maintained since negotiations avoid public court records. This approach provides greater flexibility in negotiating terms tailored to both parties' needs without strict court-imposed constraints.
Benefits of Court-Supervised Bankruptcy
Court-supervised bankruptcy offers structured debt relief under judicial oversight, ensuring a fair process for both you and creditors. It provides protection from creditor actions while allowing asset management and debt discharge in a transparent manner. This process often results in more predictable outcomes compared to out-of-court settlements or traditional bankruptcy filings, enhancing financial recovery opportunities.
Drawbacks of Out-of-Court Settlements
Out-of-court settlements often face drawbacks such as limited legal enforceability, creating risks for creditors and debtors if terms are not honored. Unlike court-supervised bankruptcy, these settlements lack formal oversight, potentially leading to unfair treatment of some parties and incomplete debt resolution. This informal nature also reduces transparency and can complicate future financial restructuring efforts.
Disadvantages of Bankruptcy Proceedings
Bankruptcy proceedings often result in significant credit score damage, hindering Your ability to secure future loans or financial services. The process can be lengthy and costly, involving court fees and legal expenses that may outweigh the benefits of debt relief. Privacy concerns also arise, as bankruptcy records become public, potentially impacting Your reputation and business relationships.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Path
Factors to consider when choosing between an out-of-court settlement, court-supervised bankruptcy, and bankruptcy include the severity of debt, impact on credit rating, and the speed of resolution. Out-of-court settlements offer faster, less formal debt restructuring with minimal credit impact, suitable for manageable debts and cooperative creditors. Court-supervised bankruptcy provides structured protection and legal oversight, ideal for complex cases with large debts, whereas full bankruptcy involves asset liquidation and the most significant long-term credit consequences.
Impact on Credit and Business Reputation
Out-of-court settlements typically have a less severe impact on credit scores and preserve business reputation better by avoiding public court records. Court-supervised bankruptcies, such as Chapter 11, offer structured debt relief but can significantly lower credit ratings and damage business credibility due to their public nature. Full bankruptcy filings, including Chapter 7 liquidations, lead to substantial credit score drops and long-lasting negative effects on business reputation, often hindering future financing opportunities.
Which Option Is Right for Your Situation?
Choosing between an out-of-court settlement, court-supervised bankruptcy, or full bankruptcy depends heavily on your financial situation, debt level, and long-term goals. Out-of-court settlements offer flexible negotiation with creditors without formal legal proceedings, ideal for manageable debt and maintaining credit score. Court-supervised bankruptcy provides structured debt relief under legal protection, while full bankruptcy involves asset liquidation to satisfy debts but offers a fresh financial start; understanding these distinctions helps you determine the best path for financial recovery.
Infographic: Out-of-court settlement vs Court-supervised bankruptcy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com