Grace period allows borrowers to delay loan payments without accruing penalties, while a moratorium period suspends payments entirely, often including both principal and interest. Explore the detailed differences between grace period and moratorium period in this article.
Table of Comparison
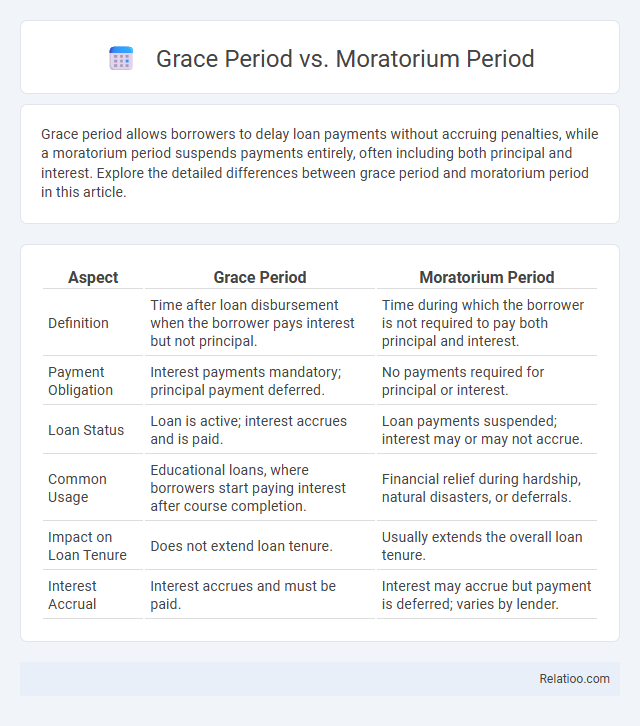
| Aspect | Grace Period | Moratorium Period |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Time after loan disbursement when the borrower pays interest but not principal. | Time during which the borrower is not required to pay both principal and interest. |
| Payment Obligation | Interest payments mandatory; principal payment deferred. | No payments required for principal or interest. |
| Loan Status | Loan is active; interest accrues and is paid. | Loan payments suspended; interest may or may not accrue. |
| Common Usage | Educational loans, where borrowers start paying interest after course completion. | Financial relief during hardship, natural disasters, or deferrals. |
| Impact on Loan Tenure | Does not extend loan tenure. | Usually extends the overall loan tenure. |
| Interest Accrual | Interest accrues and must be paid. | Interest may accrue but payment is deferred; varies by lender. |
Understanding Grace Period and Moratorium Period
Understanding Grace Period and Moratorium Period is essential for managing loan repayments effectively. Grace Period refers to the time after a loan disbursement or due date during which you are not required to make payments, often allowing interest to accrue without penalties, whereas Moratorium Period typically suspends both principal and interest payments temporarily, giving you relief during financial hardships. Knowing the differences helps you plan your finances and avoid default by leveraging these time frames strategically.
Key Definitions: Grace Period vs Moratorium Period
The Grace Period refers to a set timeframe after a loan repayment due date during which You can make payments without incurring penalties or late fees, providing temporary financial relief. The Moratorium Period is a specified duration when the borrower is allowed to pause or defer loan repayments entirely, often granted during financial hardship or special circumstances. Understanding the distinctions between Grace Period vs Moratorium Period is crucial for managing loan obligations and avoiding default.
Main Differences Between Grace and Moratorium Periods
The main differences between grace and moratorium periods lie in their impact on loan repayment and interest accrual: during the grace period, You are not required to make payments but interest usually continues to accumulate, whereas the moratorium period suspends both principal and interest payments entirely. Grace periods typically apply immediately after loan disbursement or graduation, offering temporary relief before regular payments start. Moratorium periods, often granted due to financial hardship or specific loan terms, extend the payment timeline with no added interest charges during the suspension.
Purpose and Importance of Grace Period
The grace period serves as a crucial timeframe allowing you to make loan payments without penalties, preventing immediate default and maintaining a positive credit history. Unlike the moratorium period, which typically suspends all payments during financial hardship, the grace period specifically offers temporary relief after loan disbursement or payment due dates. Understanding the importance of the grace period helps safeguard your creditworthiness and provides flexibility in managing loan obligations.
Significance of Moratorium Period in Financial Agreements
The moratorium period in financial agreements is crucial as it allows borrowers to temporarily pause loan repayments without penalties, providing relief during financial hardship. Unlike the grace period, which offers a short timeframe post-due date for payment without late fees, the moratorium period extends this flexibility, often encompassing interest relief or deferment options. Your understanding of the moratorium period's significance can help manage debt more effectively and avoid default risks.
Common Examples Where Each Period Applies
Grace periods frequently apply to credit card payments, allowing you extra time after the due date to pay without interest. Moratorium periods often occur in student loans or mortgage repayments, temporarily pausing payments during hardship without penalty. For installment loans, the deferment period enables borrowers to postpone payments under specific conditions, such as unemployment or medical emergencies.
Impact on Borrowers: Grace vs Moratorium Period
Grace Period allows borrowers to delay loan repayments temporarily, preventing immediate financial strain while interest may still accrue. Moratorium Period suspends both principal and interest payments, offering more relief but potentially extending the loan tenure. Your choice between these periods affects the total cost and repayment timeline, so understanding their implications is crucial for effective financial planning.
Legal and Financial Implications
A grace period allows borrowers extra time to make payments without penalties after a due date, often easing short-term financial strain while interest may still accrue. A moratorium period legally suspends payment obligations and interest accrual, providing temporary relief but potentially extending loan duration and costs. Understanding the distinctions helps you manage obligations effectively, avoiding legal repercussions and optimizing financial strategy.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Grace and Moratorium
Choosing between a grace period and a moratorium period depends on your financial situation and loan terms, as the grace period allows interest accrual without payments while the moratorium suspends both principal and interest payments. Consider the loan type, interest rates during deferment, and your ability to resume payments after the period ends to avoid increased debt burdens. Your decision should also factor in the long-term impact on your loan balance and credit score to ensure manageable repayment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Grace period refers to the extra time allowed after a loan due date during which payments can be made without penalty. Moratorium period specifically indicates a temporary suspension of loan repayments, often granted during financial hardships or crises, with interest sometimes still accruing. Frequently asked questions distinguish these terms by asking how interest is handled, the duration differences, and eligibility criteria for each period.
Infographic: Grace Period vs Moratorium Period
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com