Credit cards offer the advantage of building credit history and provide fraud protection, while debit cards limit spending to available funds without affecting credit scores. Explore this article to understand the key differences between credit and debit cards and determine which suits your financial goals best.
Table of Comparison
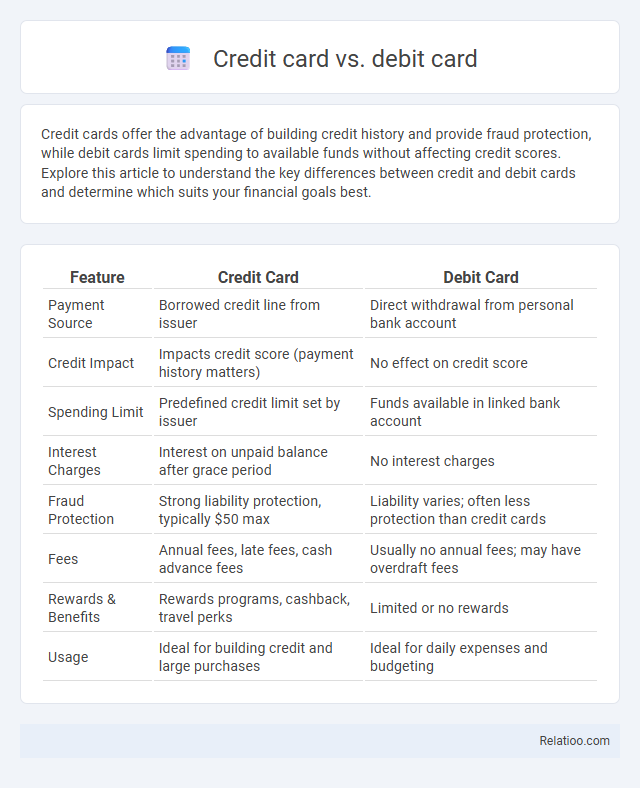
| Feature | Credit Card | Debit Card |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Source | Borrowed credit line from issuer | Direct withdrawal from personal bank account |
| Credit Impact | Impacts credit score (payment history matters) | No effect on credit score |
| Spending Limit | Predefined credit limit set by issuer | Funds available in linked bank account |
| Interest Charges | Interest on unpaid balance after grace period | No interest charges |
| Fraud Protection | Strong liability protection, typically $50 max | Liability varies; often less protection than credit cards |
| Fees | Annual fees, late fees, cash advance fees | Usually no annual fees; may have overdraft fees |
| Rewards & Benefits | Rewards programs, cashback, travel perks | Limited or no rewards |
| Usage | Ideal for building credit and large purchases | Ideal for daily expenses and budgeting |
Understanding Credit Cards and Debit Cards
Credit cards allow users to borrow funds up to a predetermined limit, facilitating purchases that can be paid off over time with interest, while debit cards directly draw money from the user's checking account for immediate transactions. Understanding the distinctions between these payment methods is crucial for managing credit scores, budgeting, and avoiding debt. Credit cards often offer benefits such as rewards and fraud protection, whereas debit cards provide a straightforward way to spend existing funds without incurring debt.
Key Features of Credit Cards
Credit cards offer revolving credit with a preset limit, allowing users to borrow funds up to that limit and repay over time with interest, providing financial flexibility for large or unexpected expenses. They often include benefits such as reward points, cashback, travel insurance, fraud protection, and credit building opportunities, which are not typically available with debit cards. Unlike debit cards that use funds directly from a checking account, credit cards enable purchases on credit, making them a powerful financial tool for managing cash flow and enhancing credit history.
Key Features of Debit Cards
Debit cards provide direct access to funds in checking or savings accounts, enabling real-time transactions without borrowing. Key features include no interest charges, daily spending limits set by the bank, and immediate deduction of expenses to prevent overspending. Unlike credit cards, debit cards do not affect credit scores and often offer ATM access and fraud protection tailored to deposited funds.
How Credit Cards Work
Credit cards allow you to borrow funds from a credit issuer up to a certain limit to make purchases or withdraw cash. When you use a credit card, the issuer pays the merchant on your behalf, and you repay the issuer later with interest if the balance is not paid in full by the due date. Understanding how credit cards work helps you manage your credit utilization and avoid high-interest debt.
How Debit Cards Work
Debit cards directly withdraw funds from Your checking account when making purchases or ATM withdrawals, providing real-time spending control without incurring debt. Unlike credit cards, which allow borrowing up to a credit limit and require monthly repayments with interest on outstanding balances, debit cards prevent overspending by only using available funds. Credit, on the other hand, involves borrowing money that must be repaid later, often with interest, while debit cards offer immediate access to Your own money for transactions.
Advantages of Credit Cards
Credit cards offer significant advantages such as building your credit score, providing fraud protection, and enabling rewards or cashback on purchases. Unlike debit cards, credit cards allow you to borrow funds up to a pre-approved limit, offering more flexibility in managing expenses. Using a credit card responsibly can enhance your financial security and improve your purchasing power.
Advantages of Debit Cards
Debit cards offer the advantage of direct access to your available funds, helping you avoid debt by preventing overspending. They typically have fewer fees compared to credit cards, as you are not charged interest or late payment penalties. Using a debit card enhances your financial control and allows you to easily monitor transactions through your linked bank account.
Risks and Drawbacks of Credit Cards
Credit cards carry significant risks such as high-interest rates that can lead to escalating debt if balances are not paid in full each month. Fraudulent charges and identity theft are common concerns, though most issuers offer protections, the resolution process can be time-consuming. Overspending due to easy access to credit often results in long-term financial instability and negatively impacts credit scores if payments are missed.
Risks and Drawbacks of Debit Cards
Debit cards carry risks such as limited fraud protection compared to credit cards, increasing the potential for unauthorized transactions to directly affect Your bank account balance. Unlike credit, debit cards do not offer opportunities to build credit history or access credit lines, which can restrict financial flexibility. Users should also be aware that debit card disputes often take longer to resolve, potentially causing delays in fund recovery.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between a credit card, debit card, and credit depends on your spending habits and financial goals. A credit card offers rewards and builds credit but requires discipline to avoid debt, while a debit card limits spending to available funds, ensuring you stay within budget. Consider your need for credit history, spending control, and potential fees to determine which option aligns best with your financial strategy.
Infographic: Credit card vs Debit card
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com