Fixed interest rates provide consistent payments and stability, while floating interest rates fluctuate with market conditions, potentially offering lower initial costs but higher risk. Discover which option suits your financial goals best in this article.
Table of Comparison
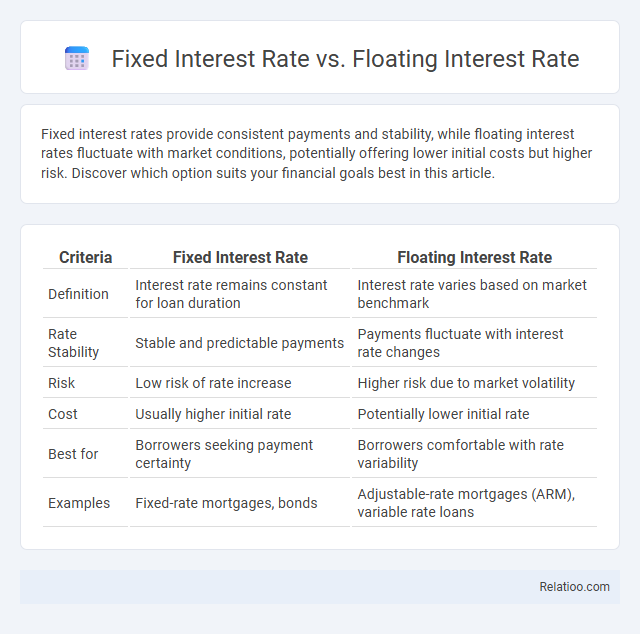
| Criteria | Fixed Interest Rate | Floating Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interest rate remains constant for loan duration | Interest rate varies based on market benchmark |
| Rate Stability | Stable and predictable payments | Payments fluctuate with interest rate changes |
| Risk | Low risk of rate increase | Higher risk due to market volatility |
| Cost | Usually higher initial rate | Potentially lower initial rate |
| Best for | Borrowers seeking payment certainty | Borrowers comfortable with rate variability |
| Examples | Fixed-rate mortgages, bonds | Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARM), variable rate loans |
Introduction to Interest Rate Types
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money or the return on investment, varying primarily between fixed and floating types. Fixed interest rates remain constant throughout the loan or investment period, providing predictable payments, whereas floating interest rates fluctuate based on benchmark rates like LIBOR or the Federal Reserve rate. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for managing financial risks and optimizing investment strategies.
What Is a Fixed Interest Rate?
A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term, providing borrowers with predictable monthly payments and protection against market fluctuations. This stability makes fixed rates ideal for long-term financing such as mortgages and personal loans. In contrast, floating interest rates vary based on benchmark indices, influencing the total interest paid over time.
What Is a Floating Interest Rate?
A floating interest rate, also known as a variable rate, fluctuates based on an underlying benchmark or index such as the LIBOR or the Federal Funds Rate, causing loan payments to vary over time. Unlike fixed interest rates that remain constant throughout the loan term, floating rates adjust periodically, reflecting changes in market conditions or monetary policy. This type of interest rate offers potential benefits during periods of declining rates but carries the risk of higher costs if benchmark rates increase.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Floating Rates
Fixed interest rates remain constant throughout the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and protection against market fluctuations. Floating interest rates fluctuate based on benchmark rates like LIBOR, potentially lowering your payments when rates decrease but increasing them when rates rise. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the most suitable loan type for your financial stability and risk tolerance.
Advantages of Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates provide the advantage of predictable monthly payments, allowing you to budget effectively and avoid sudden increases in loan costs. This stability shields borrowers from market fluctuations and rising inflation, ensuring financial security throughout the loan term. Compared to floating interest rates, fixed rates offer peace of mind by locking in a consistent rate that protects your long-term interests.
Advantages of Floating Interest Rates
Floating interest rates offer the advantage of potentially lower initial payments compared to fixed rates, as they fluctuate with market conditions, often aligning with your financial goals during periods of falling interest rates. This rate type provides flexibility, enabling you to benefit from decreasing interest trends and avoid the commitment of a higher fixed rate. Over time, the adaptability of floating interest rates can result in significant savings on interest costs, especially in a declining rate environment.
Disadvantages of Fixed Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates often lead to higher initial payments compared to floating rates, limiting potential savings when market rates decline. Borrowers are locked into a fixed payment schedule, reducing flexibility and making refinancing less attractive during periods of interest rate drops. This rigidity may result in missed opportunities to benefit from lower economic conditions and fluctuating market rates.
Disadvantages of Floating Interest Rates
Floating interest rates fluctuate with market conditions, causing unpredictable monthly payments that can strain your budget. These variable rates may rise significantly during economic uncertainty, increasing your overall loan cost. Borrowers face challenges in financial planning due to the lack of payment stability compared to fixed interest rates and standard interest terms.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Fixed and Floating Rates
When choosing between fixed interest rate and floating interest rate loans, you should consider factors such as your risk tolerance, loan duration, and current market conditions. Fixed rates provide stability and predictable payments, ideal if you prefer certainty and plan to hold the loan long-term, while floating rates can offer lower initial costs but fluctuate with benchmark rates, impacting your monthly payments. Your decision depends on whether you prioritize consistent budgeting or potential savings based on interest rate movements.
Frequently Asked Questions About Interest Rates
Fixed interest rates maintain a constant percentage over the loan term, providing predictable monthly payments and protection against market fluctuations. Floating interest rates fluctuate based on benchmark rates like the LIBOR or central bank policies, potentially offering lower initial rates but with the risk of increased payments. Interest is the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the principal amount, and understanding the differences between fixed and floating rates is crucial for managing loan affordability and financial planning.
Infographic: Fixed Interest Rate vs Floating Interest Rate
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com