Diversification involves spreading investments across various asset classes to reduce risk, while asset allocation determines the percentage of each asset class within a portfolio based on an investor's goals and risk tolerance. Explore this article to understand how balancing diversification and asset allocation can enhance portfolio performance.
Table of Comparison
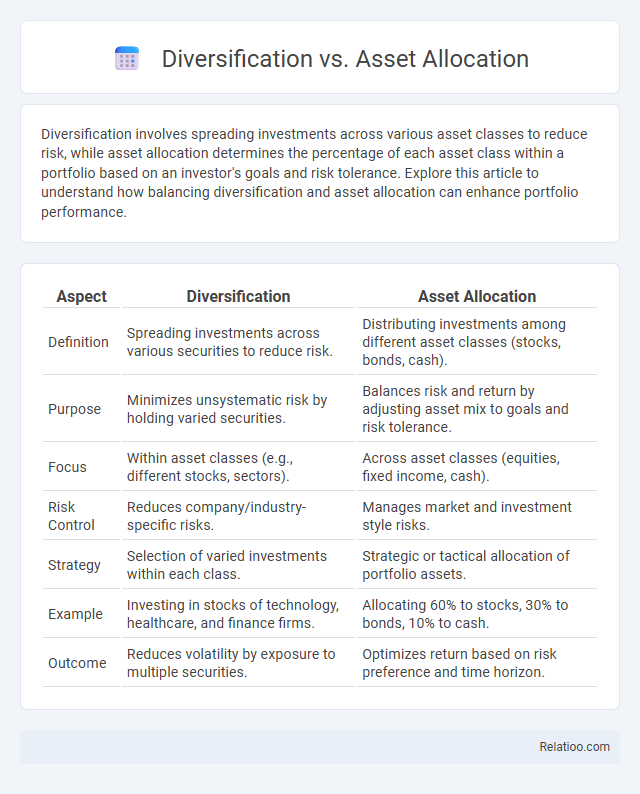
| Aspect | Diversification | Asset Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spreading investments across various securities to reduce risk. | Distributing investments among different asset classes (stocks, bonds, cash). |
| Purpose | Minimizes unsystematic risk by holding varied securities. | Balances risk and return by adjusting asset mix to goals and risk tolerance. |
| Focus | Within asset classes (e.g., different stocks, sectors). | Across asset classes (equities, fixed income, cash). |
| Risk Control | Reduces company/industry-specific risks. | Manages market and investment style risks. |
| Strategy | Selection of varied investments within each class. | Strategic or tactical allocation of portfolio assets. |
| Example | Investing in stocks of technology, healthcare, and finance firms. | Allocating 60% to stocks, 30% to bonds, 10% to cash. |
| Outcome | Reduces volatility by exposure to multiple securities. | Optimizes return based on risk preference and time horizon. |
Introduction to Diversification and Asset Allocation
Diversification involves spreading investments across various asset classes and sectors to minimize risk and enhance portfolio stability. Asset allocation refers to strategically dividing investments among different asset categories like stocks, bonds, and real estate based on an investor's risk tolerance and financial goals. Both diversification and asset allocation are foundational principles in portfolio management that aim to optimize returns while managing exposure to market volatility.
Defining Diversification in Investment
Diversification in investment involves spreading your portfolio across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce risk and enhance potential returns. Unlike asset allocation, which focuses on the proportion of different asset categories like stocks, bonds, and cash, diversification emphasizes the distribution within those categories to avoid concentration risk. Understanding diversification helps you create a balanced investment strategy that protects against market volatility and maximizes growth opportunities.
What is Asset Allocation?
Asset allocation is the strategic process of distributing investments across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash to balance risk and reward based on an investor's goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. It differs from diversification, which involves spreading investments within asset classes to minimize risk by avoiding overexposure to a single security or sector. Proper asset allocation aims to optimize portfolio performance by adjusting the proportion of each asset class in response to market conditions and individual financial objectives.
Key Differences Between Diversification and Asset Allocation
Diversification involves spreading investments across various financial instruments, industries, and other categories to reduce risk, while asset allocation refers to the strategic distribution of investment capital among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash. The key difference lies in scope: diversification is about mitigating risk within an asset class, whereas asset allocation focuses on balancing risk and return across asset classes based on investment goals and risk tolerance. Effective portfolio management requires both asset allocation for strategic planning and diversification for risk reduction within chosen asset classes.
Benefits of Investment Diversification
Investment diversification reduces risk by spreading your portfolio across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, minimizing the impact of any single investment's poor performance. Asset allocation strategically balances these diversified investments based on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon to optimize potential returns. Investing with a diversified approach enhances portfolio stability, lowers volatility, and improves the probability of achieving consistent long-term growth.
Advantages of Effective Asset Allocation
Effective asset allocation optimizes your investment portfolio by balancing risk and reward according to your financial goals and risk tolerance. This strategy enhances diversification by spreading investments across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, reducing exposure to any single market's volatility. By continuously adjusting allocations based on market conditions, you can improve potential returns while managing downside risk effectively.
Common Strategies for Diversification
Common strategies for diversification involve spreading investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate to reduce risk and enhance potential returns. Asset allocation plays a crucial role by determining the percentage of your portfolio invested in each category based on risk tolerance and financial goals. This balanced approach helps you avoid overexposure to any single investment, improving overall portfolio stability.
Popular Asset Allocation Models
Popular asset allocation models like the 60/40 portfolio balance equity and bonds to optimize risk and return, differing from diversification, which spreads investments across various sectors or asset types to reduce exposure to any single risk. Asset allocation strategically divides investments based on risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon, while diversification enhances this strategy by ensuring a mix within each asset class. Understanding the contrast between these concepts helps investors create robust portfolios that maximize growth potential while managing volatility effectively.
Diversification vs Asset Allocation: Which Matters More?
Diversification and asset allocation are both critical components of a robust investment strategy, but asset allocation often holds greater significance in managing portfolio risk and achieving desired returns. Studies by financial experts, including those from Vanguard and Morningstar, show that asset allocation decisions can explain more than 90% of portfolio performance variance over time. While diversification reduces unsystematic risk by spreading investments across various securities, asset allocation balances investments across asset classes--such as equities, bonds, and cash--to address systematic risk and align with an investor's goals and risk tolerance.
Building a Balanced Portfolio: Best Practices
Building a balanced portfolio requires understanding the distinct roles of diversification, asset allocation, and rebalancing in managing risk and optimizing returns. Diversification spreads investments across various securities to reduce risk, while asset allocation strategically divides your portfolio among asset classes like stocks, bonds, and cash based on your risk tolerance and financial goals. Consistent rebalancing aligns your holdings with your target allocation, helping you maintain balance and capitalize on market opportunities.
Infographic: Diversification vs Asset Allocation
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com