Lump sum payments provide immediate access to the full amount, while annuities offer a steady income stream over time, impacting financial planning and tax considerations differently. Discover the advantages and drawbacks of Lump Sum vs Annuity options in this article.
Table of Comparison
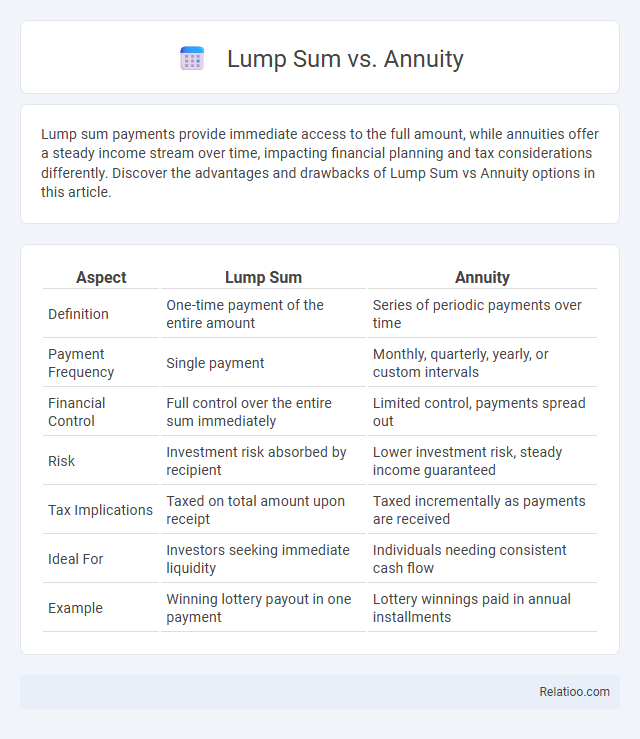
| Aspect | Lump Sum | Annuity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One-time payment of the entire amount | Series of periodic payments over time |
| Payment Frequency | Single payment | Monthly, quarterly, yearly, or custom intervals |
| Financial Control | Full control over the entire sum immediately | Limited control, payments spread out |
| Risk | Investment risk absorbed by recipient | Lower investment risk, steady income guaranteed |
| Tax Implications | Taxed on total amount upon receipt | Taxed incrementally as payments are received |
| Ideal For | Investors seeking immediate liquidity | Individuals needing consistent cash flow |
| Example | Winning lottery payout in one payment | Lottery winnings paid in annual installments |
Introduction: Understanding Lump Sum vs Annuity
A lump sum provides your entire retirement benefit as a single payment, offering immediate access to funds but requiring careful management to ensure long-term security. An annuity distributes your retirement benefits as regular, guaranteed payments over time, reducing the risk of outliving your savings. Understanding the differences between a lump sum and an annuity helps you make informed decisions about the best approach to meet your financial needs during retirement.
Defining Lump Sum and Annuity Payments
Lump sum payments deliver a one-time, fixed amount of money often used for settlements, insurance claims, or retirement payouts, providing immediate access to funds without ongoing distributions. Annuity payments, by contrast, consist of a series of periodic payments made over a specified period or for life, ensuring a steady income stream. Understanding these payment types helps you make informed decisions about managing your financial resources effectively.
Key Differences Between Lump Sum and Annuity
Lump sum payments provide a one-time full withdrawal of retirement savings, offering immediate access to the entire principal amount, whereas annuities distribute income through regular, fixed payments over a specified period or lifetime, ensuring consistent cash flow. The key difference lies in risk management: lump sums expose recipients to market volatility and longevity risk, while annuities transfer these risks to the insurance provider, promoting financial security. Tax treatment also varies, with lump sum distributions potentially resulting in higher immediate taxable income compared to the phased income taxation on annuity payments.
Pros and Cons of Taking a Lump Sum
Taking a lump sum from your pension plan provides immediate access to a large amount of capital, allowing flexibility in investment or debt repayment, but it also carries the risk of quickly depleting your retirement funds if not managed carefully. Unlike annuities or traditional pensions, a lump sum is not guaranteed to provide a steady income stream, which can expose you to longevity risk and inflation. You should weigh the pros of liquidity and control against the cons of financial discipline challenges and potential tax implications when considering this option.
Pros and Cons of Choosing an Annuity
Choosing an annuity provides a reliable income stream for your retirement, ensuring regular payments regardless of market fluctuations, which can help with financial stability. However, annuities often come with higher fees and less liquidity compared to lump sum payments, limiting your access to large sums of money if needed. Your decision should balance guaranteed income with flexibility, considering factors like longevity risk and investment goals when comparing to lump sum or pension options.
Tax Implications: Lump Sum vs Annuity
Lump sum payments are taxed as ordinary income in the year received, potentially pushing individuals into higher tax brackets and increasing immediate tax liability. Annuities spread taxable income over multiple years, allowing for better tax management and possibly lower overall tax rates. Selecting between lump sum and annuity options significantly impacts tax strategy and retirement income planning.
Investment Opportunities and Risks
Choosing between a lump sum, annuity, or pension significantly affects your investment opportunities and risks. A lump sum offers complete control to invest in diverse assets but exposes you to market volatility and the risk of outliving your savings. Annuities provide steady income and reduce longevity risk but may limit growth potential and flexibility compared to pensions, which guarantee lifetime payments but typically offer no investment control and depend on the sponsor's financial health.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Lump Sum or Annuity?
A lump sum payout is suitable for individuals with strong financial knowledge, disciplined spending habits, and alternative investment opportunities seeking flexibility and control over their retirement funds. Annuities benefit retirees who prefer stable, predictable income streams and want protection against outliving their savings. Your choice depends on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and the need for guaranteed income versus investment control.
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Choosing between a lump sum, annuity, or pension depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance, as demonstrated by real-life cases like retirees opting for lump sums to invest in diversified portfolios yielding higher returns. Case studies reveal that annuities provide steady income streams, beneficial for individuals seeking predictable cash flow, while pension plans often guarantee lifelong benefits but lack flexibility. Understanding these options through examples, such as executives leveraging lump sums for business ventures or seniors relying on annuities to cover daily expenses, highlights the practical implications of each retirement income strategy.
Conclusion: Making the Right Financial Decision
Choosing between a lump sum, annuity, and pension payout hinges on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and life expectancy. A lump sum offers immediate access to funds and investment flexibility, while an annuity provides steady income with reduced market risk. Pensions guarantee lifelong income, making them ideal for those seeking financial stability without investment management responsibilities.
Infographic: Lump Sum vs Annuity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com