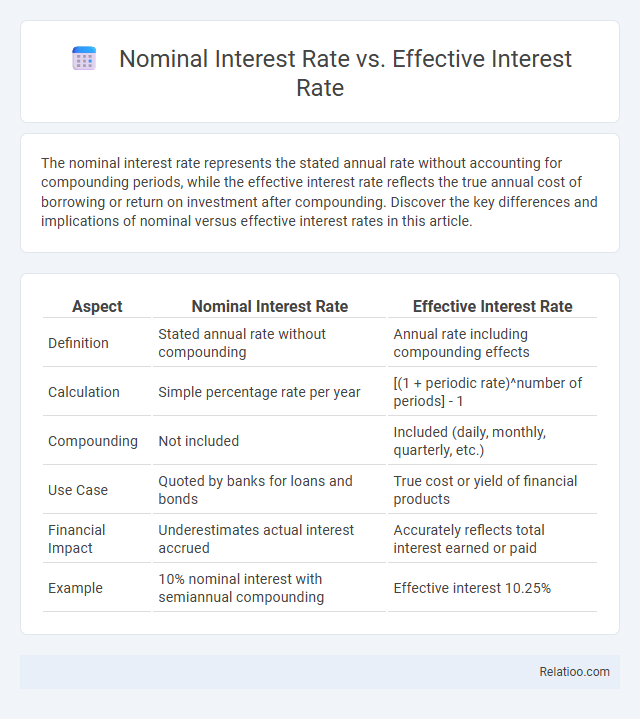
The nominal interest rate represents the stated annual rate without accounting for compounding periods, while the effective interest rate reflects the true annual cost of borrowing or return on investment after compounding. Discover the key differences and implications of nominal versus effective interest rates in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nominal Interest Rate | Effective Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stated annual rate without compounding | Annual rate including compounding effects |
| Calculation | Simple percentage rate per year | [(1 + periodic rate)^number of periods] - 1 |
| Compounding | Not included | Included (daily, monthly, quarterly, etc.) |
| Use Case | Quoted by banks for loans and bonds | True cost or yield of financial products |
| Financial Impact | Underestimates actual interest accrued | Accurately reflects total interest earned or paid |
| Example | 10% nominal interest with semiannual compounding | Effective interest 10.25% |
Introduction to Interest Rates
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing or the return on investment, expressed as a percentage of the principal amount. The Nominal Interest Rate is the stated rate without accounting for compounding within the year, while the Effective Interest Rate reflects the true annual rate by including compounding effects. Understanding these differences helps you accurately assess the real cost or yield associated with financial products and loans.
Definition of Nominal Interest Rate
The nominal interest rate represents the stated annual interest rate on a loan or investment without adjusting for inflation or compounding within the year. Unlike the effective interest rate, which accounts for compounding periods and provides the true cost or yield, the nominal rate simply reflects the basic rate agreed upon. Interest in general refers to the cost of borrowing money or the return earned on an investment, measured as a percentage of the principal.
Definition of Effective Interest Rate
Effective Interest Rate represents the true annual cost of borrowing or return on investment, accounting for compounding periods within a year, unlike the Nominal Interest Rate, which reflects the stated rate without compounding effects. Interest is the cost paid for the use of money, typically expressed as a percentage of the principal amount. Understanding the Effective Interest Rate helps you accurately compare financial products by revealing the actual interest burden or yield over time.
Key Differences Between Nominal and Effective Rates
Nominal interest rate represents the stated annual rate without accounting for compounding within the year, while effective interest rate reflects the true cost of borrowing or return on investment after compounding is considered. The key difference lies in compounding frequency, where effective interest rate provides a more accurate measure of financial growth or expense by incorporating multiple compounding periods per year. Interest in general is the cost paid for borrowing money or the earnings from invested capital, with nominal and effective rates influencing how interest is calculated over time.
How to Calculate Nominal Interest Rate
The nominal interest rate is the stated annual percentage without compounding effects, calculated by dividing the total interest earned or paid by the principal and then multiplying by the number of compounding periods per year. Effective interest rate accounts for compounding within the year, reflecting the true cost or yield of a loan or investment. Understanding your nominal interest rate helps in accurately comparing loan offers and investment returns before considering the compounding impact.
How to Calculate Effective Interest Rate
The effective interest rate reflects the true cost of borrowing or actual return on investment, accounting for compounding periods within a year. You calculate it by using the formula: Effective Interest Rate = (1 + Nominal Interest Rate / Number of Compounding Periods) ^ Number of Compounding Periods - 1. Understanding this calculation helps you compare different financial products accurately.
Impact of Compounding on Interest Rates
Nominal interest rate represents the stated annual rate without accounting for compounding periods, while the effective interest rate reflects the actual annual rate earned or paid after compounding is considered. The impact of compounding on interest rates means that your effective interest rate can be higher than the nominal rate, especially with more frequent compounding periods such as monthly or daily. Understanding this difference is crucial for accurately comparing loan costs or investment returns.
Practical Examples: Nominal vs Effective Rates
Nominal interest rate represents the stated annual rate without accounting for compounding within the year, while the effective interest rate reflects the actual annual cost of borrowing or return on investment after compounding periods are considered. For example, a nominal rate of 12% compounded monthly results in an effective rate of approximately 12.68%, meaning your actual interest paid or earned is higher than the nominal rate suggests. Understanding the difference between these rates helps you accurately compare loan offers or investment returns in practical financial decisions.
Importance of Understanding Interest Rate Types
Understanding the differences between nominal interest rate, effective interest rate, and simple interest is crucial for making informed financial decisions and maximizing returns. The nominal interest rate represents the stated annual rate without accounting for compounding periods, while the effective interest rate reflects the actual annual return considering compounding frequency. By grasping these concepts, you can accurately compare loan offers, investment products, and manage your financial planning effectively.
Choosing the Right Rate for Financial Decisions
Choosing the right rate for financial decisions involves understanding the differences between nominal interest rate, effective interest rate, and simple interest. The nominal interest rate represents the stated annual rate without compounding effects, while the effective interest rate accounts for compounding periods within the year, providing a more accurate measure of the true cost or return on investment. Your financial decisions benefit from focusing on the effective interest rate to assess the real growth or expense, ensuring better comparisons and smarter money management.
Infographic: Nominal Interest Rate vs Effective Interest Rate
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com