Public insurance provides essential healthcare coverage funded by the government, ensuring accessibility and affordability for a broad population. Private insurance offers customizable plans with faster service and wider provider networks, catering to specific individual needs; explore this article to understand the key differences and benefits of each.
Table of Comparison
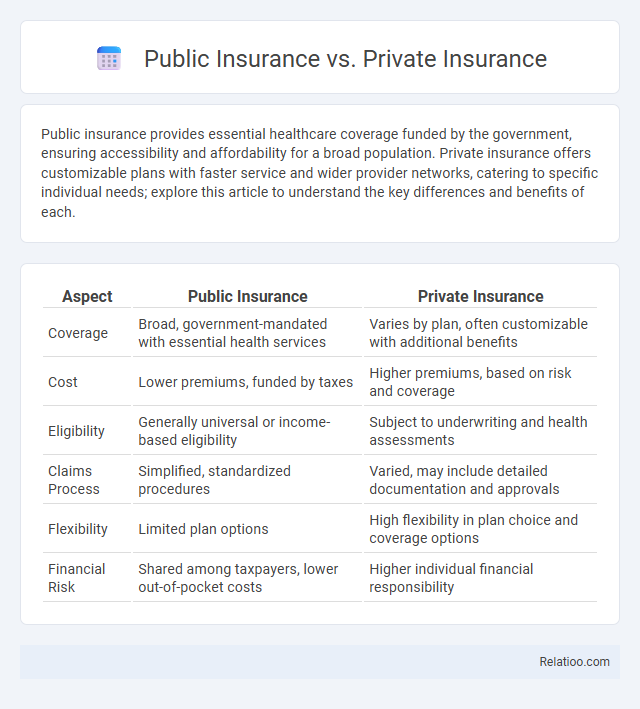
| Aspect | Public Insurance | Private Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Broad, government-mandated with essential health services | Varies by plan, often customizable with additional benefits |
| Cost | Lower premiums, funded by taxes | Higher premiums, based on risk and coverage |
| Eligibility | Generally universal or income-based eligibility | Subject to underwriting and health assessments |
| Claims Process | Simplified, standardized procedures | Varied, may include detailed documentation and approvals |
| Flexibility | Limited plan options | High flexibility in plan choice and coverage options |
| Financial Risk | Shared among taxpayers, lower out-of-pocket costs | Higher individual financial responsibility |
Introduction to Public and Private Insurance
Public insurance, funded and operated by government entities, provides essential coverage to vulnerable populations like low-income families, elderly citizens, and individuals with disabilities. Private insurance, offered by commercial companies, allows individuals and businesses to purchase tailored plans with diverse coverage options and competitive pricing. Understanding the differences in funding, eligibility, and coverage scope is crucial for consumers making informed decisions about their insurance needs.
Key Differences Between Public and Private Insurance
Public insurance is government-funded, providing broad healthcare coverage with standardized benefits and eligibility based on income or employment status. Private insurance offers customized plans through employers or direct purchase, typically featuring varied premium costs, deductibles, and enhanced provider choices. Key differences include cost structure, coverage flexibility, and access to services, with public insurance emphasizing universal access and private insurance focusing on personalized options.
Coverage Options: Public vs Private Insurance
Public insurance typically offers standardized coverage options designed to meet essential healthcare needs, often including hospital care, emergency services, and preventive treatments, with limited customization. Private insurance provides a wider range of coverage options, allowing policyholders to select plans that include specialized services, dental, vision, and additional wellness benefits tailored to individual needs. The flexibility of private insurance plans contrasts with the more uniform, government-regulated coverage found in public insurance programs.
Cost Comparison: Premiums, Deductibles, and Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Public insurance typically offers lower premiums and deductibles compared to private insurance, making it more affordable for individuals with limited income. Private insurance often comes with higher premiums but provides wider provider networks and more comprehensive coverage options, which can reduce your out-of-pocket expenses for specialized treatments. When comparing costs, consider premiums, deductibles, and co-pays carefully to determine which insurance best fits your financial and healthcare needs.
Accessibility and Eligibility Criteria
Public insurance offers broad accessibility with eligibility based on income, age, disability, or employment status, ensuring coverage for vulnerable populations like low-income families, seniors, and disabled individuals. Private insurance provides more flexible eligibility criteria but often requires higher premiums and good health status, making it less accessible to those with pre-existing conditions or limited financial resources. Insurance coverage overall varies significantly in accessibility, with public programs prioritizing inclusivity while private plans emphasize risk assessment and financial capacity.
Quality of Care: Public vs Private Providers
Quality of care often varies between public and private insurance providers due to differences in resources, patient-to-provider ratios, and service availability. Public insurance typically covers a broader population with standardized care protocols but may face longer wait times and limited specialist access, while private insurance often offers faster access to specialized services and personalized treatment options. When choosing your insurance, consider how these factors impact the quality and timeliness of care to ensure that your healthcare needs are met effectively.
Speed and Waiting Times for Services
Public insurance often involves longer waiting times due to high demand and limited resources, which can delay access to specialized treatments and elective procedures. Private insurance typically offers faster service delivery, with shorter waiting periods for consultations, diagnostics, and surgeries, providing more immediate care options. Understanding these differences helps your decision by balancing cost with the urgency of medical needs and desired speed of service.
Flexibility and Choice of Healthcare Providers
Public insurance often limits flexibility by requiring enrollment in government-approved healthcare plans and restricting access to a network of designated providers. Private insurance typically offers greater choice of healthcare providers and more customizable coverage options, allowing policyholders to select specialists and facilities without referrals. Comparing both, public insurance ensures broader basic coverage with fewer out-of-pocket costs, while private insurance provides enhanced flexibility and wider provider networks, catering to individual healthcare preferences.
Impact on Health Outcomes
Public insurance programs, such as Medicaid and Medicare, significantly improve access to essential health services, resulting in better health outcomes for low-income and elderly populations. Private insurance often offers more comprehensive coverage and quicker access to specialized care, enhancing patient satisfaction and health management. Your choice between public and private insurance can directly influence the quality of care, continuity of treatment, and ultimately, your overall health outcomes.
Choosing the Right Insurance: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right insurance involves evaluating factors such as coverage options, cost, network access, and claims processing efficiency. Public insurance often offers broader accessibility and affordability, while private insurance provides more personalized plans and expedited services. Assessing individual healthcare needs, financial capacity, and risk tolerance is essential to determine whether public, private, or hybrid insurance best suits your situation.
Infographic: Public Insurance vs Private Insurance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com