A primary borrower holds full responsibility for a loan, while a co-signer guarantees repayment if the borrower defaults, impacting both parties' credit. Understand the crucial differences and implications of co-signing versus primary borrowing in this article.
Table of Comparison
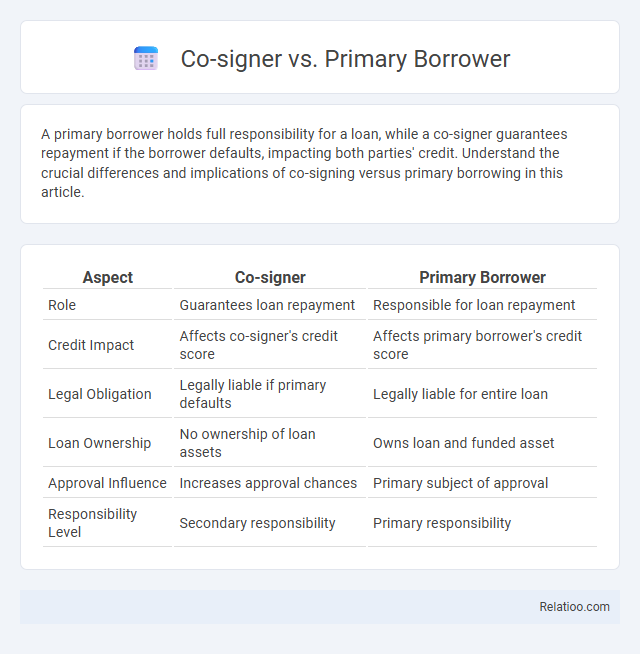
| Aspect | Co-signer | Primary Borrower |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Guarantees loan repayment | Responsible for loan repayment |
| Credit Impact | Affects co-signer's credit score | Affects primary borrower's credit score |
| Legal Obligation | Legally liable if primary defaults | Legally liable for entire loan |
| Loan Ownership | No ownership of loan assets | Owns loan and funded asset |
| Approval Influence | Increases approval chances | Primary subject of approval |
| Responsibility Level | Secondary responsibility | Primary responsibility |
Understanding the Role of a Co-signer
A co-signer shares legal responsibility for a loan without primary ownership of the borrowed funds, helping you qualify for credit by leveraging their creditworthiness. Unlike the primary borrower, who has full control and accountability for the loan, the co-signer steps in as a financial safety net to reduce lender risk. Understanding the role of a co-signer is crucial because their credit score and financial history directly impact your loan approval and repayment terms.
Defining the Primary Borrower
The primary borrower is the individual legally responsible for repaying a loan and whose credit history is the main factor lenders evaluate during approval. Unlike a co-signer, who guarantees the loan but may not receive funds directly, the primary borrower controls the loan account and manages payments. Understanding the primary borrower's role is essential for distinguishing financial responsibility and liability in loan agreements.
Key Responsibilities of a Co-signer
A co-signer assumes the legal responsibility to repay a loan if the primary borrower defaults, ensuring the lender's risk is mitigated. Your credit score can be directly impacted by the loan's repayment status, making timely payments critical. Co-signers do not own the asset but are equally liable for the debt, differentiating their role significantly from the primary borrower's ownership and control.
Obligations of the Primary Borrower
The Primary Borrower holds the main responsibility for repaying the loan, making timely payments, and ensuring the debt is fully serviced according to the loan agreement. Co-signers guarantee the loan but share secondary liability, stepping in only if the Primary Borrower defaults. Your financial obligations as the Primary Borrower are paramount, impacting your credit and financial standing directly.
Credit Impact: Co-signer vs Primary Borrower
The credit impact on a co-signer and a primary borrower differs significantly, as the primary borrower's credit is directly responsible for loan repayment and is primarily affected by payment history and defaults. A co-signer shares equal responsibility for loan repayment, and missed or late payments negatively impact both the co-signer's and the primary borrower's credit scores. Lenders consider the primary borrower's creditworthiness first, but a co-signer's credit can be equally at risk, making it crucial for co-signers to monitor and support timely payments.
Legal Liabilities of Each Role
The primary borrower holds full legal responsibility for repaying the loan, including principal and interest, and their credit is directly impacted by payment history. A co-signer legally guarantees the loan, sharing equal liability for repayment, which means they are equally responsible if the primary borrower defaults, affecting their credit score as well. Unlike a co-signer, a co-borrower equally owns the loan and collateral, bearing joint responsibility for the debt and credit implications with the primary borrower.
Benefits and Risks for Co-signers
Co-signers help borrowers secure loans by providing additional assurance to lenders, often enabling approval for those with limited credit history or lower credit scores; however, co-signers assume equal responsibility for repayment, risking damage to their credit if the primary borrower defaults. Unlike the primary borrower, who controls the loan terms and usage, co-signers have no ownership over the funds but share liability, making it crucial for them to weigh the potential financial and credit risks. Benefits for co-signers include strengthening personal relationships and possibly improving their own credit profile when payments are made on time, yet the risks involve potential legal and financial obligations if the primary borrower fails to meet loan terms.
Advantages and Disadvantages for Primary Borrowers
Primary borrowers hold full responsibility for loan repayment and typically enjoy easier approval and better interest rates compared to co-signers. However, the primary borrower assumes all financial risk, including credit impact and debt burden, if payments are missed. Unlike co-signers who share liability without ownership, primary borrowers can build credit history but face significant consequences in case of default.
How Lenders Assess Co-signers and Primary Borrowers
Lenders evaluate primary borrowers based on their credit history, income stability, and debt-to-income ratio to determine loan eligibility and interest rates. Co-signers are assessed similarly but serve as backup payers, adding security by guaranteeing loan repayment if the primary borrower defaults. Your creditworthiness as a co-signer directly impacts the loan approval process, as lenders rely on both parties' financial strength to mitigate risk.
Choosing the Right Option: Co-signer or Primary Borrower
Choosing the right option between a co-signer and a primary borrower depends on your credit profile and financial responsibility. Your creditworthiness significantly impacts loan approval and interest rates when you apply as the primary borrower, while a co-signer's strong credit can help secure better terms if your credit is limited. Understanding the differences in liability and credit impact helps you decide whether to apply as the primary borrower or enlist a co-signer for your loan.
Infographic: Co-signer vs Primary Borrower
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com