Separate accounts offer personalized investment strategies and individual asset ownership, while pooled accounts combine assets from multiple investors for collective management and diversified risk. Discover the key differences and benefits of each account type in this article.
Table of Comparison
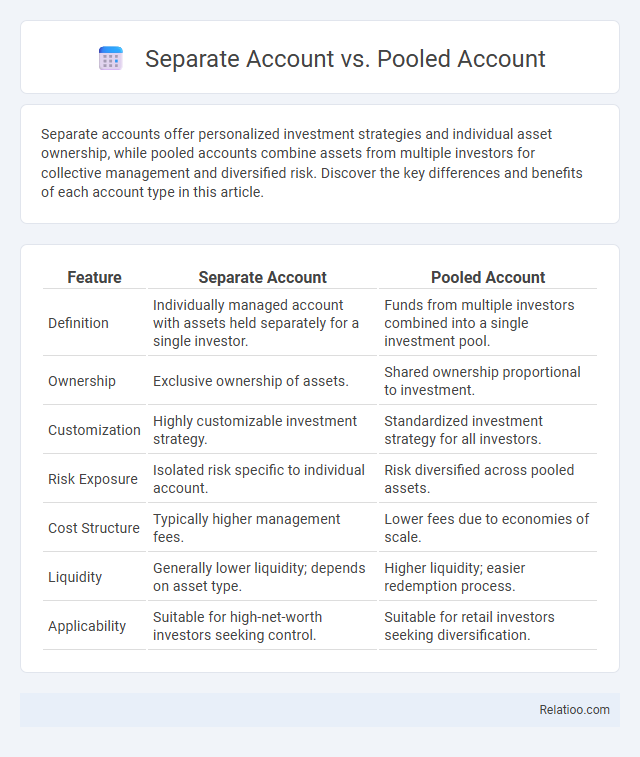
| Feature | Separate Account | Pooled Account |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individually managed account with assets held separately for a single investor. | Funds from multiple investors combined into a single investment pool. |
| Ownership | Exclusive ownership of assets. | Shared ownership proportional to investment. |
| Customization | Highly customizable investment strategy. | Standardized investment strategy for all investors. |
| Risk Exposure | Isolated risk specific to individual account. | Risk diversified across pooled assets. |
| Cost Structure | Typically higher management fees. | Lower fees due to economies of scale. |
| Liquidity | Generally lower liquidity; depends on asset type. | Higher liquidity; easier redemption process. |
| Applicability | Suitable for high-net-worth investors seeking control. | Suitable for retail investors seeking diversification. |
Introduction to Separate and Pooled Accounts
Separate accounts offer personalized investment management by holding assets individually for your portfolio, ensuring tailored strategies and direct ownership. Pooled accounts combine assets from multiple investors into a single fund, enabling diversified exposure and cost-efficient management. Understanding the distinctions between these account structures helps you choose the best option to align with your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
Definitions: What Are Separate Accounts?
Separate accounts are individualized investment portfolios managed independently for each client, offering personalized asset allocation and ownership, unlike pooled accounts where multiple investors' funds are combined into a single portfolio. Pooled accounts aggregate assets from multiple clients to achieve diversification and cost efficiency but lack the personalization found in separate accounts. You can benefit from separate accounts by having greater control, transparency, and customization in your investment strategy.
Understanding Pooled Accounts
Pooled accounts consolidate multiple clients' assets into a single investment vehicle, optimizing diversification and reducing management costs compared to separate accounts, which are individually managed portfolios tailored to each client's specific objectives. Unlike separate accounts, pooled accounts do not provide direct ownership of individual securities, which can impact transparency and control but enhance liquidity and lower minimum investment requirements. Understanding pooled accounts involves recognizing their role in collective investing, where asset commingling seeks to achieve economies of scale, diversified exposures, and professional management benefits for smaller investors.
Key Differences Between Separate and Pooled Accounts
Separate accounts provide individual investment management tailored specifically to Your financial goals, ensuring direct ownership of assets and personalized control. Pooled accounts aggregate multiple investors' funds into a single portfolio, offering diversification but less individualized control and ownership. The key difference lies in asset ownership and customization, with separate accounts granting You distinct asset titles versus shared holdings in pooled accounts, impacting transparency, fees, and investment strategy.
Advantages of Separate Accounts
Separate accounts offer greater customization and control by allowing individual investors to tailor investment portfolios according to their specific risk tolerance and financial goals. Unlike pooled accounts, separate accounts provide enhanced transparency with direct ownership of underlying assets, facilitating personalized tax management and reporting. This structure also reduces exposure to other investors' transactions, minimizing potential dilution and improving portfolio performance.
Benefits of Pooled Accounts
Pooled accounts consolidate multiple investors' funds into a single account to provide diversification, reduce management costs, and increase access to a broader range of investment opportunities. Compared to separate accounts, pooled accounts offer you enhanced liquidity and simplified administration, making it easier to manage your investments efficiently. The shared structure also enables professional management with economies of scale, which can lead to potentially higher returns and lower fees.
Risks and Considerations for Each Option
Separate accounts offer individualized control and transparency but carry risks of higher fees and less diversification compared to pooled accounts. Pooled accounts provide cost efficiency and diversification benefits but expose investors to collective risk and less customization. Evaluating separate versus pooled accounts requires examining factors such as management costs, investment objectives, liquidity needs, and risk tolerance to align with personal financial goals.
Cost and Fee Structures Compared
Separate accounts typically involve higher management fees due to individualized investment strategies and personalized service, often ranging from 0.50% to 1.50% annually. Pooled accounts, such as mutual funds, generally have lower fees, including expense ratios averaging 0.20% to 1.00%, because costs are shared among all investors. Hybrid separate accounts may charge a blend of fees reflecting both customization and pooled investment benefits, balancing cost-efficiency with tailored asset management.
Who Should Choose Separate vs Pooled Accounts?
Investors seeking personalized control and tailored investment strategies should choose separate accounts, as they offer individualized management and greater transparency. Pooled accounts are ideal for those looking for cost-efficiency and diversification without the need for a customized portfolio, making them suitable for smaller investors or those preferring a hands-off approach. Your decision between separate and pooled accounts depends on your investment size, customization needs, and preference for direct asset ownership versus collective management.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Choosing between separate accounts and pooled accounts depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and desired control over assets. Separate accounts offer personalized portfolio management and transparency but may require higher minimums and fees, while pooled accounts provide diversification and cost-efficiency through collective investment. Evaluating factors like customization needs, cost constraints, and performance expectations ensures the right account structure aligns with individual financial objectives.
Infographic: Separate Account vs Pooled Account
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com