The principal amount represents the original sum borrowed, while the loan amount includes both the principal and any accrued interest or fees. Discover the detailed impact of principal versus loan amount on your financial planning in this article.
Table of Comparison
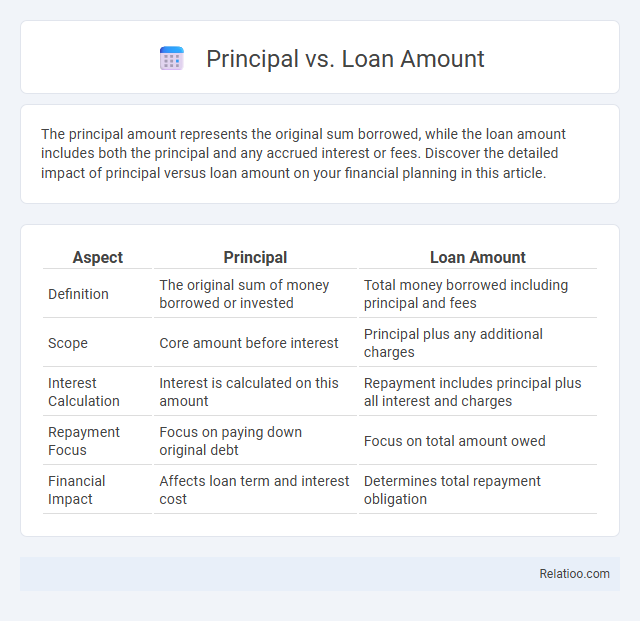
| Aspect | Principal | Loan Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The original sum of money borrowed or invested | Total money borrowed including principal and fees |
| Scope | Core amount before interest | Principal plus any additional charges |
| Interest Calculation | Interest is calculated on this amount | Repayment includes principal plus all interest and charges |
| Repayment Focus | Focus on paying down original debt | Focus on total amount owed |
| Financial Impact | Affects loan term and interest cost | Determines total repayment obligation |
Understanding the Basics: Principal vs Loan Amount
Understanding the basics of the principal versus the loan amount is crucial for managing your finances effectively. The loan amount refers to the total sum you borrow from a lender, while the principal specifically denotes the original borrowed amount excluding interest. Knowing this distinction helps you track repayments accurately and avoid confusion between the borrowed sum and the interest accruing on your loan.
Defining Loan Amount: What Does It Include?
The loan amount refers to the total sum of money borrowed from a lender, encompassing not only the principal but also any applicable fees, closing costs, and prepaid expenses. Your principal constitutes the core portion of the loan amount that must be repaid, excluding interest and additional charges. Understanding the components within the loan amount helps clarify your financial obligations and the true cost of borrowing.
What Is Principal in a Loan?
Principal in a loan refers to the original amount of money borrowed from a lender, excluding interest and fees. The loan amount typically represents the total funds provided, while the principal specifically denotes the remaining balance that must be repaid. Understanding the principal is crucial for calculating interest charges and determining the repayment schedule of a loan.
How Principal Differs From Total Loan Amount
Principal refers to the original sum of money borrowed or invested, excluding any interest or fees, while the total loan amount includes both the principal and any accrued interest or additional costs over the loan term. The principal determines the base on which interest is calculated, making it a critical figure for understanding repayment schedules and the overall cost of borrowing. Understanding the distinction between principal and total loan amount helps borrowers accurately assess their financial obligations and plan their budgets effectively.
The Role of Principal in Loan Repayment
The principal represents the original loan amount borrowed before interest and fees, which directly affects your total repayment obligations. Understanding the principal is crucial because every payment you make reduces this amount, thereby lowering future interest charges and the overall cost of the loan. Managing your principal effectively accelerates loan payoff, saving money and improving your financial health.
Interest Calculations: Principal vs Loan Amount
Interest calculations depend primarily on the principal, which is the outstanding balance on the loan excluding any fees or accrued interest. The loan amount represents the original sum borrowed, serving as the basis for calculating initial interest, but as payments are made, interest accrues only on the remaining principal. Differentiating between principal and loan amount is crucial for accurately determining interest charges over the life of a loan.
Reducing Your Principal: Strategies and Benefits
Reducing your principal early in a loan cycle significantly decreases the total interest paid over the loan term, leading to substantial savings and faster debt elimination. Strategies such as making extra payments directly toward the principal, refinancing to a lower interest rate, and avoiding loan deferment can accelerate principal reduction. Lower principal balances improve your equity position, enhance creditworthiness, and provide greater financial flexibility for future investments or emergencies.
Common Misconceptions About Loan Principal
Loan principal often confuses borrowers who mistakenly equate it with the total loan amount, which actually includes both principal and interest components. Many assume loan principal remains fixed, but repayments typically reduce the principal over time, lowering interest costs. Understanding that principal is the initial borrowed sum excluding interest helps clarify repayment schedules and loan balances.
Principal Payments and Amortization Explained
Your principal payments directly reduce the loan amount, which is the original sum borrowed before interest. Amortization schedules break down each payment into principal and interest, showing how your loan balance decreases over time. Understanding this process helps you manage your loan efficiently and plan your repayments to minimize interest costs.
Making Smart Borrowing Decisions: Principal vs Loan Amount
Understanding the difference between principal and loan amount is essential for making smart borrowing decisions. The principal refers to the original sum of money borrowed, excluding interest, while the loan amount may include fees and interest costs over the loan term. Focusing on reducing the principal early can significantly lower total interest payments and improve overall financial health.
Infographic: Principal vs Loan Amount
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com