FICO Score and VantageScore are two primary credit scoring models used by lenders to evaluate creditworthiness, with FICO being the most widely adopted and VantageScore gaining popularity for its broader data use and quicker updates. Discover the key differences and which score impacts your financial decisions more by reading this article.
Table of Comparison
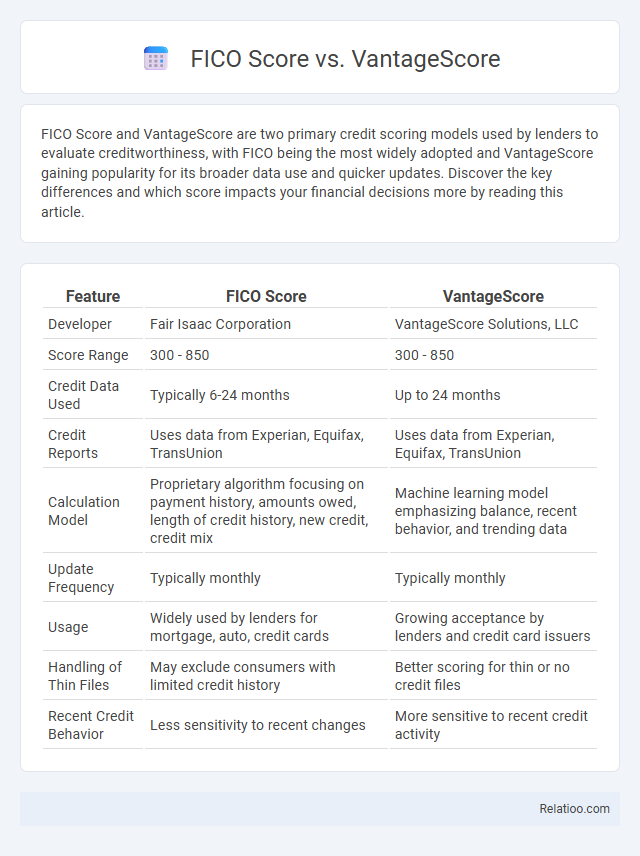
| Feature | FICO Score | VantageScore |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | Fair Isaac Corporation | VantageScore Solutions, LLC |
| Score Range | 300 - 850 | 300 - 850 |
| Credit Data Used | Typically 6-24 months | Up to 24 months |
| Credit Reports | Uses data from Experian, Equifax, TransUnion | Uses data from Experian, Equifax, TransUnion |
| Calculation Model | Proprietary algorithm focusing on payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, new credit, credit mix | Machine learning model emphasizing balance, recent behavior, and trending data |
| Update Frequency | Typically monthly | Typically monthly |
| Usage | Widely used by lenders for mortgage, auto, credit cards | Growing acceptance by lenders and credit card issuers |
| Handling of Thin Files | May exclude consumers with limited credit history | Better scoring for thin or no credit files |
| Recent Credit Behavior | Less sensitivity to recent changes | More sensitive to recent credit activity |
Understanding FICO Score: An Overview
The FICO Score is a widely used credit scoring model developed by the Fair Isaac Corporation, designed to predict your credit risk based on payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, new credit, and credit mix. FICO Scores range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness, which lenders heavily rely on for loan approvals and interest rate decisions. Compared to VantageScore and generic credit scores, the FICO Score is often considered the industry standard, making it crucial for you to understand its components and impact on your financial health.
What is VantageScore? Key Facts
VantageScore, developed collaboratively by the three major credit bureaus--Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion--is a credit scoring model designed to provide consumers and lenders with a consistent credit risk assessment. Unlike the traditional FICO Score, VantageScore uses a distinct scoring range of 300 to 850 and incorporates factors such as payment history, credit utilization, and age of credit accounts with unique weightings. Its key differentiators include the ability to score more consumers with limited credit history and more frequent model updates, allowing for potentially faster credit profile changes than some versions of the FICO Score.
FICO Score vs VantageScore: Main Differences
FICO Score and VantageScore are two leading credit scoring models used to evaluate consumer creditworthiness, with FICO Scores ranging from 300 to 850 and VantageScores also spanning 300 to 850 but differing slightly in scoring criteria. FICO emphasizes payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, new credit, and credit mix, while VantageScore includes similar factors but places more weight on recent credit behavior and is designed to score more consumers, including those with shorter credit histories. FICO Scores are widely used by lenders for mortgage, auto, and credit card decisions, whereas VantageScore is often utilized by alternative lenders and credit monitoring platforms, reflecting variations in how each model assesses risk and predicts credit default.
Scoring Models: How FICO and VantageScore Calculate Credit
FICO Score and VantageScore use different algorithms to calculate creditworthiness, impacting how lenders evaluate Your credit risk. FICO Score relies heavily on payment history and amounts owed, with weighted factors emphasizing recent activity and credit mix. VantageScore incorporates similar data but uses machine learning techniques to better predict credit behavior across broader credit profiles, often providing more inclusive scoring for thin-file borrowers.
Credit Report Data Sources Compared
FICO Score and VantageScore both utilize credit report data from the three major credit bureaus: Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion, but they differ in how they weigh specific factors like payment history and credit utilization. Your credit score's accuracy depends on the completeness and recency of data reported by lenders to these bureaus, which can vary between FICO and VantageScore models. Understanding these differences helps you better manage your credit profile and anticipate how various data sources impact your creditworthiness.
Factors Impacting FICO and VantageScore
FICO Score and VantageScore both assess creditworthiness using factors such as payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, types of credit accounts, and recent credit inquiries, but their weightings differ. FICO places significant emphasis on payment history and credit utilization, accounting for about 35% and 30% of the score respectively, while VantageScore gives more balanced weight across all categories, including total credit usage and available credit. Variations in scoring models can impact credit decisions, making it essential to understand specific factors like late payments or credit card balances that influence each score differently.
Which Lenders Use FICO vs VantageScore?
Most lenders rely on FICO scores because they have been the industry standard for decades and are used by 90% of top lenders, including mortgage, auto, and credit card companies. VantageScore, developed by the three major credit bureaus, is gaining popularity with some lenders, especially for credit card approvals and digital lending platforms, but it is still less widely used compared to FICO. Your choice between FICO and VantageScore can impact loan terms since lenders prioritize FICO scores for major financial decisions, making it essential to monitor your FICO score regularly.
How to Check Your FICO Score and VantageScore
To check your FICO Score, visit myFICO.com, the official source providing your score along with detailed credit reports from major bureaus. VantageScore can be accessed for free through various credit monitoring platforms like Credit Karma or directly on the VantageScore Solutions website, offering easy-to-understand credit insights. Both scores require your personal information, but regular monitoring helps maintain awareness of your credit health and supports informed financial decisions.
Pros and Cons: FICO Score vs VantageScore
FICO Score is widely used by 90% of top lenders, providing a reliable benchmark for creditworthiness, but its scoring model updates less frequently compared to VantageScore, which adjusts more dynamically to credit behavior changes and accepts data with shorter credit histories. VantageScore offers more accessibility for consumers with thin credit files and tends to use a consistent scoring range (300-850), whereas FICO Scores can vary slightly by specific FICO versions used by lenders. Your choice between these scores depends on whether you prioritize lender familiarity (FICO) or broader credit accessibility and more frequent scoring updates (VantageScore).
Which Score Matters More for Consumers?
FICO Score remains the most widely used credit scoring model by lenders, influencing approximately 90% of lending decisions, making it the primary score consumers should monitor. VantageScore, developed by the three major credit bureaus, offers an alternative range and scoring system used by some lenders, but it carries less weight in mortgage and auto loan approvals. Consumers benefit most by focusing on their FICO Score due to its dominant role in loan approvals, interest rates, and credit terms.
Infographic: FICO Score vs VantageScore
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com