Foreclosure and bankruptcy are legal processes used to address financial distress, with foreclosure specifically targeting the repossession of property due to unpaid mortgage, while bankruptcy offers a broader debt relief mechanism by restructuring or discharging debts. Learn more about the key differences, implications, and how to protect your assets in this article.
Table of Comparison
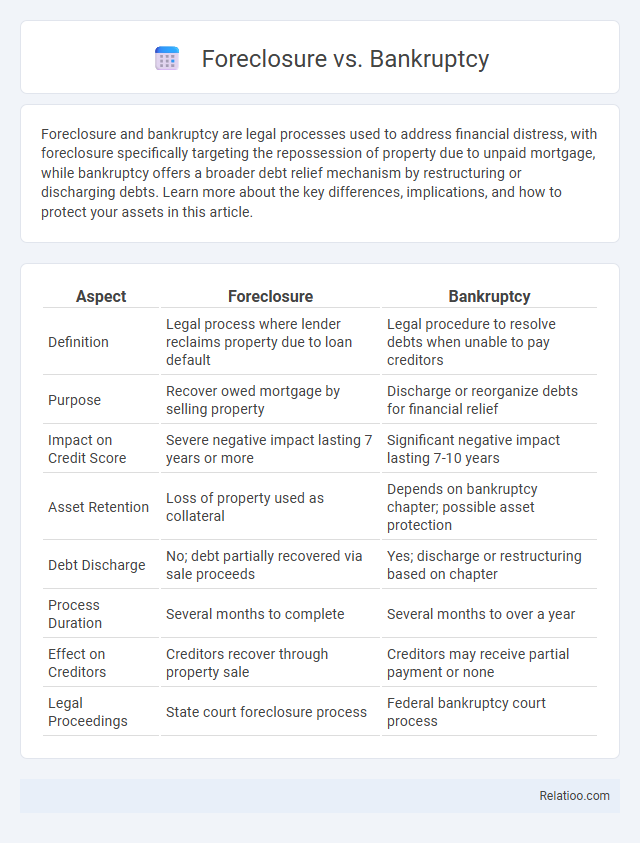
| Aspect | Foreclosure | Bankruptcy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process where lender reclaims property due to loan default | Legal procedure to resolve debts when unable to pay creditors |
| Purpose | Recover owed mortgage by selling property | Discharge or reorganize debts for financial relief |
| Impact on Credit Score | Severe negative impact lasting 7 years or more | Significant negative impact lasting 7-10 years |
| Asset Retention | Loss of property used as collateral | Depends on bankruptcy chapter; possible asset protection |
| Debt Discharge | No; debt partially recovered via sale proceeds | Yes; discharge or restructuring based on chapter |
| Process Duration | Several months to complete | Several months to over a year |
| Effect on Creditors | Creditors recover through property sale | Creditors may receive partial payment or none |
| Legal Proceedings | State court foreclosure process | Federal bankruptcy court process |
Understanding Foreclosure: Definition and Process
Foreclosure is a legal process in which a lender seizes and sells a property due to the borrower's failure to make mortgage payments. This process typically begins with a notice of default, followed by a period during which the borrower can cure the default or negotiate alternatives before the property is auctioned. Understanding the foreclosure timeline and its impact on credit scores is vital for homeowners facing financial difficulties, as it differs significantly from bankruptcy proceedings where debts are restructured or discharged.
What is Bankruptcy? Types and Overview
Bankruptcy is a legal process designed to help individuals and businesses eliminate or repay their debts under the protection of the bankruptcy court. The primary types of bankruptcy for individuals are Chapter 7, which involves liquidation of assets to pay creditors, and Chapter 13, which allows for a repayment plan over three to five years. This process provides relief from foreclosure by temporarily halting the foreclosure proceedings and enabling debt restructuring or debt discharge to protect homeowners from losing their property.
Key Differences Between Foreclosure and Bankruptcy
Foreclosure is a legal process where a lender seizes and sells a property due to the borrower's failure to pay the mortgage, directly impacting homeownership and credit score. Bankruptcy is a court-supervised process that helps individuals or businesses eliminate or repay debts under protection from creditors, affecting overall debt obligations but offering broader financial relief. Key differences include foreclosure targeting a single secured asset, typically real estate, while bankruptcy addresses multiple debts, with various types like Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 providing distinct repayment or discharge options.
How Foreclosure Affects Your Credit Score
Foreclosure significantly impacts your credit score by causing a major drop that can last for up to seven years, making it harder to obtain new loans or credit. Bankruptcy also damages your credit but differs in reporting duration and financial implications, while loan modification or short sale options can mitigate foreclosure effects. Understanding how foreclosure affects your credit helps you make informed decisions to protect your financial future.
Impact of Bankruptcy on Financial Standing
Bankruptcy significantly affects financial standing by severely damaging credit scores and remaining on credit reports for up to 10 years, making it difficult to obtain new loans or favorable interest rates. In contrast, foreclosure also harms credit but generally has a shorter impact, typically dropping credit scores by 85 to 160 points and remaining on reports for seven years. While both foreclosure and bankruptcy indicate financial distress, bankruptcy provides legal protection from creditors and can discharge debts, whereas foreclosure results in loss of property without necessarily eliminating other liabilities.
Pros and Cons of Foreclosure
Foreclosure allows you to stop mortgage payments and potentially remove unsecured debts, but it severely damages your credit score and remains on your credit report for up to seven years. Foreclosure can free you from an unaffordable loan but often leads to loss of home equity and may result in deficiency judgments depending on state laws. Understanding the pros and cons of foreclosure helps you decide if alternatives like bankruptcy or loan modification better suit your financial situation.
Pros and Cons of Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy offers a legal solution to manage overwhelming debt by providing debt relief and the possibility of discharging many types of unsecured debts. The pros of bankruptcy include stopping foreclosure through an automatic stay, eliminating collection calls, and enabling a fresh financial start, but cons involve potential damage to credit scores lasting 7-10 years and the risk of losing certain assets depending on the chapter filed. Unlike foreclosure, which directly results in loss of property, bankruptcy addresses broader financial issues but may carry long-term financial consequences and complex legal requirements.
When to Choose Foreclosure Over Bankruptcy
Choosing foreclosure over bankruptcy may be appropriate when your primary goal is to quickly eliminate mortgage debt without enduring the lengthy bankruptcy process. Foreclosure allows you to give up your property and discharge your mortgage obligation, which can be beneficial if you have few other debts and want to avoid the impact of bankruptcy on your credit report. Your decision should consider the timing, cost, and long-term effects on your financial health, emphasizing immediate debt relief and streamlined procedures.
Legal Implications: Foreclosure vs Bankruptcy
Foreclosure involves the legal process where a lender seeks to recover the balance of a loan by forcing the sale of the borrower's property due to default, resulting in loss of home ownership and damage to credit scores for up to seven years. Bankruptcy, particularly Chapter 7 or Chapter 13, offers protection from creditors, allowing for the potential discharge or restructuring of debts, including mortgage arrears, which can temporarily halt foreclosure through an automatic stay. Understanding these legal implications helps homeowners evaluate options: foreclosure leads to property loss and credit impact, while bankruptcy provides a strategic legal shield with possible debt relief and foreclosure postponement.
Preventing Foreclosure and Bankruptcy: Tips and Strategies
Preventing foreclosure and bankruptcy requires proactive financial management, including negotiating loan modifications or forbearance agreements with lenders to reduce monthly payments temporarily. Building an emergency fund and seeking credit counseling services can provide essential support and guidance for managing debts effectively. Exploring alternatives like refinancing or short sales may also help homeowners avoid the severe impacts of foreclosure and bankruptcy.
Infographic: Foreclosure vs Bankruptcy
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com