A co-signer shares equal responsibility for a loan's repayment, while an endorser guarantees payment only if the primary borrower defaults. Discover more about the differences between co-signers and endorsers in this article.
Table of Comparison
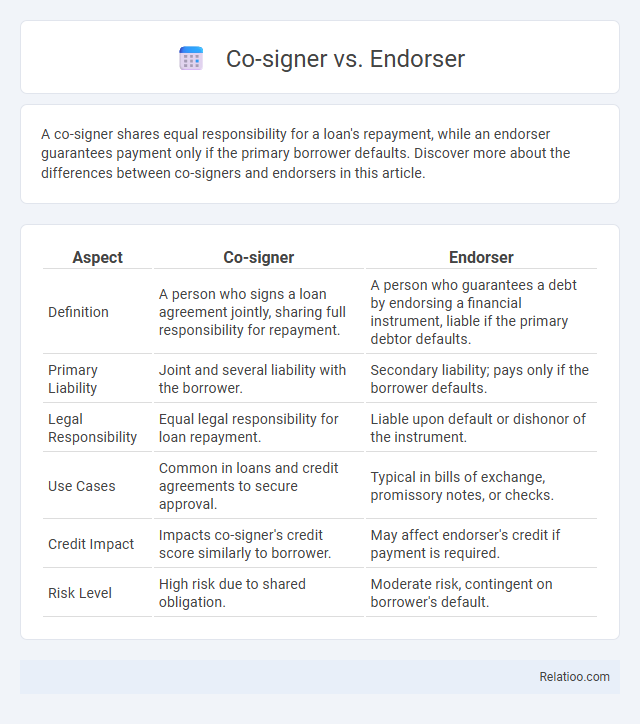
| Aspect | Co-signer | Endorser |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A person who signs a loan agreement jointly, sharing full responsibility for repayment. | A person who guarantees a debt by endorsing a financial instrument, liable if the primary debtor defaults. |
| Primary Liability | Joint and several liability with the borrower. | Secondary liability; pays only if the borrower defaults. |
| Legal Responsibility | Equal legal responsibility for loan repayment. | Liable upon default or dishonor of the instrument. |
| Use Cases | Common in loans and credit agreements to secure approval. | Typical in bills of exchange, promissory notes, or checks. |
| Credit Impact | Impacts co-signer's credit score similarly to borrower. | May affect endorser's credit if payment is required. |
| Risk Level | High risk due to shared obligation. | Moderate risk, contingent on borrower's default. |
Introduction to Co-signers and Endorsers
Co-signers and endorsers both play crucial roles in securing loans and credit, yet their responsibilities and implications differ significantly. A co-signer agrees to take legal responsibility for your debt if you default, directly impacting their credit score, while an endorser guarantees payment on a promissory note or check without necessarily affecting their credit unless payment is missed. Understanding these distinctions helps you determine the best option to support your financial obligations while managing risk for those involved.
Defining a Co-signer: Roles and Responsibilities
A co-signer is a person who agrees to take equal responsibility for a loan or financial obligation alongside the primary borrower, ensuring repayment if You default. Unlike an endorser who merely guarantees payment on negotiable instruments without full liability, a co-signer has a legally binding commitment that affects their credit since missed payments impact both parties. Understanding these distinct roles helps clarify financial responsibilities and better protect Your creditworthiness.
Understanding an Endorser: Key Functions
An endorser plays a crucial role by guaranteeing payment on a negotiable instrument, such as a check or promissory note, if the primary party defaults. Unlike a co-signer who shares equal responsibility for the entire debt, an endorser's liability is typically limited to the amount endorsed. Understanding your position as an endorser ensures you know when you might be legally obligated to fulfill payment if the original debtor fails to pay.
Legal Implications for Co-signers
Co-signers bear full legal responsibility for the debt, making them equally liable as the primary borrower if payments are missed or defaults occur. Unlike endorsers who primarily guarantee a negotiable instrument like a promissory note without direct loan obligation, co-signers face credit risk and potential lawsuits for unpaid balances. Understanding these distinctions is crucial, as co-signers' credit scores and financial standing are directly impacted by the borrower's repayment behavior.
Legal Responsibilities for Endorsers
Endorsers legally guarantee payment by signing a negotiable instrument, assuming primary responsibility if the issuer defaults. Unlike co-signers who share equal liability on loans or credit agreements, endorsers have liability specific to the terms of the instrument and may be held personally accountable in legal actions. Understanding your role as an endorser is crucial since your legal obligations can directly impact your financial standing without involvement in the original contract.
Differences Between Co-signers and Endorsers
Co-signers and endorsers both guarantee a loan or financial obligation, but co-signers share equal responsibility for repayment, directly impacting their credit score, while endorsers primarily assure payment if the primary borrower defaults, often with less immediate liability. Co-signers typically sign the loan agreement, making them legally responsible alongside the borrower, whereas endorsers usually sign negotiable instruments like checks or promissory notes to guarantee payment. Understanding these differences helps clarify the extent of financial commitment and legal obligations associated with each role.
Pros and Cons of Using a Co-signer
Using a co-signer can improve the chances of loan approval by adding creditworthiness, often resulting in lower interest rates and better terms. However, co-signers assume equal responsibility for repayment, risking credit damage and financial liability if the primary borrower defaults. Unlike endorsers or guarantors, co-signers have a direct obligation on the debt, which requires careful consideration before agreement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Having an Endorser
Having an endorser can improve your loan approval chances by sharing responsibility without the strict liability that co-signers face, but they may have less legal obligation, potentially weakening creditor security. While a co-signer directly guarantees the loan repayment and is equally liable, an endorser's involvement typically applies to negotiable instruments, making their liability conditional and sometimes harder to enforce. Your decision to involve an endorser should weigh the advantage of potentially easier credit access against the disadvantage of reduced creditor assurance compared to a co-signer, which could affect loan terms and interest rates.
When to Choose a Co-signer vs Endorser
You should choose a co-signer when you need someone to share full responsibility for a loan or credit agreement, ensuring approval if your credit is insufficient. An endorser is more suitable when you want someone to guarantee payment by endorsing a promissory note without joint obligation, typically for short-term or personal loans. Understanding the level of risk and legal commitment each role carries helps you select the best option to secure your financial agreement.
Frequently Asked Questions: Co-signer vs Endorser
A co-signer agrees to be responsible for a loan or debt if the primary borrower defaults, whereas an endorser guarantees payment on a negotiable instrument like a check or promissory note. The key difference lies in the type of obligation; co-signers are typically involved in loans, while endorsers are linked to negotiable instruments. Often, questions arise about liability, with co-signers sharing full responsibility for repayment and endorsers being liable only if the primary party fails to pay.
Infographic: Co-signer vs Endorser
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com