A lease allows you to use an asset for a fixed period with lower monthly payments and no ownership, while a loan requires full repayment and grants ownership of the asset. Explore this article to understand the benefits and drawbacks of lease vs loan for smarter financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
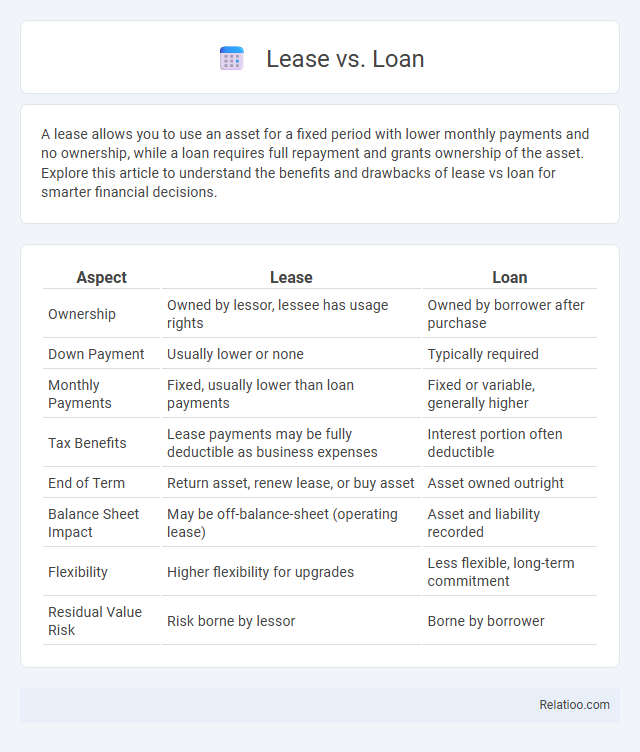
| Aspect | Lease | Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Owned by lessor, lessee has usage rights | Owned by borrower after purchase |
| Down Payment | Usually lower or none | Typically required |
| Monthly Payments | Fixed, usually lower than loan payments | Fixed or variable, generally higher |
| Tax Benefits | Lease payments may be fully deductible as business expenses | Interest portion often deductible |
| End of Term | Return asset, renew lease, or buy asset | Asset owned outright |
| Balance Sheet Impact | May be off-balance-sheet (operating lease) | Asset and liability recorded |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility for upgrades | Less flexible, long-term commitment |
| Residual Value Risk | Risk borne by lessor | Borne by borrower |
Introduction to Lease vs Loan
Leasing a vehicle allows users to pay for the depreciation during a fixed term, often resulting in lower monthly payments compared to loans. Loans involve borrowing the full purchase price of the asset, with payments spread over time including interest, leading to eventual ownership. Payment plans typically divide the total cost into manageable installments without interest, commonly used for smaller purchases or services.
Understanding Leasing: Definition and Types
Leasing involves acquiring the use of an asset, such as a vehicle or equipment, for a specified period through regular payments without owning it, offering flexibility and lower upfront costs compared to loans. Common types include operating leases, which are short-term and off-balance-sheet, and finance leases, which are long-term and resemble asset purchases, each affecting your financial statements differently. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the best option based on your cash flow, asset management goals, and long-term financial strategy.
What is a Loan? Key Features and Options
A loan is a financial agreement where a borrower receives a lump sum of money upfront, which must be repaid with interest over a set period. Key features of loans include fixed or variable interest rates, defined repayment terms, and potential collateral requirements. Loan options vary widely, ranging from personal and auto loans to mortgages and business loans, each tailored to specific financial needs and credit profiles.
Key Differences Between Leasing and Loan
Leasing involves paying for the use of an asset over a set period without ownership, while loans provide funds to purchase the asset outright, resulting in full ownership after repayment. Lease agreements typically have lower monthly payments and restrictions on usage, whereas loans require higher monthly payments but allow unlimited usage and eventual asset possession. Understanding the cost structure, ownership rights, and flexibility is crucial when choosing between leasing and loan financing options.
Pros and Cons of Leasing
Leasing offers lower monthly payments and allows access to the latest models with minimal upfront costs, making it ideal for individuals who prefer driving new vehicles regularly and avoid long-term commitment. However, leasing typically includes mileage limits and potential fees for excess wear and tear, which can result in additional expenses if terms are exceeded. Unlike loans or payment plans that build equity and ownership, leasing does not contribute to vehicle ownership, limiting long-term asset value.
Pros and Cons of Loans
Loans offer the advantage of ownership after full repayment, allowing you to build equity in your asset and potentially improve your credit score with consistent payments. However, loans often involve higher monthly payments compared to leases and payment plans, along with the risk of interest accumulation and potential penalties for early repayment. Your financial situation and long-term goals determine whether the stability and eventual ownership of a loan outweigh these costs and obligations.
Financial Implications: Cost Comparison
Leases often have lower monthly payments than loans but may result in higher overall costs due to interest and fees without ownership equity. Loans typically require higher monthly payments but build ownership, which can lead to long-term financial benefits once fully paid. Payment plans spread the total cost without interest, offering predictable expenses but may require full ownership upfront or upon final payment.
Ownership, Equity, and Depreciation
Lease agreements allow you to use an asset without gaining ownership, meaning no equity is built and depreciation affects the lessor, not you. Loans provide full ownership from the start, letting you build equity as you repay the principal, with depreciation reducing the asset's value over time but benefiting your owned asset. Payment plans often resemble loan structures, granting ownership upon completion while spreading costs, enabling equity accumulation, and exposing you to depreciation risks.
When to Choose Leasing Over a Loan
Leasing is ideal for individuals or businesses seeking lower monthly payments and the flexibility to upgrade assets frequently without long-term commitment, especially for vehicles or equipment. When cash flow management and tax advantages from operational expense deductions are priorities, leasing often outperforms loans. Choose leasing over a loan when ownership is less important than usage, and minimizing upfront costs is crucial.
Conclusion: Making the Right Decision
Choosing between a lease, loan, or payment plan depends on your financial goals, budget flexibility, and long-term asset ownership preferences. Leasing offers lower monthly payments and less commitment, while loans provide full ownership and equity build-up over time. Payment plans can balance affordability with gradual ownership, making it essential to assess your cash flow and future plans to make the right decision.
Infographic: Lease vs Loan
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com