Late fees are charges applied when a payment is overdue, typically calculated as a flat rate or a percentage of the missed amount, while penalties are more severe financial consequences or legal actions triggered by non-compliance or repeated offenses. Understanding the differences between late fees and penalties can help you manage your financial obligations more effectively; learn more in this article.
Table of Comparison
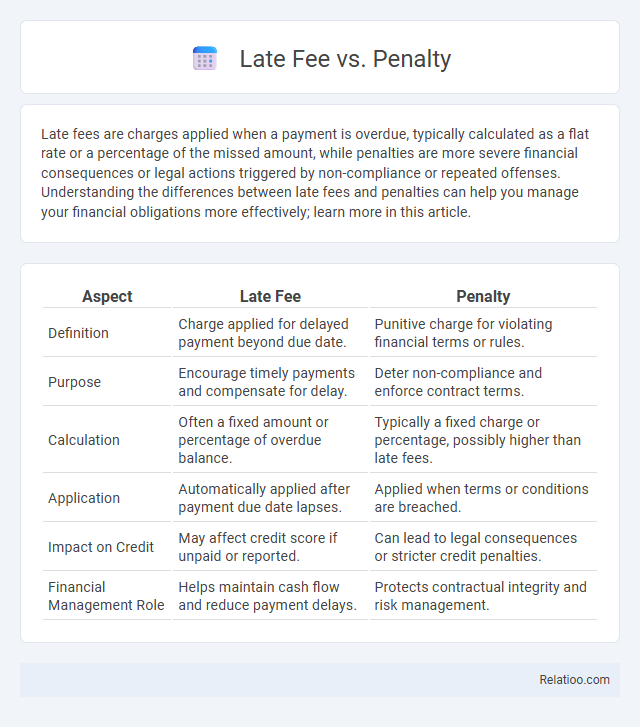
| Aspect | Late Fee | Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Charge applied for delayed payment beyond due date. | Punitive charge for violating financial terms or rules. |
| Purpose | Encourage timely payments and compensate for delay. | Deter non-compliance and enforce contract terms. |
| Calculation | Often a fixed amount or percentage of overdue balance. | Typically a fixed charge or percentage, possibly higher than late fees. |
| Application | Automatically applied after payment due date lapses. | Applied when terms or conditions are breached. |
| Impact on Credit | May affect credit score if unpaid or reported. | Can lead to legal consequences or stricter credit penalties. |
| Financial Management Role | Helps maintain cash flow and reduce payment delays. | Protects contractual integrity and risk management. |
Understanding Late Fees and Penalties
Late fees and penalties are charges imposed for missed payments but differ in purpose and calculation; late fees typically represent a fixed or percentage-based charge applied after a due date, while penalties may include additional consequences such as account suspension or legal action. Understanding the terms requires recognizing that late fees compensate for administrative costs incurred by the lender or service provider, whereas penalties serve as deterrents to encourage timely compliance. Businesses and consumers should review contract terms to identify the specific conditions that trigger late fees and penalties, as well as their respective amounts and enforcement policies.
Key Differences Between Late Fees and Penalties
Late fees are specific charges imposed for missed or delayed payments, usually calculated as a percentage of the outstanding amount or a fixed sum, designed to motivate timely payment without being punitive. Penalties generally carry a harsher connotation, often representing punitive measures for breaches of contract or violations beyond just late payments, potentially including legal consequences. Understanding the key differences, late fees serve primarily as financial incentives to encourage promptness, while penalties may entail broader disciplinary actions and higher costs to deter non-compliance.
Common Scenarios for Late Fees
Late fees commonly apply when rent or loan payments are not received by the due date, typically calculated as a fixed amount or a percentage of the overdue sum. Penalties, contrastingly, may include additional charges or restrictions imposed for contract violations beyond mere late payment. In rental agreements, late fees incentivize timely payments, often outlined as daily or monthly fees to compensate landlords for administrative costs and potential cash flow disruptions.
Situations Where Penalties Apply
Penalties typically apply in situations where late fees alone are insufficient to enforce compliance, such as repeated payment defaults or contractual breaches involving significant financial harm. Unlike standard late fees, which are fixed charges for overdue payments, penalties often escalate based on the severity or frequency of non-compliance, serving as a stronger deterrent. Examples include regulatory fines for missed tax deadlines, service contract violations triggering penalties beyond mere late fees, and loan agreements imposing penalties after grace periods expire.
Legal Definitions: Late Fee vs Penalty
Late fees are predetermined charges imposed for overdue payments, typically defined in contracts to compensate for administrative costs without being punitive. Penalties, in contrast, serve as punitive sanctions designed to discourage breaches of contract or non-compliance, often exceeding actual damages. Legal jurisdictions differentiate these terms to prevent penalties from being unenforceable due to their punitive nature, favoring late fees that align with reasonable cost recovery principles.
Financial Impact on Consumers
Late fees directly increase the cost to consumers by charging a fixed amount or percentage for missed payments, impacting cash flow and credit scores if recurring. Penalties can include interest rate hikes or service restrictions, further elevating financial burdens and increasing debt costs over time. Understanding the differences helps consumers manage obligations effectively and avoid excessive financial strain caused by compounded charges.
How Businesses Calculate Late Fees and Penalties
Businesses calculate late fees and penalties based on the terms outlined in contracts or invoices, often using a fixed amount or a percentage of the outstanding balance due. Late fees typically accrue daily or monthly after a specified grace period, while penalties may be assessed as one-time charges for non-compliance or missed deadlines. Understanding your payment schedule and contract terms helps you avoid unexpected charges and manage your finances effectively.
Ways to Avoid Late Fees and Penalties
Understanding the differences between late fees, penalties, and interest charges is crucial for managing your finances effectively. You can avoid late fees and penalties by setting up automatic payments, maintaining a budget to ensure timely bill payments, and regularly monitoring due dates through alerts or reminders. Consistently paying on time helps protect your credit score and saves you money by preventing unnecessary charges.
Late Fee and Penalty Policies in Different Sectors
Late fee and penalty policies vary significantly across sectors, with financial institutions typically imposing late fees as a fixed percentage or flat rate for missed payments, while penalties often include additional consequences like interest charges or service restrictions. In telecommunications and utilities, late fees are commonly implemented as a recurring charge for overdue bills, whereas penalties may result in service suspension or termination. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for consumers and businesses to manage compliance and avoid escalating costs effectively.
Best Practices for Managing Late Payments and Penalties
Implement clear payment terms and communicate them upfront to reduce late fees and penalties, ensuring customers understand due dates and consequences. Implement automated reminders and flexible payment options to encourage timely payments and minimize financial penalties. Consistently apply late fees and penalties in accordance with contract terms to maintain fairness and improve cash flow management.
Infographic: Late Fee vs Penalty
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com