Health proxies grant designated individuals authority to make medical decisions on behalf of patients, while guardianship involves court-appointed individuals managing broader personal and financial affairs. Discover the key differences and legal implications of Health Proxy vs Guardianship in this article.
Table of Comparison
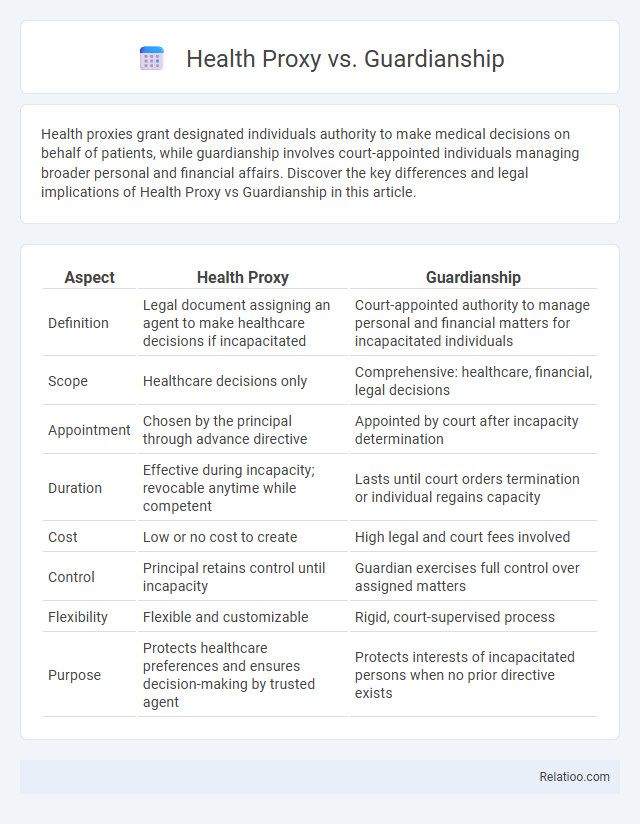
| Aspect | Health Proxy | Guardianship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal document assigning an agent to make healthcare decisions if incapacitated | Court-appointed authority to manage personal and financial matters for incapacitated individuals |
| Scope | Healthcare decisions only | Comprehensive: healthcare, financial, legal decisions |
| Appointment | Chosen by the principal through advance directive | Appointed by court after incapacity determination |
| Duration | Effective during incapacity; revocable anytime while competent | Lasts until court orders termination or individual regains capacity |
| Cost | Low or no cost to create | High legal and court fees involved |
| Control | Principal retains control until incapacity | Guardian exercises full control over assigned matters |
| Flexibility | Flexible and customizable | Rigid, court-supervised process |
| Purpose | Protects healthcare preferences and ensures decision-making by trusted agent | Protects interests of incapacitated persons when no prior directive exists |
Introduction to Health Proxy and Guardianship
A health proxy is a legal document that designates someone to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, ensuring your healthcare preferences are respected. Guardianship involves a court-appointed individual who gains authority over personal and medical decisions when you are deemed unable to manage your affairs. Understanding the difference between health proxy and guardianship empowers you to make informed choices about who controls your healthcare decisions.
Defining Health Proxy: Roles and Responsibilities
A Health Proxy is a legal document that designates an individual to make medical decisions on Your behalf if you become incapacitated. This appointed agent holds the responsibility to communicate with healthcare providers, approve or refuse treatments, and ensure that Your medical preferences are honored. It differs from guardianship, which often involves court-appointed authority over broader personal and financial matters, while a Health Proxy specifically focuses on healthcare decisions.
Understanding Guardianship in Healthcare Decisions
Understanding guardianship in healthcare decisions involves recognizing it as a legal arrangement where a court appoints an individual to make medical choices for someone who is incapacitated. Unlike a health proxy, which you designate voluntarily through an advance directive, guardianship requires formal legal proceedings and may limit your autonomy. This distinction is crucial when planning your healthcare decisions to ensure your preferences are respected if you become unable to communicate.
Key Differences Between Health Proxy and Guardianship
Health proxy grants You the authority to make medical decisions on behalf of another individual if they become incapacitated, specifically focusing on healthcare choices. Guardianship, however, is a broader legal arrangement where a court appoints a guardian to manage not only medical decisions but also personal, financial, and legal matters for an incapacitated person. Key differences between health proxy and guardianship include the scope of authority, the process of appointment--with health proxy established through a legal document and guardianship requiring court involvement--and the level of oversight, as guardianship often involves ongoing court supervision.
When is a Health Proxy Needed?
A health proxy is needed when you want to designate someone to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated and unable to communicate your wishes. Unlike guardianship, which is court-appointed and often involves a broader scope of responsibility, a health proxy is a voluntary, legal document specifying your chosen healthcare agent. Understanding the differences helps ensure your healthcare preferences are honored, protecting Your medical autonomy during critical situations.
Circumstances Requiring Guardianship
Circumstances requiring guardianship typically arise when an individual is incapacitated and unable to make personal or financial decisions, often due to severe cognitive impairments, mental illness, or developmental disabilities. A health proxy allows you to designate someone to make healthcare decisions on your behalf if you become temporarily or permanently incapacitated, whereas guardianship involves a court-appointed guardian with broad authority over personal, medical, and financial matters. Understanding the distinctions between health proxy and guardianship is crucial when planning for your care in situations of diminished capacity.
Legal Processes for Appointing a Health Proxy
The legal process for appointing a health proxy typically involves completing a formal document known as a healthcare power of attorney, which must be signed, witnessed, and sometimes notarized according to state laws. Guardianship requires a court proceeding where a judge evaluates your capacity and appoints a guardian if you are deemed unable to make healthcare decisions. You should understand that a health proxy allows you to designate someone to make medical decisions on your behalf without court intervention, streamlining the process compared to guardianship.
Establishing Guardianship: Legal Steps Involved
Establishing guardianship involves a formal legal process requiring the filing of a petition with the court, followed by a hearing where evidence of incapacity is presented. Unlike a health proxy, which grants a designated person authority to make medical decisions through a power of attorney, guardianship appoints a guardian authorized by the court to manage healthcare and personal affairs for an incapacitated individual. The court's decision prioritizes the best interest and welfare of the ward, often involving ongoing oversight and periodic reviews to ensure compliance with guardianship obligations.
Pros and Cons: Health Proxy vs. Guardianship
Health proxy grants you the power to appoint someone to make healthcare decisions on your behalf, ensuring your preferences are respected without court involvement, which offers flexibility but depends heavily on trust and clarity in the proxy document. Guardianship involves a court-appointed guardian managing your health and personal decisions, providing legal oversight that can protect you if you are incapacitated, though it may limit your autonomy and result in costly, time-consuming legal processes. Your choice between health proxy and guardianship should consider the balance between maintaining your control and the need for legal protection.
Choosing the Right Option for Healthcare Decision-Making
Choosing the right option for healthcare decision-making depends on individual needs and legal considerations: a health proxy grants a designated person authority to make medical decisions when one is incapacitated, offering flexibility and specificity. Guardianship involves a court-appointed individual who has broader decision-making powers beyond healthcare and often requires a formal legal process, making it suitable for those unable to manage their overall personal affairs. Health proxies are generally preferred for their simplicity and control over healthcare choices, while guardianship suits complex cases needing comprehensive oversight.
Infographic: Health Proxy vs Guardianship
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com