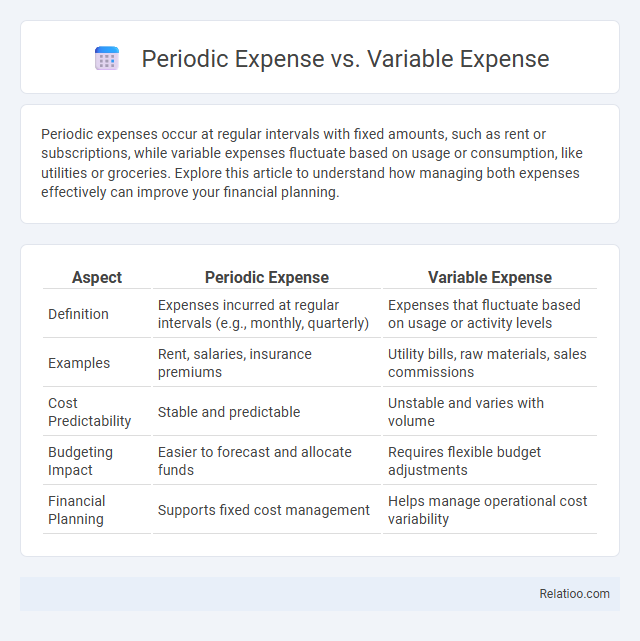
Periodic expenses occur at regular intervals with fixed amounts, such as rent or subscriptions, while variable expenses fluctuate based on usage or consumption, like utilities or groceries. Explore this article to understand how managing both expenses effectively can improve your financial planning.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Periodic Expense | Variable Expense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expenses incurred at regular intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly) | Expenses that fluctuate based on usage or activity levels |
| Examples | Rent, salaries, insurance premiums | Utility bills, raw materials, sales commissions |
| Cost Predictability | Stable and predictable | Unstable and varies with volume |
| Budgeting Impact | Easier to forecast and allocate funds | Requires flexible budget adjustments |
| Financial Planning | Supports fixed cost management | Helps manage operational cost variability |
Understanding Periodic Expenses
Periodic expenses occur at irregular intervals and often arise from planned or seasonal costs, such as insurance premiums or property taxes. Variable expenses fluctuate directly with usage or activity levels, including utilities and raw materials, making them more unpredictable compared to fixed or periodic costs. Understanding periodic expenses is crucial for accurate budgeting and cash flow management, as they require setting aside funds in advance for future payments that do not occur monthly.
Defining Variable Expenses
Variable expenses fluctuate directly with business activity levels, such as raw materials and sales commissions, rising when production or sales increase and falling when they decrease. Periodic expenses occur at regular intervals but are not tied to production volume, examples include insurance premiums and equipment maintenance. Fixed expenses remain constant regardless of business activity, covering costs like rent and salaried employee wages.
Key Differences Between Periodic and Variable Expenses
Periodic expenses, such as insurance premiums and property taxes, occur at regular intervals and typically involve fixed amounts, making budget planning more predictable. Variable expenses, including utilities and groceries, fluctuate monthly based on consumption or usage, requiring more flexible budgeting strategies. Key differences lie in timing and predictability; periodic expenses happen less frequently with set costs, while variable expenses vary continuously and impact cash flow dynamically.
Common Examples of Periodic Expenses
Common examples of periodic expenses include annual insurance premiums, semi-annual property taxes, and quarterly utility bills, which occur at irregular intervals but are predictable in amount. Variable expenses, such as groceries and fuel, fluctuate monthly based on consumption levels, unlike fixed expenses like rent that remain constant. Understanding these differences helps in effective budgeting and cash flow management.
Common Examples of Variable Expenses
Common examples of variable expenses include utility bills, groceries, fuel costs, and entertainment expenses, which fluctuate based on usage or consumption. Periodic expenses typically occur less frequently and include insurance premiums and property taxes, while fixed expenses remain constant, such as rent or mortgage payments. Understanding these distinctions helps in budgeting by allowing for accurate predictions of monthly financial obligations.
Impact on Budget Planning
Periodic expenses, occurring at irregular intervals like annual insurance premiums, require advance budgeting to avoid cash flow disruptions. Variable expenses fluctuate monthly, such as utility bills and groceries, demanding flexible budget adjustments to maintain financial balance. Fixed expenses, including rent and subscriptions, provide predictability, enabling consistent allocation in budget planning for better expense management.
Tracking and Managing Periodic vs. Variable Expenses
Tracking Your periodic expenses, such as insurance premiums and subscription fees, involves scheduling payments that occur at regular intervals, helping you plan cash flow accurately. Variable expenses, like utility bills and groceries, fluctuate monthly and require close monitoring through budgeting tools to avoid overspending. Managing both types effectively ensures financial stability by aligning fixed commitments with adaptable spending habits.
Strategies to Control Variable Expenses
Variable expenses fluctuate based on your consumption or business activity, requiring careful monitoring to maintain financial stability. Strategies to control variable expenses include setting strict budgets, regularly analyzing spending patterns, and negotiating better rates with suppliers to minimize costs without compromising quality. Implementing these measures helps you manage cash flow effectively and reduce the impact of unpredictable costs.
Tips to Prepare for Periodic Expenses
Periodic expenses occur infrequently but require advance planning due to their irregular timing, such as insurance premiums or annual subscriptions. To prepare for periodic expenses, create a dedicated savings fund by estimating the total annual cost and setting aside monthly amounts to avoid financial strain. Tracking these expenses alongside variable costs like utilities ensures a balanced budget and prevents unexpected financial shortfalls.
Importance of Differentiating Expenses in Personal Finance
Understanding the differences between periodic, fixed, and variable expenses is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. Fixed expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, remain constant, while variable expenses, like groceries and utilities, fluctuate monthly, and periodic expenses, including annual insurance premiums or car maintenance, occur irregularly but significantly impact cash flow. By accurately categorizing your expenses, you can create a more reliable budget, anticipate financial needs, and improve your ability to manage cash flow, ensuring better control over your financial health.
Infographic: Periodic Expense vs Variable Expense
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com