A Health Proxy designates a trusted person to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, whereas an Advance Directive outlines your specific healthcare preferences in writing. Learn more about how these documents protect your medical wishes in this article.
Table of Comparison
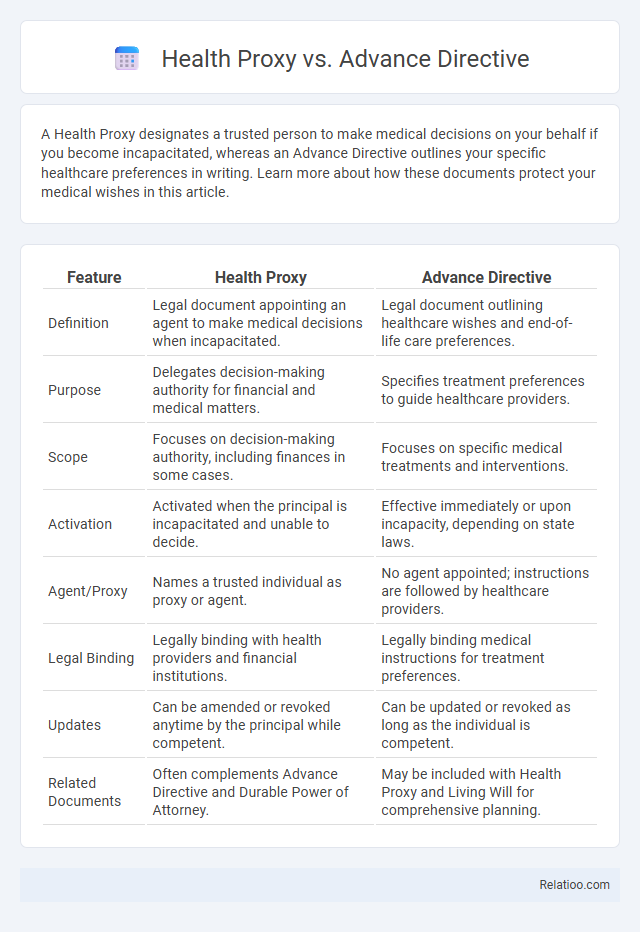
| Feature | Health Proxy | Advance Directive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal document appointing an agent to make medical decisions when incapacitated. | Legal document outlining healthcare wishes and end-of-life care preferences. |
| Purpose | Delegates decision-making authority for financial and medical matters. | Specifies treatment preferences to guide healthcare providers. |
| Scope | Focuses on decision-making authority, including finances in some cases. | Focuses on specific medical treatments and interventions. |
| Activation | Activated when the principal is incapacitated and unable to decide. | Effective immediately or upon incapacity, depending on state laws. |
| Agent/Proxy | Names a trusted individual as proxy or agent. | No agent appointed; instructions are followed by healthcare providers. |
| Legal Binding | Legally binding with health providers and financial institutions. | Legally binding medical instructions for treatment preferences. |
| Updates | Can be amended or revoked anytime by the principal while competent. | Can be updated or revoked as long as the individual is competent. |
| Related Documents | Often complements Advance Directive and Durable Power of Attorney. | May be included with Health Proxy and Living Will for comprehensive planning. |
Understanding Health Proxy: Definition and Purpose
A Health Proxy is a legal document that designates a trusted individual to make medical decisions on Your behalf if You become incapacitated. Unlike an Advance Directive, which includes instructions about Your healthcare preferences, a Health Proxy focuses specifically on appointing a decision-maker. Understanding the purpose of a Health Proxy helps ensure Your medical choices are respected when You cannot communicate them yourself.
What Is an Advance Directive?
An advance directive is a legal document that specifies a person's preferences for medical treatment and care if they become unable to make decisions themselves. It typically includes a living will, outlining desired treatments, and may appoint a health proxy or durable power of attorney for healthcare to make decisions on the individual's behalf. Unlike a health proxy, which solely designates a decision-maker, an advance directive provides comprehensive guidance on treatment preferences.
Key Differences Between Health Proxy and Advance Directive
A Health Proxy is a legal document designating an individual to make healthcare decisions on behalf of a patient if they become incapacitated, whereas an Advance Directive encompasses a broader range of instructions, including living wills that specify desired medical treatments. The key difference lies in the Health Proxy's focus on appointing a decision-maker, while the Advance Directive provides explicit treatment preferences and end-of-life care instructions. Together, these documents ensure comprehensive healthcare planning by combining appointed decision authority with clear patient wishes.
Legal Requirements for Health Proxies
Legal requirements for health proxies vary by jurisdiction but generally require a written document designating a trusted individual to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated. An advance directive often includes a health proxy designation and outlines your healthcare preferences in detail, serving as both a living will and a power of attorney for healthcare. Understanding the distinctions ensures your legal documents comply with state laws, safeguarding your right to personalized medical decision-making.
Legal Requirements for Advance Directives
Advance Directives require specific legal formalities, including written documentation, signatures, and often notarization or witness verification, varying by state law to ensure validity. Health Proxies, a key component within Advance Directives, enable Your appointed agent to make medical decisions when You are incapacitated, adhering to state-specific authorization protocols. Understanding the precise legal requirements in Your jurisdiction is essential to create an enforceable Advance Directive that accurately reflects Your healthcare preferences and grants appropriate decision-making authority.
Situations When a Health Proxy Is Needed
A health proxy is essential when an individual becomes incapacitated and cannot communicate medical decisions, ensuring a trusted agent makes healthcare choices on their behalf. Unlike an advance directive, which outlines specific treatment preferences, a health proxy appoints a representative to interpret and implement those preferences in real-time. Situations requiring a health proxy often involve sudden illness, surgery complications, or cognitive decline, where immediate decision-making authority is critical to effective medical care.
When to Use an Advance Directive
An advance directive is essential when you want to outline your healthcare preferences in case you become incapacitated, ensuring your wishes are respected without delay. Unlike a health proxy, which appoints someone to make decisions on your behalf, the advance directive provides clear written instructions for your medical treatment. Use an advance directive before serious illness or surgery to guide your healthcare team and protect your autonomy.
Benefits of Having Both Documents
Having both a Health Proxy and an Advance Directive ensures comprehensive medical decision-making support, allowing appointed agents to make real-time health choices while clearly outlining personal treatment preferences. This dual documentation reduces ambiguity, prevents family conflicts, and guarantees adherence to the patient's wishes during incapacitation. Combining these legal tools enhances patient autonomy and provides healthcare professionals with clear guidance to deliver appropriate care.
How to Create a Health Proxy and Advance Directive
Creating a Health Proxy involves selecting a trusted individual to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, often documented through a legal form called a Medical Power of Attorney. An Advance Directive outlines your specific healthcare preferences and instructions for end-of-life care, ensuring your wishes are respected when you cannot communicate them yourself. Your healthcare provider or an attorney can help you complete these documents accurately, and it's essential to review and update them periodically to reflect any changes in your health or preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions About Health Proxy vs Advance Directive
Health proxies and advance directives both serve to protect your medical decisions when you cannot communicate them yourself. A health proxy specifically designates an individual to make healthcare decisions on your behalf, while an advance directive provides detailed instructions about your medical preferences. Understanding these differences helps ensure your wishes are respected during critical health situations.
Infographic: Health Proxy vs Advance Directive
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com