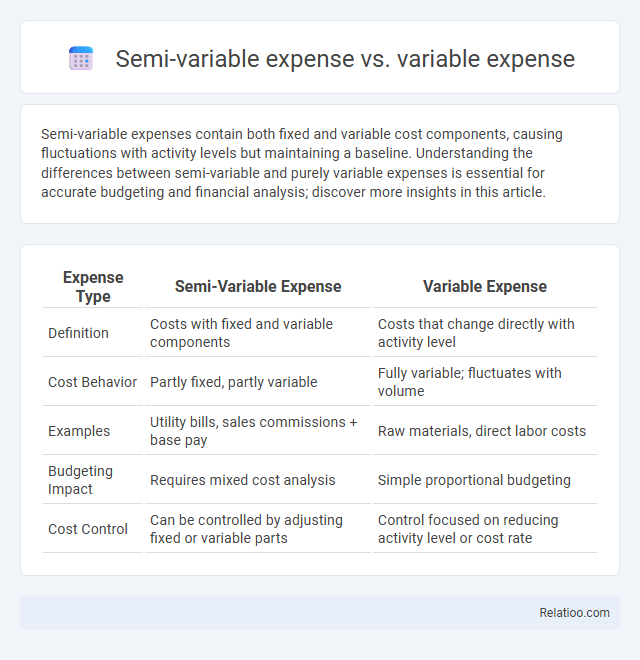
Semi-variable expenses contain both fixed and variable cost components, causing fluctuations with activity levels but maintaining a baseline. Understanding the differences between semi-variable and purely variable expenses is essential for accurate budgeting and financial analysis; discover more insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Expense Type | Semi-Variable Expense | Variable Expense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs with fixed and variable components | Costs that change directly with activity level |
| Cost Behavior | Partly fixed, partly variable | Fully variable; fluctuates with volume |
| Examples | Utility bills, sales commissions + base pay | Raw materials, direct labor costs |
| Budgeting Impact | Requires mixed cost analysis | Simple proportional budgeting |
| Cost Control | Can be controlled by adjusting fixed or variable parts | Control focused on reducing activity level or cost rate |
Understanding Semi-Variable and Variable Expenses
Semi-variable expenses combine fixed and variable cost elements, meaning a portion remains constant regardless of activity levels, while the variable portion fluctuates with production or sales volume. Variable expenses change directly in proportion to business activity, such as raw materials, making them unpredictable but controllable. Understanding the distinction helps you manage budgets more effectively by identifying which costs will vary and which remain stable under different operational scenarios.
Key Differences Between Semi-Variable and Variable Expenses
Semi-variable expenses contain both fixed and variable cost components, meaning they fluctuate with activity level but never drop to zero, unlike pure variable expenses, which vary directly and proportionally with production or sales volume. Semi-variable expenses include costs like utility bills or salaried plus commission wages, whereas variable expenses strictly encompass costs such as raw materials and direct labor. Understanding these differences is essential for accurate budgeting, cost control, and financial forecasting in business operations.
Common Examples of Semi-Variable Expenses
Semi-variable expenses blend fixed and variable costs, fluctuating with production or usage while maintaining a baseline expense; common examples include utility bills, where a fixed monthly charge exists alongside variable consumption costs, and salaried workers who receive a fixed wage plus overtime pay. Variable expenses change directly with production volume or activity, such as raw materials or direct labor costs, while fixed expenses remain constant regardless of business activity. Your understanding of these distinctions helps optimize budgeting and financial forecasting.
Typical Examples of Variable Expenses
Typical examples of variable expenses include raw materials, direct labor costs, sales commissions, and utility costs that fluctuate with production levels. Semi-variable expenses combine fixed and variable components, such as a telephone bill with a fixed subscription plus variable call charges. Unlike semi-variable and fixed expenses, purely variable expenses change proportionally with business activity or sales volume.
How Semi-Variable and Variable Expenses Affect Budgeting
Semi-variable expenses combine fixed and variable cost components, causing budgeting challenges due to their partial unpredictability, while variable expenses fluctuate directly with production levels or sales volume, requiring constant monitoring and adjustment. Accurate forecasting of semi-variable costs demands separating fixed baseline costs from variable increments, enhancing budget precision. Variable expenses impact cash flow management by varying with operational activities, necessitating flexible budget strategies to maintain financial stability.
Calculating Semi-Variable vs Variable Costs
Calculating semi-variable costs requires separating fixed components, which remain constant regardless of production volume, from variable components that fluctuate with activity levels, typically using the high-low method or regression analysis. Variable expenses change directly in proportion to production output, making their calculation straightforward by multiplying the variable cost rate per unit by the number of units produced. Accurate differentiation between semi-variable and variable expenses enables precise budgeting, cost control, and financial forecasting in operational management.
Impact on Business Profitability and Financial Planning
Semi-variable expenses combine fixed and variable cost elements, impacting profitability by providing flexibility in cost management during fluctuating production levels. Variable expenses directly vary with production output, influencing profit margins more immediately and requiring precise forecasting to avoid overspending or underutilization. Understanding the distinctions aids financial planning by enabling businesses to predict cash flow needs accurately and adjust operational strategies for optimal profitability.
Managing and Controlling Semi-Variable and Variable Expenses
Managing semi-variable and variable expenses requires understanding their cost behavior patterns to implement effective control strategies. Semi-variable expenses, which combine fixed and variable components, can be controlled by monitoring the fixed base cost while optimizing the variable portion based on activity levels. Your focus should be on adjusting variable expenses directly linked to production or sales volume and maintaining operational efficiency to reduce unnecessary costs.
Pros and Cons of Each Expense Type
Semi-variable expenses combine fixed and variable cost elements, offering flexibility in budgeting but complicating accurate expense forecasting due to their mixed nature. Variable expenses fluctuate directly with production levels, providing precise cost control, though they can lead to unpredictable cash flow during demand swings. Fixed expenses remain constant regardless of activity, facilitating stable financial planning, but lack adaptability, which may result in inefficiencies during periods of low production.
Best Practices for Tracking and Analyzing Costs
Effective tracking of semi-variable, variable, and fixed expenses requires detailed categorization to distinguish fixed costs from variable components that fluctuate with production or usage. Implement best-in-class expense management software that enables dynamic real-time cost monitoring, integrates predictive analytics, and provides granular reporting for each expense type. Regular variance analysis and cost behavior evaluation support informed budgeting, improve cost control, and optimize financial decision-making.
Infographic: Semi-Variable Expense vs Variable Expense
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com