A penalty is a punishment imposed for violating contract terms, often involving a monetary charge to discourage breaches. A fee is a fixed payment for services rendered or permissions granted; to understand the nuanced differences between penalties and fees, explore more in this article.
Table of Comparison
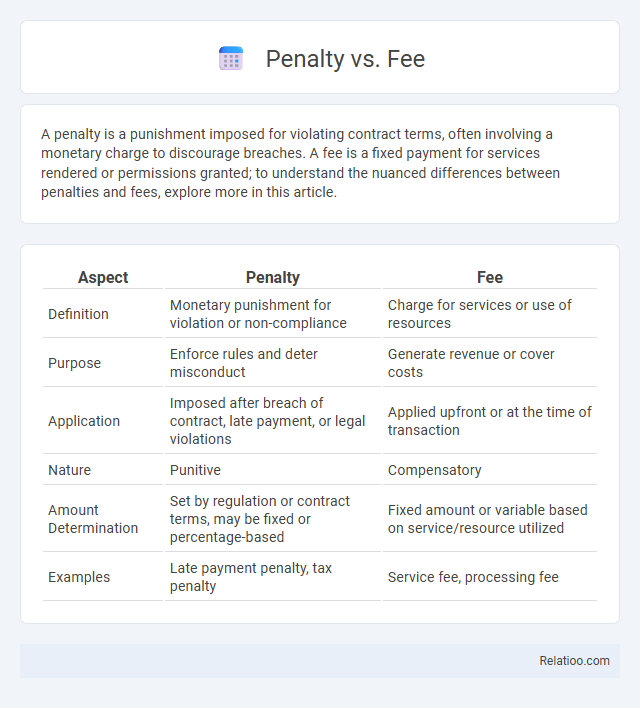
| Aspect | Penalty | Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary punishment for violation or non-compliance | Charge for services or use of resources |
| Purpose | Enforce rules and deter misconduct | Generate revenue or cover costs |
| Application | Imposed after breach of contract, late payment, or legal violations | Applied upfront or at the time of transaction |
| Nature | Punitive | Compensatory |
| Amount Determination | Set by regulation or contract terms, may be fixed or percentage-based | Fixed amount or variable based on service/resource utilized |
| Examples | Late payment penalty, tax penalty | Service fee, processing fee |
Understanding the Difference: Penalty vs Fee
A penalty is a punitive charge imposed as a consequence of violating rules or missing deadlines, aimed at discouraging undesirable behavior. A fee is a fixed or variable cost paid for services or administrative purposes, not designed to punish but to cover expenses. Understanding the difference between penalty and fee helps clarify obligations, with penalties enforcing compliance and fees representing routine charges.
Definitions: What is a Penalty? What is a Fee?
A penalty is a punitive charge imposed as a consequence of violating a rule, law, or agreement, often designed to discourage undesirable behavior. A fee is a fixed charge paid for a specific service or privilege, representing a cost rather than a punishment. Understanding the distinction between penalties and fees helps you accurately assess financial obligations and avoid unintended consequences.
Legal Implications of Penalties and Fees
Penalties and fees serve distinct legal purposes, with penalties typically imposed as punitive measures for violations or non-compliance, while fees are charges for services or administrative costs. Legal implications of penalties often involve strict regulatory frameworks, potential litigation, and enforcement actions, emphasizing deterrence and accountability. Fees, conversely, generally carry fewer legal risks but must comply with statutory limits and transparency requirements to avoid disputes and ensure lawful collection.
Common Examples of Penalties and Fees
Common examples of penalties include late payment charges on credit cards, tax penalties for underreporting income, and fines for traffic violations. Fees often involve service charges such as ATM withdrawal fees, membership fees, or application fees for loans. Understanding these differences helps you manage your finances more effectively and avoid unnecessary costs.
Financial Impact: Penalties vs Fees
Fees generally represent fixed charges for services or administrative costs, imposing predictable financial obligations on individuals or businesses. Penalties, by contrast, result from violations or non-compliance, often carrying variable amounts designed to deter undesirable behavior, thus potentially causing significantly higher financial impact. The financial consequences of penalties typically exceed fees, as they include punitive measures influencing cash flow and overall economic stability.
When Are Penalties Imposed vs Fees Charged?
Penalties are imposed as a consequence of violating laws, regulations, or contractual terms, often involving financial punishments for actions like late tax payments or breaches of contract. Fees are charged as predetermined amounts for services rendered or administrative processes, such as application processing or membership dues, regardless of compliance or violations. Understanding the context when penalties target wrongdoing and fees cover operational costs helps differentiate their roles in financial assessments.
Regulatory Guidelines for Penalties and Fees
Regulatory guidelines differentiate penalties and fees by their purpose and enforcement mechanisms, with penalties aimed at punitive measures for non-compliance and fees structured as charges for services or administrative processing. Penalties typically involve fixed or escalating fines imposed for violations of laws or regulations, adhering to statutory limits and procedural fairness standards outlined in regulatory frameworks. Fees are governed by cost-recovery principles, ensuring they reflect the fair value of services provided without serving as punitive tools, as mandated by agencies such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Consumer Rights Regarding Penalties and Fees
Consumers are entitled to clear disclosures of penalties and fees associated with contracts, ensuring transparency and fairness in financial transactions. Penalties often refer to charges for breaching terms, while fees are standard costs for services rendered; understanding these distinctions protects consumers from unfair or hidden costs. Regulatory bodies enforce consumer rights by mandating that penalties and fees be reasonable, disclosed upfront, and not oppressive, safeguarding consumers from exploitative practices.
How to Avoid Penalties and Minimize Fees
To avoid penalties and minimize fees, it is essential to understand the specific terms and conditions of contracts, tax regulations, or service agreements that govern charges. Timely payments, accurate filings, and adherence to deadlines significantly reduce the risk of incurring penalties, which are often harsher than standard fees. Utilizing financial tools, reminders, and professional advice helps in managing obligations proactively, ensuring compliance while minimizing unnecessary expenses.
Penalty vs Fee: Which Is More Detrimental?
A penalty typically involves a punishment for violating a rule or contract, often resulting in financial loss or legal consequences, whereas a fee is a charge for a service or privilege. Penalties tend to be more detrimental because they not only impose a financial cost but can also damage reputations, incur legal action, and affect credit scores. In contrast, fees are predictable expenses, primarily impacting budgets without additional negative consequences.
Infographic: Penalty vs Fee
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com