Health Proxy grants a designated person the authority to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, while Power of Attorney covers broader financial and legal decision-making powers. Discover the key differences and choose the right option for your needs in this article.
Table of Comparison
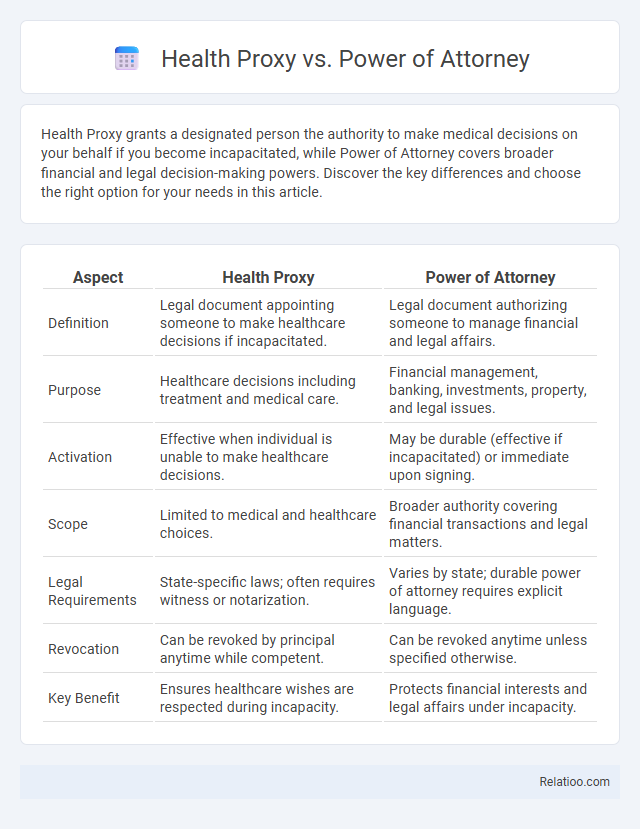
| Aspect | Health Proxy | Power of Attorney |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal document appointing someone to make healthcare decisions if incapacitated. | Legal document authorizing someone to manage financial and legal affairs. |
| Purpose | Healthcare decisions including treatment and medical care. | Financial management, banking, investments, property, and legal issues. |
| Activation | Effective when individual is unable to make healthcare decisions. | May be durable (effective if incapacitated) or immediate upon signing. |
| Scope | Limited to medical and healthcare choices. | Broader authority covering financial transactions and legal matters. |
| Legal Requirements | State-specific laws; often requires witness or notarization. | Varies by state; durable power of attorney requires explicit language. |
| Revocation | Can be revoked by principal anytime while competent. | Can be revoked anytime unless specified otherwise. |
| Key Benefit | Ensures healthcare wishes are respected during incapacity. | Protects financial interests and legal affairs under incapacity. |
Understanding Health Proxy and Power of Attorney
Understanding a Health Proxy involves designating a trusted individual to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, ensuring your healthcare preferences are respected. A Power of Attorney (POA) grants a person authority to handle financial or legal matters, with some versions specifically focused on health-related decisions, often called a Medical Power of Attorney. Distinguishing between a Health Proxy and a Power of Attorney is crucial, as the former is strictly for healthcare directives, while the latter encompasses broader decision-making powers beyond medical care.
Definition of Health Proxy
A Health Proxy is a legal document that designates an individual to make healthcare decisions on behalf of another person if they become incapacitated. Unlike a Power of Attorney, which may cover financial and legal affairs, a Health Proxy specifically addresses medical treatment and healthcare preferences. This designation ensures that the appointed agent has authority to communicate with healthcare providers and make critical decisions aligned with the patient's wishes.
Definition of Power of Attorney
Power of Attorney is a legal document that grants an individual the authority to make financial, legal, or medical decisions on behalf of another person, known as the principal, in cases where they become incapacitated. A Health Proxy specifically authorizes someone to make healthcare decisions, while a broader Power of Attorney can cover a range of personal, financial, and legal matters. Understanding these distinctions helps ensure your wishes are clearly communicated and legally enforced.
Key Differences Between Health Proxy and Power of Attorney
A Health Proxy specifically grants someone the authority to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, whereas a Power of Attorney can cover a broader range of financial and legal decisions beyond healthcare. Your Health Proxy only becomes active when you are unable to communicate your healthcare wishes, while a Power of Attorney can be effective immediately or upon a specified event. Understanding these distinctions ensures you appoint the right person to manage either your medical care or personal affairs according to your needs.
Roles and Responsibilities: Health Proxy vs Power of Attorney
A Health Proxy specifically authorizes an individual to make medical decisions on your behalf if you become incapacitated, ensuring your healthcare preferences are honored. In contrast, a Power of Attorney grants broader authority, allowing your agent to manage financial, legal, and personal matters beyond healthcare decisions. Understanding these distinct roles helps you assign the right responsibilities and protect your interests effectively.
When to Use a Health Proxy
A Health Proxy is used specifically to appoint someone to make medical decisions on your behalf when you are incapacitated, ensuring your healthcare preferences are respected. Unlike a general Power of Attorney, which covers financial and legal matters broadly, a Health Proxy is solely focused on healthcare decisions. Use a Health Proxy when you want a trusted person to manage medical treatments, consent to procedures, or review your health records if you cannot communicate your wishes yourself.
When to Use a Power of Attorney
A Power of Attorney (POA) is used when an individual needs to designate someone to handle financial and legal matters on their behalf, especially during incapacity or absence. Unlike a Health Proxy, which grants authority strictly over healthcare decisions, a POA covers broader powers including property management and banking transactions. Utilize a POA when comprehensive decision-making authority is necessary beyond medical care to ensure seamless management of personal affairs.
Legal Requirements and Documentation
Health Proxy and Power of Attorney serve different legal purposes; a Health Proxy specifically authorizes someone to make medical decisions when you are incapacitated, requiring a signed and notarized health care directive form in most states. Power of Attorney typically grants broad authority over financial or legal matters, necessitating a legally executed document that complies with state-specific statutes. Understanding your jurisdiction's legal requirements for each document ensures your health and financial interests are protected appropriately.
Choosing the Right Representative
Choosing the right representative involves understanding the distinct roles of a Health Proxy and a Power of Attorney. A Health Proxy specifically grants authority to make medical decisions when the individual is incapacitated, ensuring healthcare preferences are honored. In contrast, a Power of Attorney can encompass broader legal and financial decision-making powers, so selecting an agent aligned with the specific responsibilities required is crucial for effective representation.
Importance of Advance Directives in Healthcare Decisions
Advance directives, including Health Proxy and Power of Attorney, are critical legal tools that empower individuals to specify their healthcare preferences and designate trusted agents to make medical decisions if they become incapacitated. A Health Proxy specifically authorizes a person to make health-related decisions, while a Power of Attorney can cover a broader scope, including financial matters. Establishing these directives ensures patients' wishes are respected, reduces family conflict, and guides healthcare providers in delivering care aligned with the patient's values and intentions.
Infographic: Health Proxy vs Power of Attorney
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com