Fixed expenses remain constant each month regardless of activity, while variable expenses fluctuate based on usage or consumption. Explore this article to understand how managing the balance between fixed and variable expenses impacts financial stability.
Table of Comparison
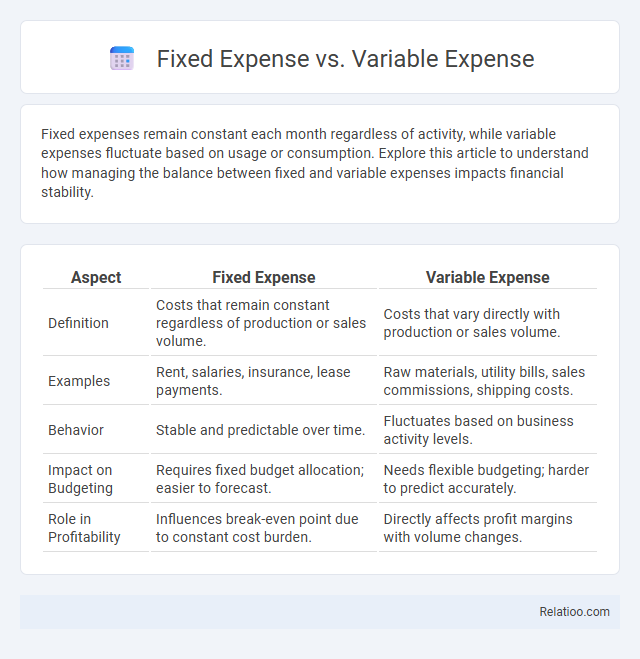
| Aspect | Fixed Expense | Variable Expense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs that remain constant regardless of production or sales volume. | Costs that vary directly with production or sales volume. |
| Examples | Rent, salaries, insurance, lease payments. | Raw materials, utility bills, sales commissions, shipping costs. |
| Behavior | Stable and predictable over time. | Fluctuates based on business activity levels. |
| Impact on Budgeting | Requires fixed budget allocation; easier to forecast. | Needs flexible budgeting; harder to predict accurately. |
| Role in Profitability | Influences break-even point due to constant cost burden. | Directly affects profit margins with volume changes. |
Introduction to Fixed and Variable Expenses
Fixed expenses represent consistent costs such as rent, mortgage payments, and insurance premiums that remain unchanged over a specific period. Variable expenses fluctuate based on consumption or usage, including utilities, groceries, and entertainment costs, which vary monthly. Understanding the distinction between fixed and variable expenses is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning.
Defining Fixed Expenses
Fixed expenses are regular, predictable costs that remain constant regardless of business activity or personal usage, such as rent, mortgage payments, and insurance premiums. These costs are critical for budgeting because they provide a stable financial foundation, unlike variable expenses like utilities or groceries that fluctuate monthly. Understanding your fixed expenses allows you to manage your finances more effectively by ensuring that essential bills are covered before allocating funds to variable spending.
Defining Variable Expenses
Variable expenses fluctuate based on your consumption or production levels, such as utilities, raw materials, and sales commissions. Unlike fixed expenses, which remain constant month-to-month, and semi-variable expenses that combine fixed and variable components, variable costs directly impact your budgeting flexibility. Understanding variable expenses helps you manage cash flow effectively by anticipating changes tied to your business activity.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Variable Expenses
Fixed expenses remain constant regardless of your business activity, such as rent, salaries, and insurance premiums, providing predictable financial planning. Variable expenses fluctuate with your operations, including costs like raw materials, utilities, and sales commissions, which scale directly with production or sales volume. Understanding the key differences between fixed and variable expenses helps you manage cash flow effectively, optimize budgeting, and improve financial decision-making.
Common Examples of Fixed Expenses
Common examples of fixed expenses include rent, mortgage payments, insurance premiums, and property taxes, which remain constant regardless of business activity or personal consumption. These costs provide predictability in budgeting as they do not fluctuate with changes in production volume or service usage. Unlike variable expenses such as utility bills or raw materials, fixed expenses must be paid regularly and form the baseline for financial planning.
Common Examples of Variable Expenses
Common examples of variable expenses include utility bills, groceries, fuel for transportation, and entertainment costs, which fluctuate based on usage or consumption. Unlike fixed expenses such as rent or mortgage payments that remain constant each month, variable expenses adjust with lifestyle changes or seasonal demands. Tracking variable expenses enables better budget management and financial planning by identifying areas where spending can be controlled or reduced.
Impact of Fixed and Variable Expenses on Budgeting
Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, create predictable costs that stabilize your budget, enabling more accurate financial planning. Variable expenses, including utilities and groceries, fluctuate monthly and require flexible budgeting to accommodate unexpected changes in spending. Understanding the impact of both fixed and variable expenses is essential to maintain a balanced budget and avoid overspending.
How to Track and Manage Expenses Efficiently
Tracking and managing fixed, variable, and semi-variable expenses efficiently requires detailed categorization in budgeting tools or spreadsheets to monitor consistent patterns and fluctuations. Automated expense tracking apps synced with bank accounts can categorize transactions, making it easier to identify fixed obligations such as rent and insurance, variable expenses like utilities and entertainment, and semi-variable costs that combine both. Regularly reviewing expense reports and setting alerts for unusual spending helps maintain control and optimize cash flow management.
Adjusting Your Budget: Fixed vs Variable Costs
Adjusting your budget requires a clear understanding of fixed and variable expenses to manage cash flow effectively. Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, remain constant each month, providing a predictable foundation for budgeting. Variable expenses fluctuate with usage or consumption, including utilities and groceries, allowing flexibility to cut costs when necessary and optimize financial control.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Expense Strategy
Your financial success depends on effectively managing fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, alongside variable expenses like utilities and groceries. Prioritizing fixed expenses ensures stability and predictability, while carefully controlling variable expenses allows flexibility and potential savings. Balancing both types tailored to your income and lifestyle creates an optimal expense strategy for long-term financial health.
Infographic: Fixed Expense vs Variable Expense
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com