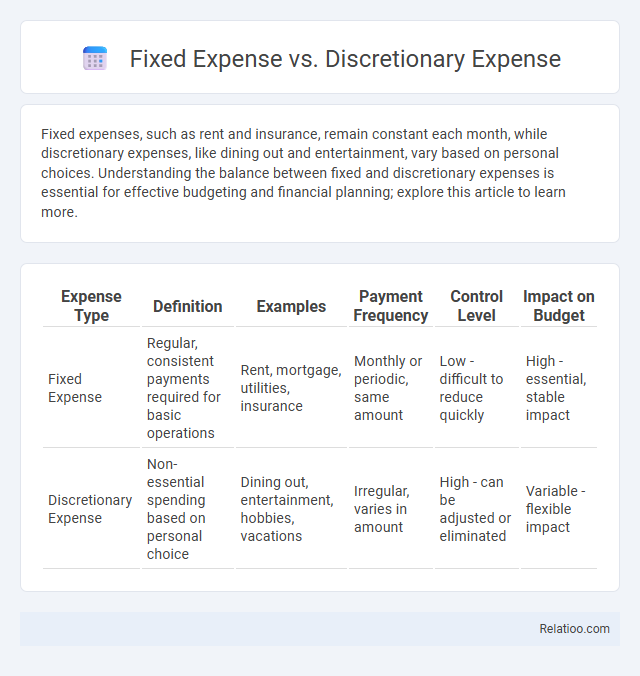
Fixed expenses, such as rent and insurance, remain constant each month, while discretionary expenses, like dining out and entertainment, vary based on personal choices. Understanding the balance between fixed and discretionary expenses is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning; explore this article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
| Expense Type | Definition | Examples | Payment Frequency | Control Level | Impact on Budget |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Expense | Regular, consistent payments required for basic operations | Rent, mortgage, utilities, insurance | Monthly or periodic, same amount | Low - difficult to reduce quickly | High - essential, stable impact |
| Discretionary Expense | Non-essential spending based on personal choice | Dining out, entertainment, hobbies, vacations | Irregular, varies in amount | High - can be adjusted or eliminated | Variable - flexible impact |
Understanding Fixed and Discretionary Expenses
Fixed expenses are regular, mandatory costs such as rent, insurance, and loan payments that remain constant each month, providing a stable foundation for your budget. Discretionary expenses vary based on personal choices and lifestyle, including dining out, entertainment, and travel, allowing flexibility in spending. Understanding the distinction between fixed and discretionary expenses helps you manage your finances effectively by prioritizing essential costs while controlling optional spending.
Defining Fixed Expenses
Fixed expenses are regular, predictable costs that remain constant each month, such as rent, mortgage payments, and insurance premiums. These expenses are essential for maintaining your basic living standards and do not fluctuate with your spending habits. Understanding your fixed expenses helps you manage your budget by distinguishing them from discretionary expenses, which are variable and based on personal choices.
Examples of Common Fixed Expenses
Common fixed expenses include rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, insurance premiums, and car loan payments, which remain constant regardless of your monthly income or spending habits. These recurring costs contrast with discretionary expenses, like dining out or entertainment, which fluctuate based on personal choices. Understanding the distinction between fixed and discretionary expenses helps you better manage your budget and plan for long-term financial stability.
What Are Discretionary Expenses?
Discretionary expenses are non-essential costs that you can adjust or eliminate based on your financial priorities, such as dining out, entertainment, or luxury items. Unlike fixed expenses, which remain constant each month like rent or mortgage payments, discretionary expenses offer flexibility in your budget management. Understanding the difference between fixed, discretionary, and variable expenses helps you make smarter financial decisions and maintain control over your spending.
Examples of Discretionary Expenses
Discretionary expenses include non-essential spending such as dining out, vacations, entertainment, and luxury purchases that can be adjusted or eliminated based on your financial goals. Unlike fixed expenses, which remain constant monthly payments like rent or mortgage, and variable expenses that fluctuate but are necessary, discretionary expenses offer flexibility in budgeting. Understanding the examples of discretionary expenses helps you identify where you can cut costs to increase savings or allocate funds more efficiently.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Discretionary Expenses
Fixed expenses remain constant each month, such as rent or loan payments, while discretionary expenses vary based on your choices, like dining out or entertainment. Understanding key differences helps you manage your budget by prioritizing fixed obligations before allocating funds to discretionary spending. Monitoring these expenses ensures better financial planning and control over your overall spending habits.
Impact of Fixed and Discretionary Expenses on Budgeting
Fixed expenses, such as rent and loan payments, provide stability in budgeting due to their consistent amounts, enabling predictable cash flow management. Discretionary expenses, including dining out and entertainment, fluctuate based on personal choices, allowing flexibility but requiring careful monitoring to avoid budget overruns. Balancing fixed and discretionary expenses is crucial for effective budget planning, as fixed costs ensure essential obligations are met while discretionary spending offers opportunities for financial adjustments and savings.
Strategies to Manage Fixed Expenses
Effective strategies to manage fixed expenses include negotiating lower rent or mortgage rates, refinancing loans to secure reduced interest rates, and automating bill payments to avoid late fees. Regularly reviewing fixed costs such as insurance premiums and subscription services can identify opportunities for savings or cancellations. Implementing budget limits and forecasting expenses helps maintain control over fixed outflows, ensuring financial stability.
Tips to Control Discretionary Spending
Tracking discretionary expenses, such as dining out, entertainment, and hobbies, allows for better budgeting and identifies areas to cut back. Setting clear spending limits and prioritizing essential expenses helps prevent overspending on non-essential items. Using budgeting apps or cash envelopes can effectively monitor and control discretionary spending habits.
How to Balance Fixed and Discretionary Expenses for Financial Health
Balancing fixed and discretionary expenses is crucial for maintaining financial health by ensuring predictable costs like rent and utilities are covered before allocating funds to variable spending such as dining out or entertainment. Implementing a budget that dedicates a specific percentage of income to fixed expenses--typically 50%--helps create stability, while reserving a controlled portion, around 20-30%, for discretionary expenses supports flexibility and lifestyle enjoyment without jeopardizing savings. Regularly reviewing and adjusting spending habits enables individuals to optimize cash flow, avoid debt, and build emergency funds effectively.
Infographic: Fixed Expense vs Discretionary Expense
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com