An emergency fund typically holds three to six months' worth of living expenses in a liquid account, designed to cover unexpected financial crises, whereas general savings accumulate for planned future purchases or goals. Discover detailed strategies to optimize both in this article.
Table of Comparison
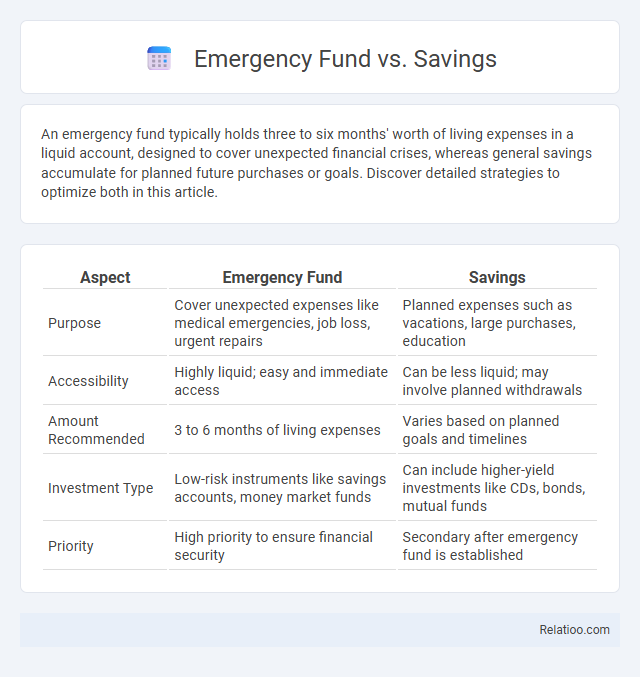
| Aspect | Emergency Fund | Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cover unexpected expenses like medical emergencies, job loss, urgent repairs | Planned expenses such as vacations, large purchases, education |
| Accessibility | Highly liquid; easy and immediate access | Can be less liquid; may involve planned withdrawals |
| Amount Recommended | 3 to 6 months of living expenses | Varies based on planned goals and timelines |
| Investment Type | Low-risk instruments like savings accounts, money market funds | Can include higher-yield investments like CDs, bonds, mutual funds |
| Priority | High priority to ensure financial security | Secondary after emergency fund is established |
Understanding Emergency Funds vs Savings
An emergency fund is a dedicated financial reserve designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or job loss, typically equivalent to three to six months of living expenses. Savings, by contrast, include money set aside for planned goals like vacations, purchases, or retirement, often lacking the immediate accessibility and liquidity that emergency funds require. Prioritizing an emergency fund ensures financial stability during crises without disrupting long-term savings objectives or incurring debt.
Key Differences Between Emergency Funds and Savings
Emergency funds are specifically designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies or job loss, typically held in highly liquid accounts for immediate access. Savings accounts, on the other hand, are intended for planned future expenditures like vacations or large purchases and may offer higher interest rates but less accessibility. The primary difference lies in the purpose and accessibility: emergency funds prioritize liquidity and security, whereas savings prioritize growth and goal-oriented planning.
Purpose of an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund specifically serves as a financial safety net designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or job loss, distinguishing it from general savings which may be allocated for planned expenses like vacations or large purchases. Unlike savings accounts that can include money set aside for future goals, an emergency fund is typically kept liquid and separate to ensure quick access during financial crises. Prioritizing an emergency fund helps maintain financial stability and prevent debt accumulation when unforeseen costs arise.
The Role of General Savings
General savings serve as a flexible financial resource for planned expenses and short-term goals, unlike emergency funds which are specifically reserved for unforeseen crises such as medical emergencies or job loss. An emergency fund typically consists of three to six months' worth of living expenses, providing a safety net that prevents reliance on credit during urgent situations. Maintaining both accounts ensures financial stability by segregating funds for daily needs and unpredictable emergencies, optimizing overall wealth management and risk mitigation.
How Much to Save in Each Fund
Determining how much to save in your emergency fund typically involves setting aside three to six months' worth of essential living expenses to cover unexpected situations such as job loss or medical emergencies. Savings accounts, on the other hand, are usually allocated for short- to medium-term goals and can range from 10% to 20% of your monthly income depending on your financial objectives. Your investment fund should be built with a long-term perspective, often targeting a diversified portfolio aimed at achieving growth over time, with the amount depending on your retirement goals and risk tolerance.
Where to Keep Your Emergency Fund
Your emergency fund should be kept in a highly liquid and easily accessible account, such as a high-yield savings account or a money market account, to ensure immediate access during financial emergencies. Unlike regular savings, which may be used for planned expenses or goals, your emergency fund is specifically designed to cover unforeseen costs without risking investment losses or penalties. Prioritizing liquidity and safety over high returns allows your emergency fund to serve its purpose effectively when you need it most.
Accessibility and Liquidity Comparison
Emergency funds prioritize high liquidity and immediate accessibility, often held in savings accounts or money market funds for quick access during financial crises. Savings accounts offer moderate liquidity but may impose withdrawal limits or delays, making them less ideal for emergencies but suitable for planned expenses. Compared to emergency funds, traditional investments or long-term savings lack liquidity due to potential penalties and market risks, reducing accessibility in urgent situations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Confusing an emergency fund with general savings often leads to insufficient funds during urgent situations, as emergency funds should be highly liquid and reserved solely for unexpected expenses. Many people mistakenly dip into their emergency fund for planned expenses or non-essential purchases, jeopardizing financial security when true emergencies arise. To safeguard your financial well-being, keep your emergency fund separate, adequately funded, and only use it for genuine emergencies.
Building Both: Practical Steps
Building both an emergency fund and regular savings ensures financial security by addressing immediate unexpected expenses and long-term goals. You can start by allocating a portion of your monthly income to an emergency fund, ideally covering three to six months of essential living costs, while simultaneously contributing to savings for future investments or large purchases. Automating these contributions and regularly reviewing your budget helps maintain balance and achieve financial resilience.
Choosing the Right Strategy for You
Choosing the right financial strategy depends on your unique needs and goals, as an emergency fund specifically covers unexpected expenses like medical bills or car repairs, while general savings can be used for planned purchases or future investments. Allocating a portion of your income to an emergency fund ensures quick access to cash during crises without disrupting long-term savings. Evaluate your monthly expenses, job stability, and financial obligations to tailor a financial plan that balances security with growth effectively.
Infographic: Emergency Fund vs Savings
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com