Building an emergency fund with three to six months' living expenses ensures financial stability before pursuing high-return investments. Discover the optimal balance between saving and investing strategies to secure your financial future in this article.
Table of Comparison
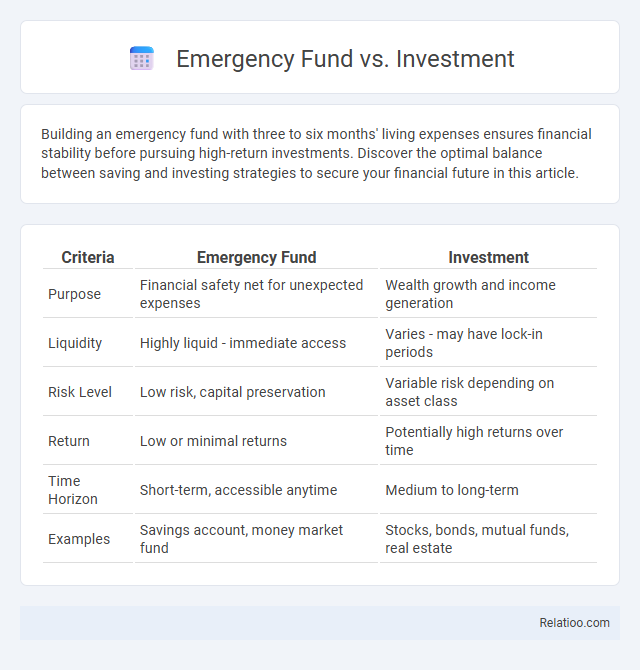
| Criteria | Emergency Fund | Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Financial safety net for unexpected expenses | Wealth growth and income generation |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid - immediate access | Varies - may have lock-in periods |
| Risk Level | Low risk, capital preservation | Variable risk depending on asset class |
| Return | Low or minimal returns | Potentially high returns over time |
| Time Horizon | Short-term, accessible anytime | Medium to long-term |
| Examples | Savings account, money market fund | Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate |
Understanding Emergency Funds
An emergency fund is a crucial financial safety net designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or sudden job loss, typically equivalent to three to six months of living expenses. Unlike investments aimed at wealth growth, emergency funds prioritize liquidity and stability, ensuring immediate access without market risk. Maintaining a well-funded emergency reserve prevents debt accumulation and provides peace of mind during financial uncertainties.
What Is an Investment Portfolio?
An investment portfolio is a collection of diverse financial assets such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate, designed to achieve specific financial goals over time. It balances risk and return by diversifying across asset classes to optimize growth potential while managing exposure to market volatility. Unlike an emergency fund, which is a liquid reserve for unexpected expenses, an investment portfolio aims for long-term wealth accumulation through strategic asset allocation and periodic rebalancing.
Key Differences: Emergency Funds vs Investments
Emergency funds provide immediate liquidity for unforeseen expenses, prioritizing safety and accessibility, whereas investments focus on long-term growth with varying risk levels and less liquidity. You should maintain an emergency fund that covers 3-6 months of living expenses to ensure financial stability before allocating money toward investments. Understanding this key difference helps balance your financial strategy between security and wealth accumulation.
Financial Security: Purpose of an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund serves as a critical financial safety net designed to cover unexpected expenses such as medical emergencies, job loss, or urgent repairs, providing immediate liquidity without the risks associated with investments. Investments aim to grow wealth over time but often carry market risks and lack the instant accessibility needed during emergencies. Prioritizing an adequately funded emergency fund ensures financial security by maintaining stability and protecting long-term assets from being liquidated under distress.
Building Wealth: Role of Investments
Investments play a crucial role in building wealth by offering potential growth through stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, which typically outperform emergency funds in the long term. Your emergency fund should cover three to six months of living expenses to provide financial security in case of unforeseen events, but it generally offers lower returns due to its liquidity and safety focus. Prioritizing a solid emergency fund first allows you to take calculated risks with your investments, maximizing wealth creation while maintaining financial stability.
Liquidity Needs: Emergency Fund vs Investment Options
Emergency funds provide immediate liquidity, allowing you to access cash quickly for unexpected expenses without risking asset loss, unlike many investment options that may require time to liquidate or face market fluctuations. Investments typically offer higher returns but lack the same level of liquidity and can expose your funds to volatility, making them less ideal for urgent financial needs. Balancing your emergency fund with carefully chosen investments ensures that your liquidity needs are met while your money grows effectively over time.
Risk Factors: Comparing Safety and Returns
Emergency funds prioritize liquidity and capital preservation, providing immediate access with minimal risk, whereas investments typically offer higher potential returns but come with market fluctuations and greater risk of loss. Your emergency fund should be kept in low-risk, easily accessible accounts like savings or money market funds to ensure safety during financial crises. Balancing these financial tools involves maintaining a secure emergency fund while strategically investing excess funds to maximize growth without compromising financial stability.
How Much to Allocate: Emergency Fund vs Investment
Allocating between an emergency fund and investments depends on individual financial stability and risk tolerance, with experts often recommending 3 to 6 months' worth of living expenses as a baseline for the emergency fund to ensure liquidity during unexpected events. Investments should be considered for funds exceeding this emergency reserve, enabling long-term wealth growth through diversified assets like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. Prioritizing the emergency fund solidifies a financial safety net, while consistent investment contributes to building assets that outpace inflation.
When to Use Each: Emergency vs Growth Goals
An emergency fund is designed for immediate access during unexpected financial crises, ensuring liquidity and safety without risking principal. Investment accounts target long-term growth goals by leveraging market opportunities, accepting risk and potential volatility to achieve higher returns. Balancing the two involves using emergency funds for short-term needs while allocating surplus resources toward investments aimed at wealth accumulation and future financial goals.
Best Practices for Financial Balance
Maintaining a balanced financial strategy involves prioritizing an emergency fund with three to six months' worth of living expenses to provide immediate liquidity during unforeseen circumstances. Investing in diversified assets such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds helps build long-term wealth by capitalizing on market growth and compound interest. Best practices include regularly evaluating financial goals, ensuring the emergency fund is easily accessible, and aligning investments with risk tolerance and time horizon for optimal financial stability.
Infographic: Emergency Fund vs Investment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com