Deferred annuities allow investors to accumulate funds tax-deferred until a future payout date, while immediate annuities begin disbursing income shortly after a lump-sum investment. Explore the key differences and benefits of deferred versus immediate annuities in this article.
Table of Comparison
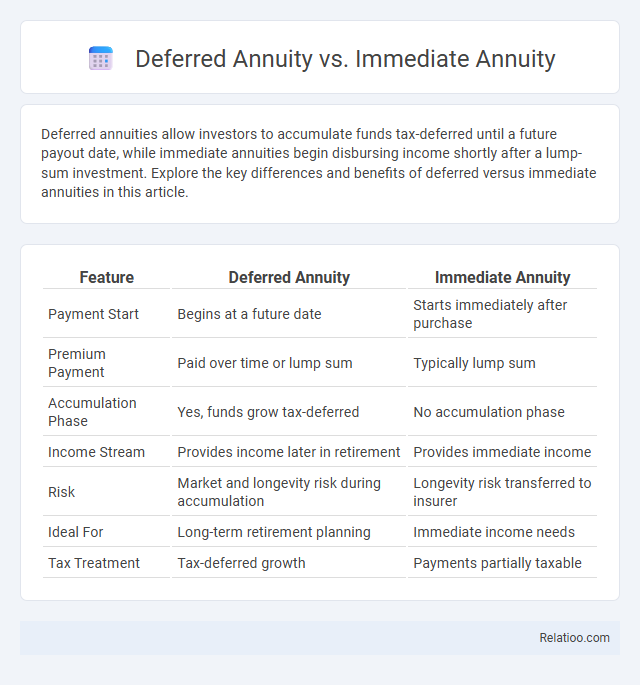
| Feature | Deferred Annuity | Immediate Annuity |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Start | Begins at a future date | Starts immediately after purchase |
| Premium Payment | Paid over time or lump sum | Typically lump sum |
| Accumulation Phase | Yes, funds grow tax-deferred | No accumulation phase |
| Income Stream | Provides income later in retirement | Provides immediate income |
| Risk | Market and longevity risk during accumulation | Longevity risk transferred to insurer |
| Ideal For | Long-term retirement planning | Immediate income needs |
| Tax Treatment | Tax-deferred growth | Payments partially taxable |
Understanding Deferred Annuities
Deferred annuities accumulate funds over time, allowing investments to grow tax-deferred until withdrawals begin, usually during retirement. Immediate annuities start paying income shortly after a lump sum is invested, providing a steady cash flow without an accumulation phase. Understanding deferred annuities is crucial for long-term financial planning, as they offer flexibility in contribution amounts and timing, along with potential benefits like guaranteed lifetime income and growth through tax-deferred interest.
What Is an Immediate Annuity?
An immediate annuity is a financial product that begins paying income almost immediately after a lump sum is invested, typically within one month, providing a steady stream of payments for life or a set period. Unlike deferred annuities, which accumulate funds over time before distributing payments, immediate annuities are designed for those seeking instant income, often in retirement. Understanding your income needs and timeline will help determine if an immediate annuity fits your retirement strategy compared to deferred or other annuity types.
Key Differences Between Deferred and Immediate Annuities
Deferred annuities accumulate funds over time with tax-deferred growth, allowing individuals to invest during their working years before receiving payouts at a later date, while immediate annuities start payments almost immediately after a lump sum investment, providing a steady income stream. Key differences include the timing of income payments, with deferred annuities offering a growth phase before payouts, and immediate annuities focusing on immediate income distribution. Both types of annuities provide options for guaranteed lifetime income, but deferred annuities are geared towards long-term retirement planning, whereas immediate annuities suit those seeking instant income.
How Deferred Annuities Work
Deferred annuities accumulate funds tax-deferred until a specified future date, allowing your investment to grow over time before payouts begin. Unlike immediate annuities, which start disbursing income shortly after a lump-sum deposit, deferred annuities separate the accumulation phase from the distribution phase. This flexibility helps you build a substantial retirement nest egg while managing the timing and amount of your future income stream.
How Immediate Annuities Operate
Immediate annuities begin providing income payments to you shortly after a lump-sum investment, typically within one month. These annuities convert your principal into a steady stream of guaranteed income lasting for a specific period or your lifetime. Unlike deferred annuities, which accumulate value over time before distributions start, immediate annuities focus on prompt income generation based on the initial premium and the annuitant's age and life expectancy.
Pros and Cons of Deferred Annuities
Deferred annuities offer the advantage of tax-deferred growth, allowing funds to accumulate over time before payouts begin, which benefits long-term retirement planning. However, they often come with surrender charges and limited liquidity during the accumulation phase, making access to funds costly or restricted. Compared to immediate annuities that provide instant income, deferred annuities may pose risks related to market performance and inflation, impacting future payout values.
Pros and Cons of Immediate Annuities
Immediate annuities provide guaranteed income payments starting almost immediately after a lump-sum investment, offering financial security and predictable cash flow. You benefit from steady income, which is ideal for retirees seeking stability, but sacrifices liquidity and potential for higher returns compared to deferred annuities. Unlike general annuities that may accumulate value over time, immediate annuities limit flexibility, and once started, payments typically cannot be altered or accessed as a lump sum.
Choosing the Right Annuity for Retirement Planning
Choosing the right annuity for your retirement planning depends on your income needs and risk tolerance. Deferred annuities offer tax-deferred growth until you begin withdrawals, making them ideal for long-term savings, while immediate annuities start paying income shortly after a lump sum is invested, providing guaranteed cash flow. Understanding the differences between deferred annuities, immediate annuities, and general annuity options can help you optimize your retirement income strategy.
Tax Implications: Deferred vs Immediate Annuities
Deferred annuities allow your investment to grow tax-deferred until you begin withdrawals, typically during retirement when you may be in a lower tax bracket. Immediate annuities start payments right away, and the income received is partially tax-free since it represents a return of your principal, with the remainder taxable as ordinary income. Understanding these tax implications helps you optimize your retirement income strategy while minimizing your tax burden.
Frequently Asked Questions on Annuity Options
Deferred annuities allow individuals to accumulate funds tax-deferred until payouts begin at a future date, contrasting with immediate annuities which start disbursing payments shortly after a lump-sum investment. Common FAQs on annuity options include inquiries about the tax implications, payout flexibility, and the differences in risk and return between deferred and immediate annuities. Understanding how each annuity type fits retirement income strategies helps ensure beneficiaries select options aligned with their financial goals and liquidity needs.
Infographic: Deferred Annuity vs Immediate Annuity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com